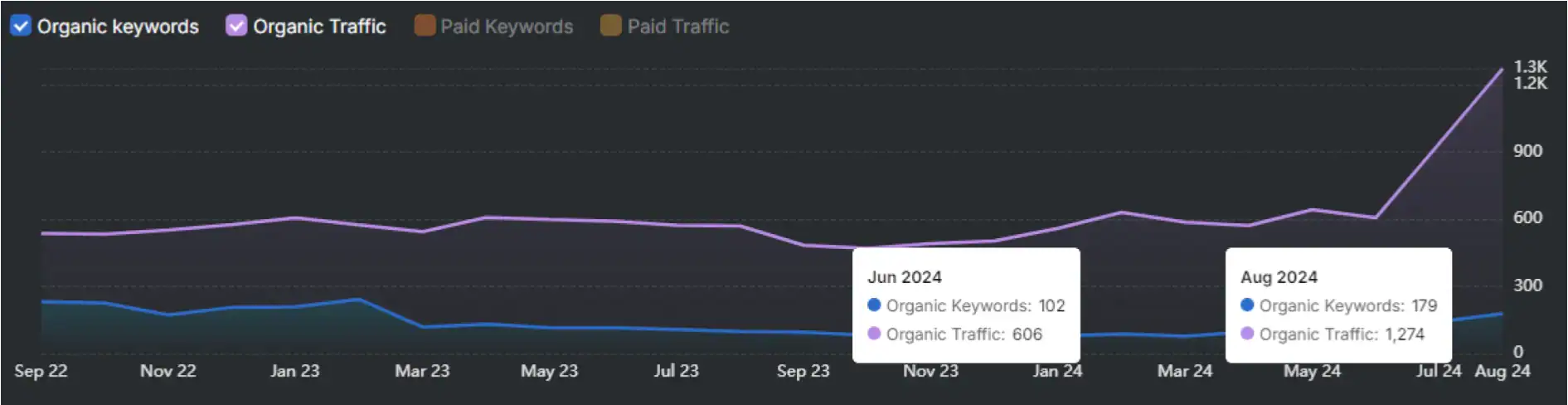
You may also read a concise version of this research in our blog: Local SEO Ranking Factors by Industry: Machine Learning Insights
1. Executive Summary
In the evolving landscape of local search, ranking prominently on Google’s local results — particularly in the map pack — can drive significant visibility, engagement, and revenue for businesses. Yet the mechanics of why some businesses appear higher than others remain opaque. This white paper investigates key features influencing local rankings across 7,718 businesses, 676 sectors, and 18 grouped industries, leveraging structured SERP grid data and advanced machine learning.
To investigate these ranking factors, we developed a robust, scalable Shiny application that trains XGBoost models on filtered slices of local SEO data. These models assess how average Google Business Profile (GBP) position — a proxy for local visibility — responds to business attributes, review signals, and content relevance. Analyses were performed both globally and within specific industries (e.g. Food, Health, Legal, Beauty) to capture sector-specific ranking dynamics and differences in algorithmic behavior.
The findings consistently show that proximity to the search centroid is the dominant ranking factor across all industries. However, as we zoom into top-ranking businesses — especially those within the top 10 positions — review volume, semantic keyword alignment in customer reviews, and keyword relevance in business names become far more influential. These behavioral signals often outweigh technical SEO metrics and reflect Google’s emphasis on trust, relevance, and user experience.
Moreover, sector-specific models consistently achieved higher R² scores than the global model, confirming that industry-specific strategies are essential for maximizing local search performance. By comparing businesses ranked in the top 10 versus those across the full ranking spectrum, we also reveal how feature importance shifts as competition intensifies.
This analysis yields concrete, data-backed recommendations: optimize for proximity when possible, prioritize keyword-rich and authentic customer reviews, and align branding and GBP metadata with user intent. These strategies improve performance in competitive SERPs and enable more precise, vertically-aligned local SEO efforts.
2. Introduction
In today’s hyper-local digital landscape, visibility in Google’s local results — especially the “map pack” — can drive measurable increases in foot traffic, phone calls, and website conversions for small and large businesses alike. As more consumers use Google to find nearby services, local businesses that appear in the map pack have a prime opportunity to connect with high-intent audiences.
Despite their importance, local search ranking systems remain a black box. Previous studies have quantified the benefits of appearing in the map pack, but none have answered why some businesses consistently appear at the top while others remain buried deep in the listings. While proximity has long been known as a factor, distance alone doesn’t guarantee top visibility, as Google also uses prominence and relevance signals to determine rankings. Also, businesses with similar locations often perform very differently in the same local SERP — prompting critical questions:
- What other variables determine local pack performance?
- How much do reviews, ratings, content relevance, or GBP metadata influence ranking position?
- Do these ranking signals vary by industry or rank tier?
To address these questions, this white paper applies a data science approach to uncover the relative influence of local SEO features on GBP ranking performance. We analyze a dataset of 7,718 businesses across 676 sectors and 18 industries including Real Estate, Education, Handyman Services, Technology / Creative, Healthcare, Events & Entertainment, Food & Restaurants, Retail, Construction, Accounting & Finance, Logistics, Automotive Services, Legal Services, Manufacturing, Personal Care Services, Professional Services, Public Sector, and Hospitality & Travel , using advanced XGBoost modeling to identify which factors most strongly correlate with average GBP position.
The core features analyzed include:
- Proximity to the grid centroid
- Review count, rating, and review-to-keyword semantic similarity
- Keyword alignment in GBP business names and website content
- GBP metadata completeness and industry classification
The analysis is performed at both a global level and within sector-specific models, revealing that ranking behavior varies significantly between industries like Food, Health, Legal, and Beauty. Additionally, we compare model outputs for businesses ranked within the top 10 positions versus all ranked positions (1–21), exposing how feature importance shifts for elite placement.
Through this structured analysis, readers will gain a clear, evidence-based understanding of:
- Which factors most impact local rankings overall
- How those factors change depending on the industry and rank tier
- What actionable strategies can be used to optimize for local SEO outcomes
Whether you’re managing a single location or scaling local visibility across hundreds of listings, this white paper provides the empirical clarity needed to prioritize your optimization efforts and make informed, sector-aware SEO decisions.
3. Methodology
To understand the drivers of Google Business Profile rankings across local industries, we applied a reproducible and data-rich pipeline combining structured SERP data, semantic content features, and machine learning models. The following methodology outlines how data was collected, engineered, and analyzed to model GBP ranking behavior.
Data Collection & Sources
Data was sourced from multiple internal PostgreSQL databases that track Google SERP behavior at a highly granular level. Specifically:
- kw_keywordlocalserpgrid: Provided the core keyword-to-location visibility grid, including average GBP position per business across SERP tiles
- kw_googlemybusiness: Contained business metadata including name, category, rating, and review count
- ca_urlhtmlanalysis: Contained extracted website content and entity-level information associated with each business
- gbp_locationreview: Included raw and pre-processed customer review text
- kw_urlanalysismetrics & kw_competitorresearchv2: Provided backlink data, anchor text, and off-page metrics like Domain Authority, Domain Rating and URL Rating
Additional joins incorporated metadata from auxiliary systems like otto_ppc (for ad insights) and gsc (for search console data) where available.
Preprocessing & Feature Engineering
Data preprocessing and transformation were conducted in R using the dplyr, sf, and text2vec packages. Key steps included:
- Normalization & Deduplication: Business names and URLs were normalized to lowercase, stripped of tracking parameters, and deduplicated to avoid multiple counts per keyword-business pair.
- Spatial Calculations: All business locations and SERP grid tiles were transformed into lat/lon geometries, enabling precise calculation of proximity via the Haversine formula (captured as distance_kmeters).
- Semantic Matching:
- Review relevance (review_keyword_relevance_score) and GBP profile relevance (relevance_keyword_gbp_profile) were computed using cosine similarity between TF-IDF vectors of the keyword and textual metadata.
- Anchor text and website content were processed similarly to capture keyword-topic alignment.
- Review relevance (review_keyword_relevance_score) and GBP profile relevance (relevance_keyword_gbp_profile) were computed using cosine similarity between TF-IDF vectors of the keyword and textual metadata.
- Business Completeness Score: A composite metric (gbpalgo) was derived from the presence of critical GBP metadata fields, such as operating hours, services, and address consistency.
- Outlier Filtering: Extreme values for reviews, ratings, and distance were removed using IQR-based filtering to prevent distortion in regression modeling.
- Industry Grouping: 676 unique sectors were mapped into 28 aggregated industries for comparative analysis across verticals.
Target Variable
The primary response variable for all models was gmb_average_position, a numeric value representing the average map rank of a business across a SERP grid for a specific keyword. Lower values indicate better ranking performance (i.e., position 1 is top-ranked).
Machine Learning Approach
To evaluate feature importance and predictive power, we employed XGBoost, a gradient boosting decision tree algorithm well-suited for:
- Nonlinear interactions
- Mixed-scale data
- High-dimensional tabular data
We implemented XGBoost regression models using the xgboost package in R. Key hyperparameters included:
- objective = “reg:squarederror” for continuous outcome modeling
- nrounds = 50 to ensure sufficient training cycles
- max_depth = 6, eta = 0.2 for balance between model complexity and generalization
- Models were trained using default subsampling and column sampling settings for simplicity
The model output includes:
- Gain: How much each feature contributed to improving the model’s predictive accuracy
- Cover: The relative number of observations affected by a given feature (used in exploratory stages)
Feature importance was visualized using ggplot2 and an interactive Shiny dashboard, allowing real-time model recomputation across:
- Industries
- Position ranges (e.g., 1–5 vs. 1–21)
- Review count, rating, and ranking filters
All models used memoization (memoise package) to optimize performance and caching for repeat computation.
Model Evaluation
Model performance was assessed using R² (coefficient of determination), calculated using the caret::R2() function. This metric quantifies how well the model explains the variation in GMB average position. Interpretations:
- R² > 0.70: Strong explanatory model
- R² > 0.90: Excellent fit for top-position models
We compared global models (all businesses across industries) against sector-specific models (e.g., Food, Health, Legal, Beauty) to assess whether vertical-specific ranking logic differs. We also compared models trained on:
- All ranked positions (1–21)
- Top-ranked businesses only (positions 1–5 or 1–10)
These comparative runs allowed us to observe how feature importance shifts depending on rank tier and industry competitiveness.
Why XGBoost? Justification for Methodology
XGBoost was selected due to:
- Superior handling of nonlinear relationships
- Built-in feature importance metrics
- Efficiency and scalability for real-time re-training via Shiny
- Interpretability: Easily communicated insights using bar charts and normalized gain scores
- Robustness against multicollinearity and noisy features
While alternatives like random forests or linear regression were considered, XGBoost consistently yielded higher R² values and more stable rankings of feature importance across subsets.
This methodological framework provides a reliable, transparent, and replicable way to quantify what drives local search rankings — ensuring findings can be trusted, extended, and adapted by other researchers and SEO professionals.
4. Analysis and Results
a. All Businesses vs Top-Ranked GMB Ranking Factors
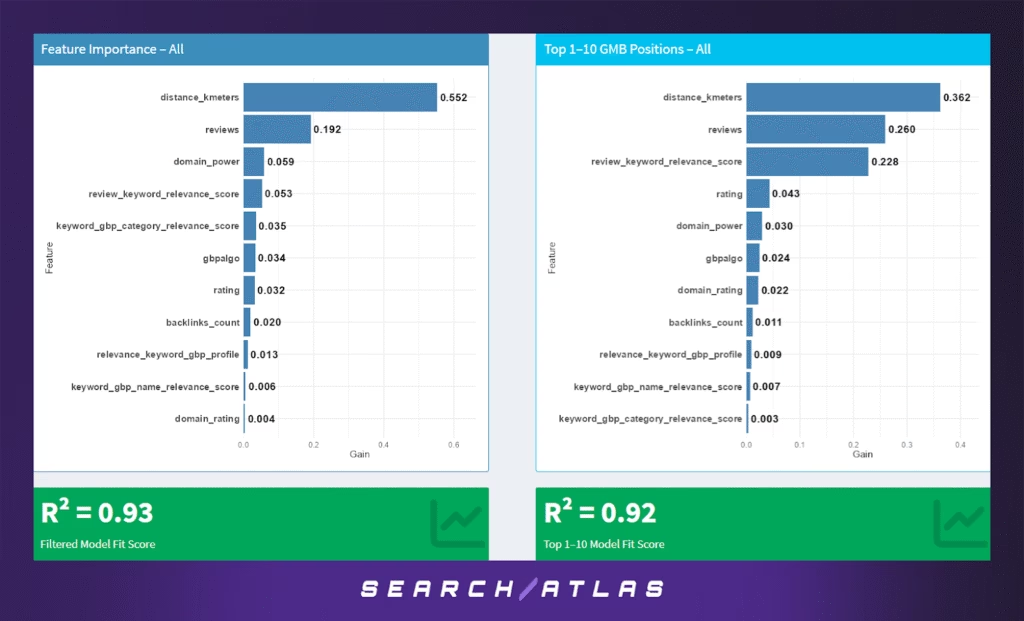
To understand which factors most strongly influence Google Business Profile (GBP) rankings across all sectors, we trained gradient-boosted tree models on the full dataset and separately on businesses appearing in the top 10 positions. These two models—visualized in the figure above—highlight both consistent patterns and sharp differences in what drives top visibility.
Key Findings (All Businesses)
In the model trained on all businesses, the most important predictor of average GBP position is distance_kmeters — the proximity of the business to the search centroid — which alone accounts for over 55% of the gain in the model. This confirms Google’s strong proximity bias in local search.
Following distance, review count (reviews) is the second-most influential factor, capturing 19% of the model gain. Other noteworthy but weaker contributors include:
- domain_power (5.9%) – a proxy for the business’s broader web authority
- review_keyword_relevance_score (5.3%) – indicating how well reviews semantically align with the search query
- keyword_gbp_category_relevance_score and gbpalgo – likely representing category-topic alignment and possible reverse-engineered ranking behaviors
Overall, this model reached an R² of 0.93, indicating high explanatory power.
Key Findings (Top 1–10 Only)
When the model is retrained on only top-performing businesses, distance still matters—but its relative weight drops sharply to 36%, while review-related features gain more importance.
Specifically:
- Review keyword relevance rises to 22.8%, suggesting that among already competitive businesses, semantic review quality becomes a key differentiator.
- Raw review count increases to 26%, now ranking second.
- Rating and domain authority maintain a modest influence, while backlink metrics and GBP field match scores fall further in relevance.
This model maintains a strong fit with an R² of 0.92, underscoring its reliability even on a narrowed cohort.
Interpretation
These results suggest a two-phase ranking mechanism:
- To enter the map pack, proximity is most important. Google prioritizes physical nearness to the search origin when choosing which businesses to show.
- To climb within the pack, review quality and volume have the next greatest impact. Once within striking distance of the top 10 positions, businesses with keyword-rich and topically aligned reviews pull ahead.
Thus, local SEO strategies must be context-sensitive: optimizing location data and address accuracy is essential for visibility, but sustained performance hinges on cultivating high-quality, semantically relevant reviews.
b. Accounting & Finance GBP Ranking Factors
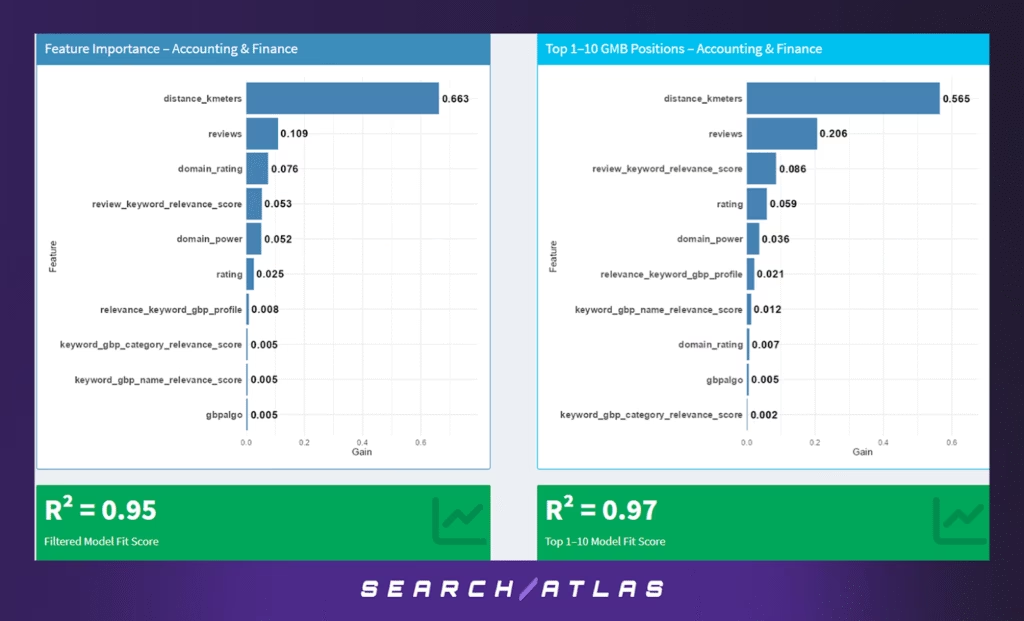
To explore whether local ranking signals vary by industry, we drilled down into the Accounting & Finance sector. This subset included only businesses labeled under financial services, bookkeeping, and tax advisory categories. As before, we compared two models: one trained on all businesses in the sector, and another restricted to the top 10 ranked listings.
Key Findings (All Positions – Accounting & Finance)
Unsurprisingly, proximity to the search centroid (distance_kmeters) again emerged as the most influential feature, accounting for a massive 66% of the predictive power. This reinforces that even in professional service industries, location remains a dominant factor for local visibility.
Secondary features included:
- Review count (reviews) – 10.9% gain contribution
- Domain rating and domain power – each contributing ~5%, reflecting that online authority still carries weight in trust-based industries
- Review keyword relevance score – 5.3%, suggesting moderate influence of topical alignment in reviews
This model achieved an excellent R² of 0.95, showing very strong fit.
Key Findings (Top 1–10 Only – Accounting & Finance)
Among only the top 10 ranked listings, proximity still leads (56.5%) but its dominance shrinks slightly, allowing reviews (20.6%) and review keyword relevance (8.6%) to gain prominence.
Other subtle shifts emerge:
- Rating and domain authority metrics rise modestly in influence.
- GBP field keyword matches (name/profile/category) become slightly more important, but remain minor contributors overall.
The model for top performers had an even stronger R² of 0.97, indicating highly consistent patterns.
Interpretation
For Accounting & Finance, location trumps all, even more than in consumer service industries. However, to break into the top rankings, businesses benefit significantly from robust review profiles — both in volume and in keyword alignment. These findings highlight that trust signals and topical relevance are pivotal once a business is already competitive in proximity.
GBP metadata (e.g. business name, category) plays a minimal role, suggesting that professional credibility and real-world reputation (via reviews and links) matter more than keyword inclusion or profile tweaks in this industry.
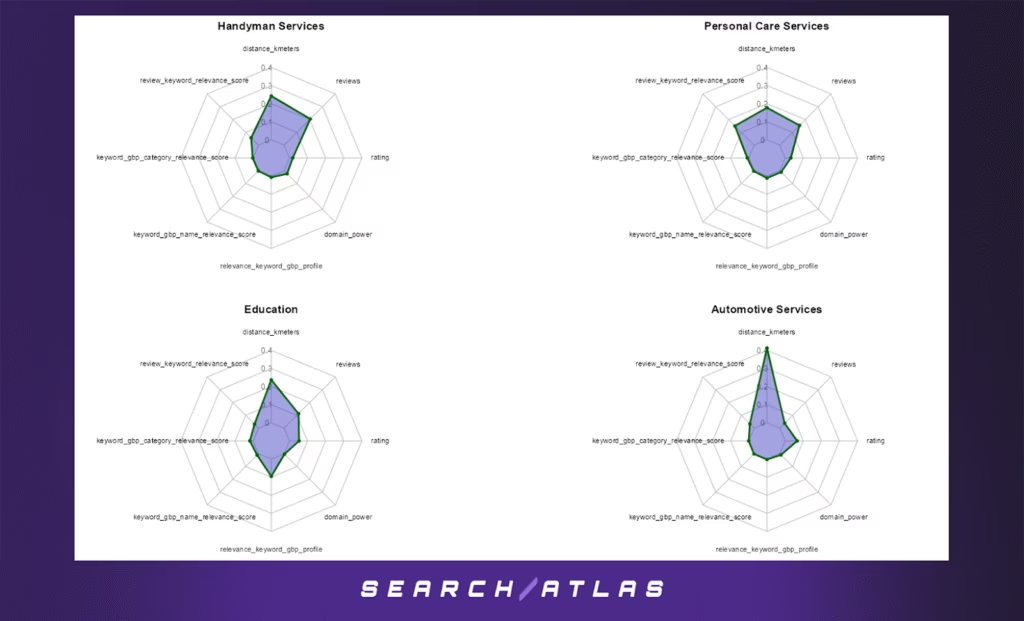
c. Automotive Services GBP Ranking Factors
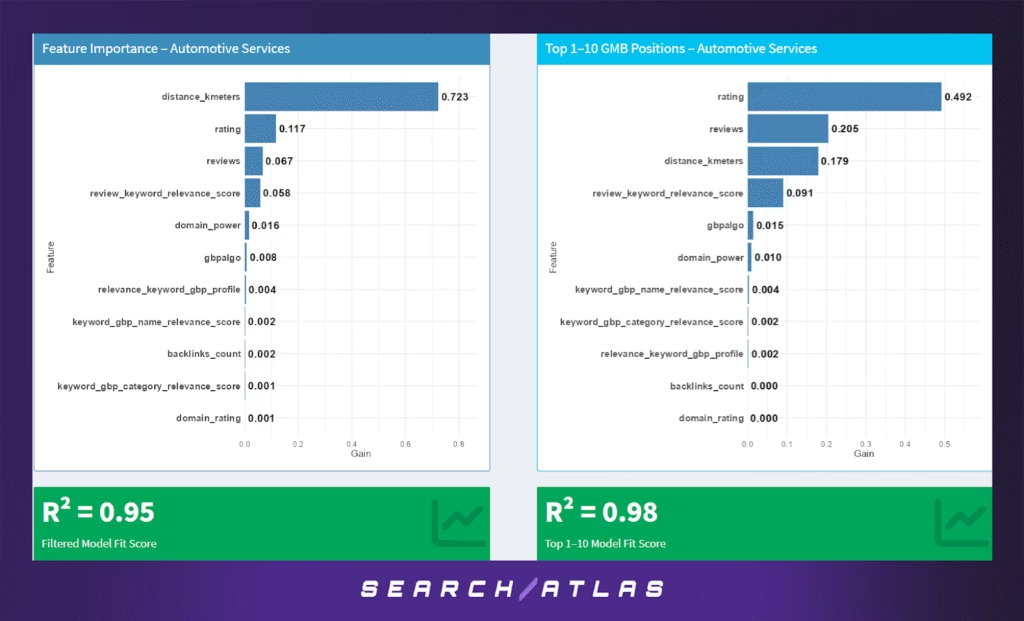
The Automotive Services industry — covering auto repair shops, tire dealers, mechanics, and related businesses — presents a clear two-stage ranking mechanism that separates general eligibility from competitive dominance.
Model Results (All GBP Positions)
In the complete dataset for this vertical, proximity is by far the most influential factor, contributing 72.3% to the model. This underscores the importance of being physically close to the search centroid for appearing anywhere in the local map pack.
Secondary but notable features:
- Rating (11.7%) and review volume (6.7%) show that quality still plays a role.
- Review keyword relevance (5.8%) indicates that semantic cues in reviews slightly improve visibility.
The model explains 95% of the variance (R² = 0.95), suggesting high predictability.
Model Results (Top 1–10 Rankings Only)
When isolating just the top 10 businesses, the ranking dynamics shift dramatically:
- Rating becomes the dominant factor with 49.2% contribution.
- Reviews and review keyword relevance rise to 20.5% and 9.1% respectively.
- Proximity drops to 17.9%, indicating that while being nearby is still important, review quality and sentiment become the top differentiators at the top.
The R² for this model jumps to 0.98, implying a very stable pattern among top-ranked automotive listings.
Strategic Takeaways
- To be listed, automotive businesses need to be physically close to the user.
- To stay competitive in the top 10, they must accumulate excellent ratings, authentic reviews, and positive review content with semantically aligned language.
- Traditional SEO factors (domain authority, backlinks) and GBP keyword tuning offer little to no value here.
This finding is consistent with the nature of auto services: urgency, trust, and location proximity drive customer behavior — and Google’s local ranking algorithm reflects that prioritization.
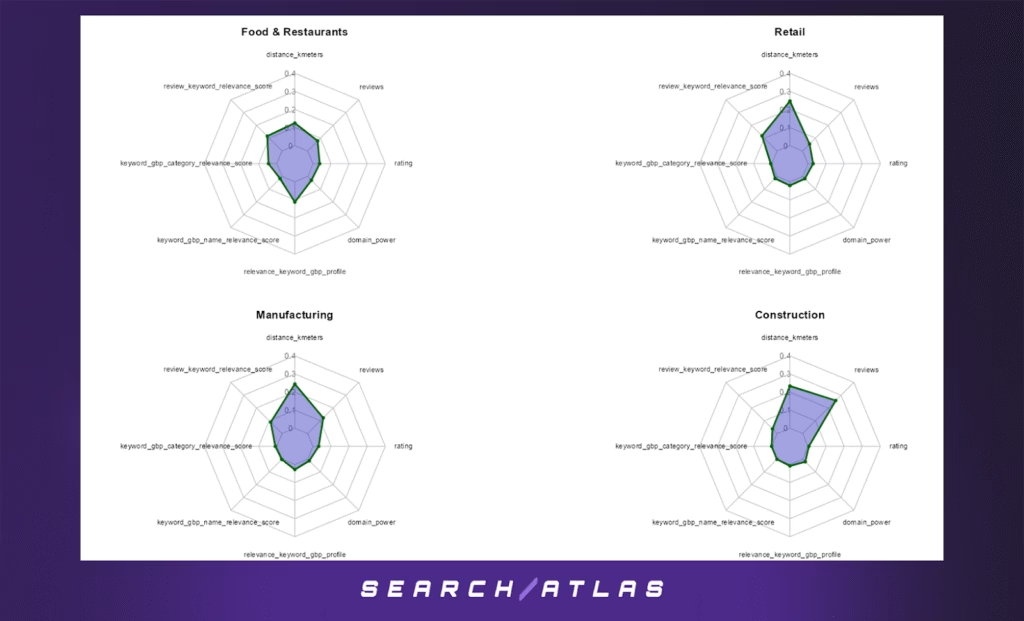
d. Construction GBP Ranking Factors
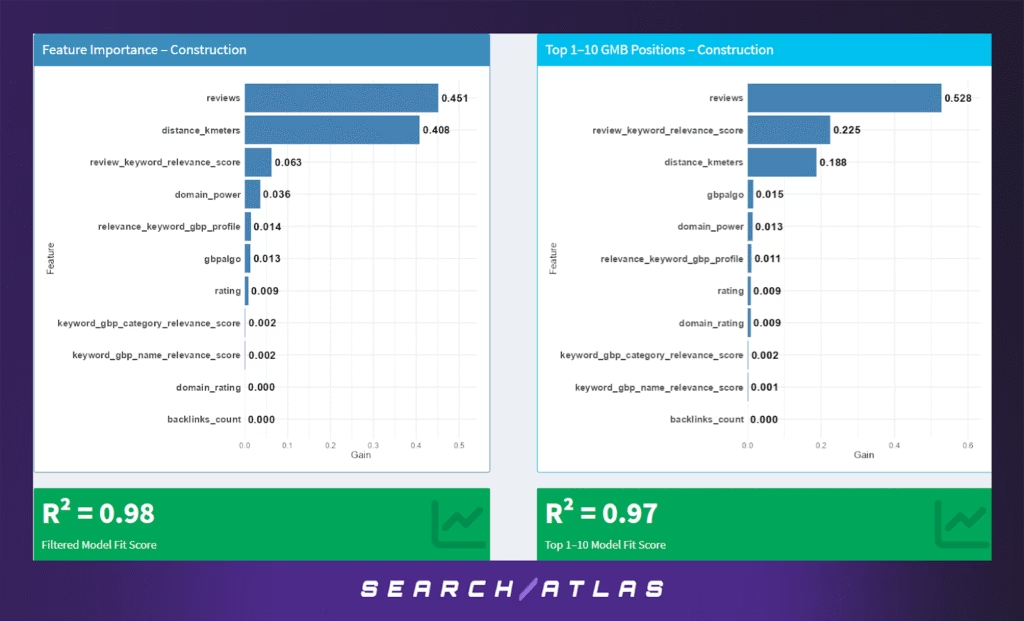
The Construction industry — spanning general contractors, home builders, roofing, plumbing, and renovation firms — reveals a distinct blend of trust signals and proximity in determining local search performance.
Model Results (All GBP Positions)
In the full sample, review count (45.1%) and proximity (40.8%) are nearly equally important, underscoring a dual dependency on location and volume of customer validation. Unlike some other verticals, rating quality plays a minimal role (0.9%), suggesting that presence and visibility are driven more by quantity than quality of reviews.
Additional contributors:
- Review keyword relevance (6.3%) indicates mild benefits from semantic alignment between reviews and target queries.
- Domain power also has some relevance (3.6%), possibly reflecting reputation signals for larger, regional firms.
The model explains 98% of ranking variance, one of the highest across sectors.
Model Results (Top 1–10 Rankings Only)
Among the top 10 positions:
- Review volume becomes the dominant signal (52.8%).
- Review keyword relevance increases to 22.5%.
- Proximity drops to 18.8%, implying that once a business is close enough, semantic and reputational factors become more critical for ranking at the top.
Rating, backlinks, and GBP category relevance remain largely insignificant throughout, reinforcing the notion that in construction, visibility hinges on being well-reviewed and within the service area — not necessarily on polished branding or SEO depth.
Strategic Takeaways
- Volume of reviews is the single most powerful lever in both general and top-tier rankings.
- Businesses should encourage customer reviews that include contextual keywords (e.g., “kitchen remodel”, “roof repair”).
- Location still matters but is less dominant at the top.
- Traditional SEO metrics like domain authority or backlink count show almost no influence in this vertical.
This analysis validates the trust-first, proximity-second nature of how users and Google evaluate construction services in local searches.
e. Education GBP Ranking Factors
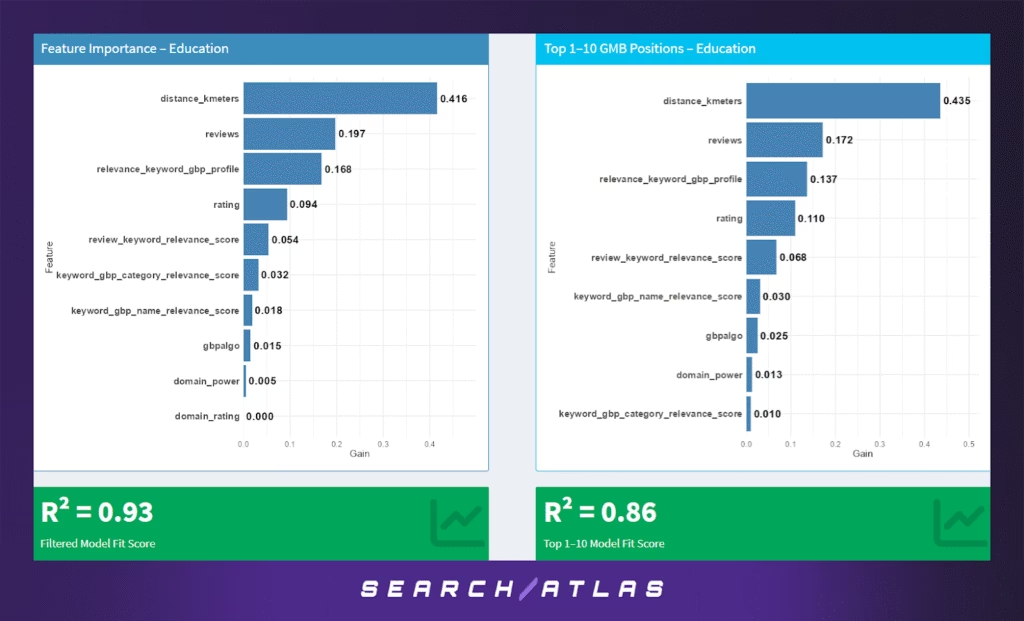
The Education sector encompasses tutoring centers, private schools, test prep providers, and language institutes. In this industry, decision-making is deeply tied to trust, locality, and relevance to user queries — and this is reflected in the ranking dynamics.
Model Results (All GBP Positions)
The most influential factor is distance from the searcher (41.6%), which aligns with expectations for location-based services such as nearby tutoring or educational support. Following that:
- Review count (19.7%) and profile-keyword relevance (16.8%) contribute significantly — the latter highlighting that how well a business profile semantically matches the query matters substantially in this space.
- Rating (9.4%) and review keyword relevance (5.4%) also provide measurable but smaller influence.
Traditional SEO indicators such as domain power and backlinks have little to no impact, reinforcing that Google Business Profile (GBP) optimization outweighs web authority in this vertical.
The model explains 93% of the variance in average GBP position across the dataset — indicating strong confidence in the predictive insights.
Model Results (Top 1–10 Rankings Only)
For the top-ranking businesses:
- Proximity remains dominant (43.5%) and even increases slightly.
- Profile-keyword relevance (13.7%) and review-based signals (reviews: 17.2%, keyword relevance: 6.8%) still matter, but we see a modest rise in the importance of rating (11.0%) — suggesting that among top-ranked educational businesses, user satisfaction plays a larger role in maintaining position.
The R² score for the top-10 model dips to 0.86, indicating that other unobserved factors may influence top placements, such as specific trust signals, content accuracy, or real-time engagement metrics (e.g., Q&A, post activity).
Strategic Takeaways
- Education providers must focus on local relevance and review volume to appear in GBP results.
- Once in the top 10, profile optimization (GBP keyword relevance) and quality ratings become increasingly important.
- Domain authority is largely irrelevant, meaning resources are better spent on GBP completeness and review acquisition than link-building.
These results reinforce the unique dual emphasis in education: being nearby and being trusted.
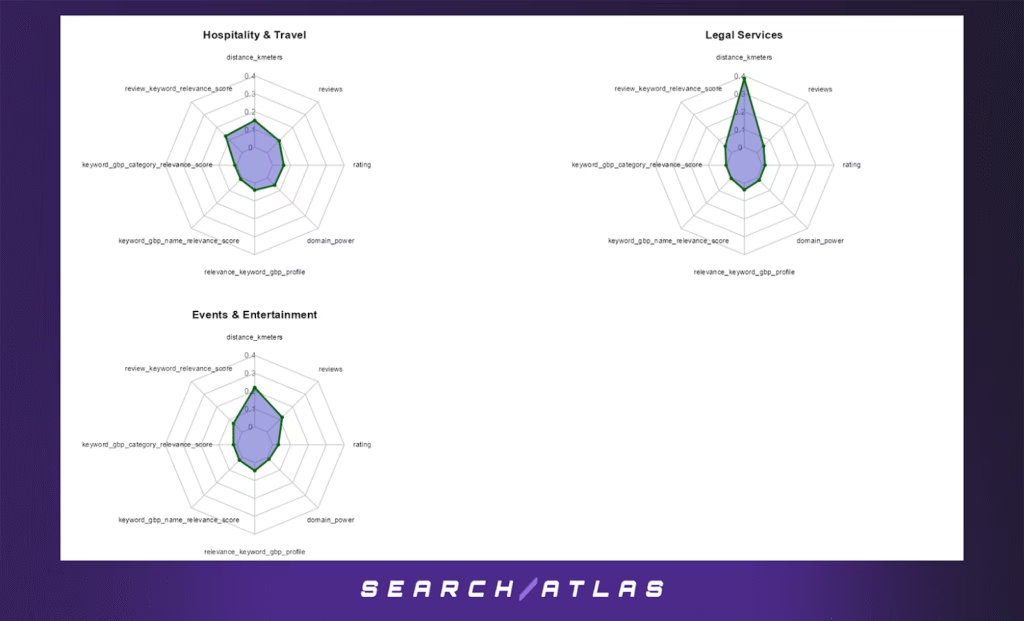
f. Events & Entertainment GBP Ranking Factors
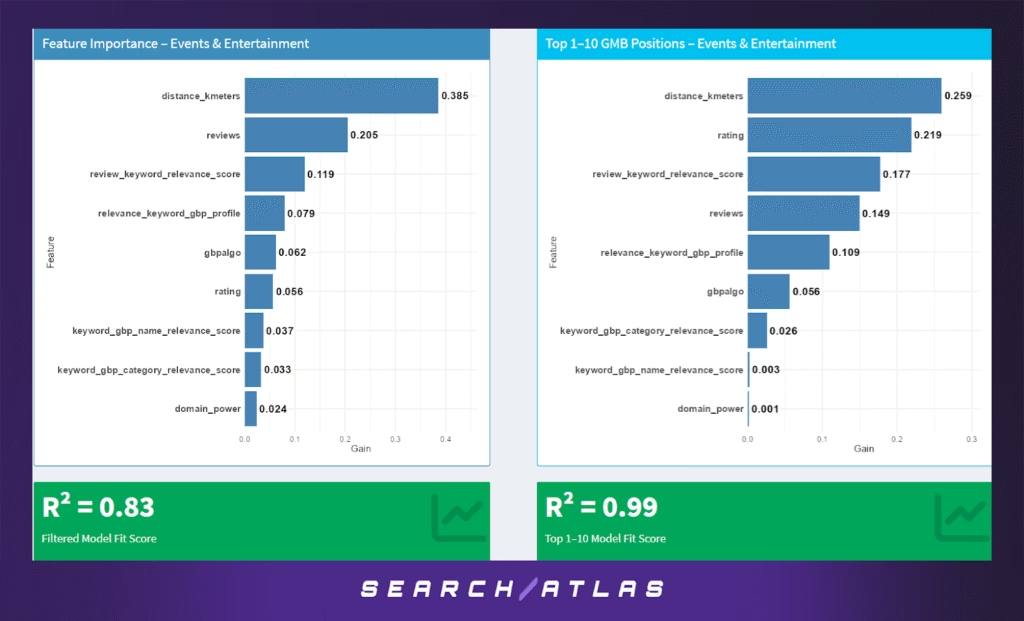
The Events & Entertainment sector — including music venues, festivals, escape rooms, theaters, and local attractions — depends heavily on timely discovery and strong consumer sentiment. User proximity and real-time context matter deeply for this highly experiential and intent-driven vertical.
Model Results (All GBP Positions)
For the general model across all GBP positions:
- Proximity again emerges as the strongest predictor of local ranking (38.5%), reflecting the deeply local nature of event discovery and entertainment consumption.
- Review count (20.5%) and review keyword relevance (11.9%) reinforce the impact of social proof and semantic alignment in users’ own language.
- GBP keyword relevance in the business profile (7.9%) and Google’s internal GBP algorithm indicator (6.2%) also contribute meaningful signal strength.
- Traditional SEO signals like domain power (2.4%) remain marginal in influence.
The overall R² score of 0.83 suggests that while key patterns exist, ranking behavior in this sector may be affected by external or temporal factors, such as event seasonality, ticket availability, or freshness of updates.
Model Results (Top 1–10 Rankings Only)
Among top-performing listings:
- Distance still matters (25.9%) but its share decreases relative to other features.
- Rating (21.9%) becomes highly influential — indicating that perceived quality is especially important when users make final choices.
- Review keyword relevance (17.7%) and review count (14.9%) continue to have strong predictive value, suggesting that rich, keyword-aligned reviews are critical for top-tier visibility.
- The role of GBP profile relevance (10.9%) and Google’s algo score (5.6%) also holds firm, affirming the value of well-aligned profile content.
The R² score rises sharply to 0.99, implying the model captures nearly all ranking variance for top listings — likely due to clearer differentiation among top contenders.
Strategic Takeaways
- Proximity, high ratings, and keyword-rich reviews are indispensable in this sector.
- Entertainment businesses should proactively curate and encourage review content that semantically aligns with popular search phrases.
- GBP profile optimization is essential — especially for top 10 performance — while website authority metrics play almost no role.
In a vertical where consumers seek nearby, high-quality, and trustworthy experiences, the rankings reward exactly those dimensions.
g. Food & Restaurants GBP Ranking Factors
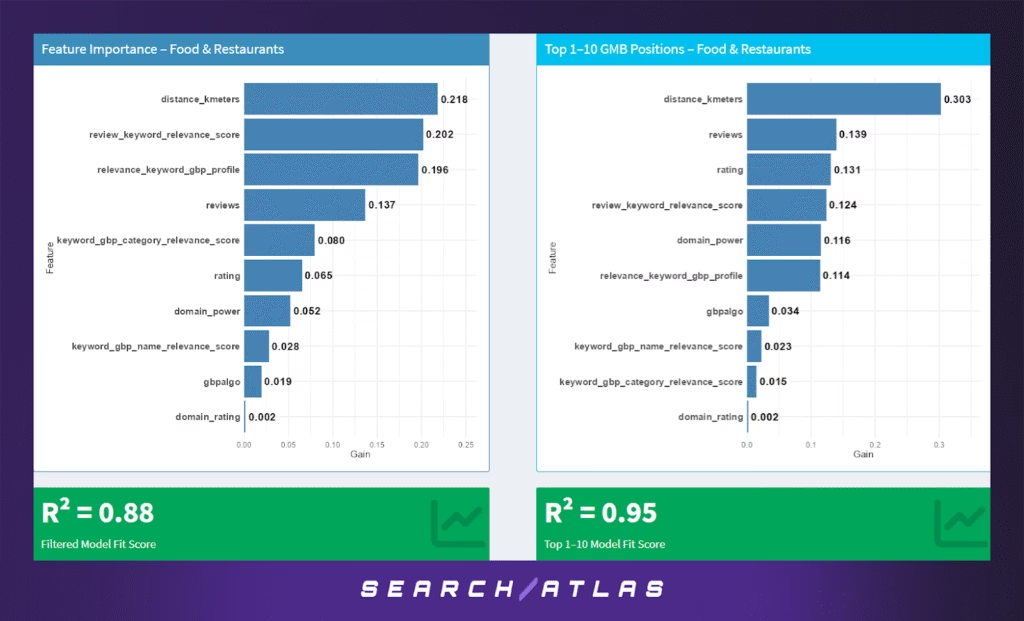
The Food & Restaurants sector — encompassing quick service restaurants, cafes, bakeries, food trucks, and fine dining — operates in a highly competitive, proximity-sensitive environment. Real-time consumer intent and social proof are key to driving local visibility and decision-making.
Model Results (All GBP Positions)
In the full-position model:
- Proximity (21.8%), while important, is not as dominant as in other sectors. This suggests that consumers may travel slightly farther for food options — particularly for well-reviewed or highly relevant ones.
- Review keyword relevance (20.2%) and GBP profile relevance (19.6%) emerge as strong signals, showing the critical importance of semantic alignment between user intent and content in business listings.
- Review count (13.7%) and category relevance (8.0%) reinforce the need for both volume and alignment of reviews with user queries.
- Rating (6.5%) and domain power (5.2%) show moderate importance, while Domain Rating (0.2%) is essentially negligible.
The R² value of 0.88 indicates a solid fit, capturing a significant portion of ranking variability — although likely affected by additional unobserved signals such as real-time updates or menu-specific content.
Model Results (Top 1–10 GBP Positions)
Among the top-ranking listings:
- Proximity (30.3%) becomes the most decisive factor — diners looking for food often prioritize what’s nearest.
- Reviews (13.9%), ratings (13.1%), and review keyword relevance (12.4%) all contribute strongly, reflecting the social proof required to earn top spots.
- Domain power (11.6%) and GBP profile relevance (11.4%) gain importance, likely due to brand strength and comprehensive profile optimization being more common among high performers.
- Google’s internal business algo score (3.4%) also adds predictive power.
With a high R² of 0.95, the top 10 model performs well, highlighting clearer differentiators among highly competitive food establishments.
Strategic Takeaways
- Success in this sector hinges on three pillars: proximity, review content, and GBP keyword alignment.
- Restaurants must actively manage review acquisition and quality, focusing on keyword-rich customer feedback.
- For premium visibility, comprehensive GBP optimization (titles, categories, services) and brand authority also matter.
Overall, local food visibility depends not just on being nearby, but on offering proof of satisfaction and relevance through the customer voice and content alignment.
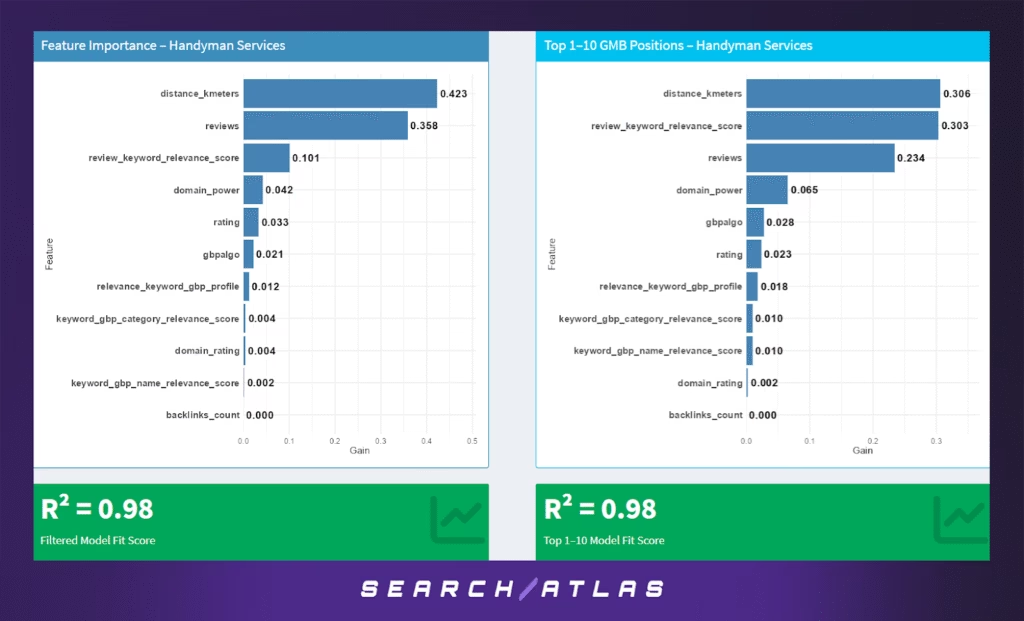
h. Handyman Services GBP Ranking Factors
The Handyman Services sector includes professionals offering repair, maintenance, and installation services—often for urgent or on-demand jobs. Visibility in the local pack is critical for lead generation, particularly for users searching with immediate intent.
Model Results (All GBP Positions)
In the full-model analysis:
- Proximity (42.3%) and review count (35.8%) dominate the ranking signal landscape. This emphasizes the importance of local availability and social proof—key when users prioritize convenience and trust.
- Review keyword relevance (10.1%) also plays a significant role, indicating that review content describing specific services (e.g. “fixed faucet”, “door repair”) improves discoverability.
- Other signals, including domain power (4.2%), rating (3.3%), and Google’s internal algorithm score (2.1%), play minor yet measurable roles.
- GBP-specific keyword relevance features contribute minimally (all <2%).
The model achieves a very strong R² = 0.98, indicating high predictive power and strong signal clarity.
Model Results (Top 1–10 GBP Positions)
In the top-tier local results:
- Proximity (30.6%) remains important, but review keyword relevance (30.3%) now holds nearly equal weight—suggesting that top-performing businesses are those whose review content aligns closely with the user query.
- Review count (23.4%) continues to matter significantly, supporting the idea that volume of feedback builds trust.
- Domain power (6.5%), Google’s internal score (2.8%), and ratings (2.3%) contribute modestly.
- Keyword and GBP profile relevance contribute only minor incremental value.
This model also achieves R² = 0.98, indicating excellent fit even at the top positions.
Strategic Takeaways
- Hyper-local presence and semantic-rich reviews are essential. Businesses should encourage customers to mention specific services and outcomes in their reviews.
- While GBP profile optimization and rating scores are useful, the volume and detail of review content ultimately differentiate the highest performers.
- Reputation management and proximity targeting (e.g. local pages or service area refinement) are key levers for improving visibility.
Handyman visibility is all about trust, clarity, and locality—and the data confirms that proximity and highly relevant customer reviews drive results.
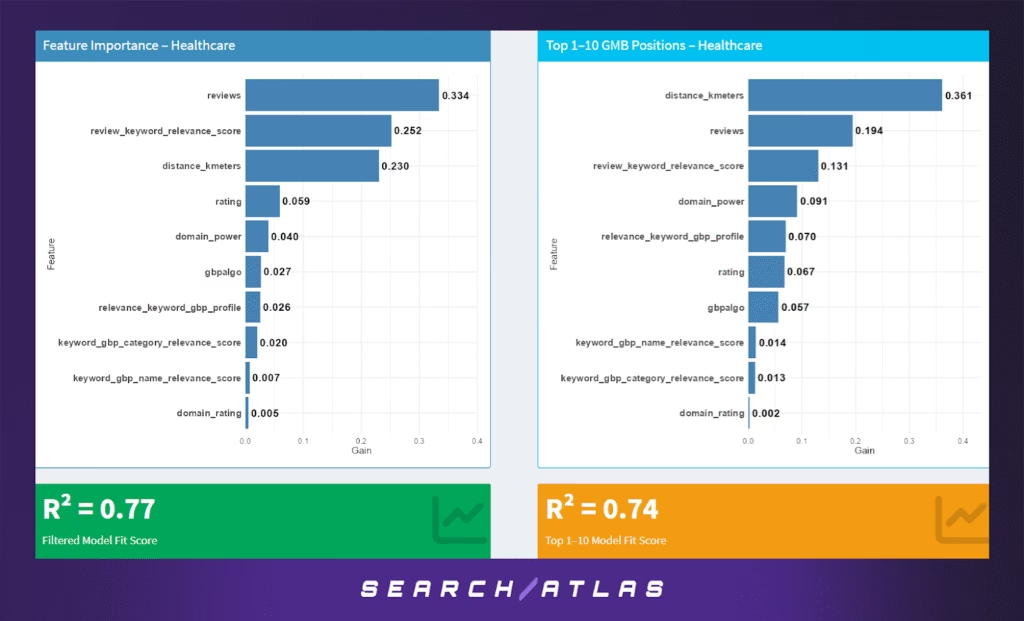
i. Healthcare GBP Ranking Factors
In the Healthcare sector, trust and accessibility are paramount, particularly for services involving sensitive, urgent, or high-stakes needs. Unlike consumer services, SEO performance here reflects not only relevance and reputation but also compliance with professional standards.
Model Results (All GBP Positions)
Across the full GBP position range:
- Review volume (33.4%) and review keyword relevance (25.2%) are the most dominant ranking signals. This aligns with the importance of word-of-mouth validation and semantic alignment of reviews with service queries (e.g., “pediatrician,” “urgent care,” “clean office”).
- Proximity (23.0%) still plays a strong role, especially when patients seek nearby clinics or practitioners.
- Rating (5.9%), domain power (4.0%), and Google’s internal algorithm score (2.7%) are present but secondary.
- Profile keyword alignment and Domain Authority carry relatively minor weight.
The model achieved an R² = 0.77, indicating moderate fit. This suggests that while known features explain much of the variance, other unobserved or regulated variables may influence visibility, such as licensure, business hours, or behavioral engagement signals.
Model Results (Top 1–10 GBP Positions)
In the top pack:
- Proximity (36.1%) becomes the single most important factor, likely driven by mobile “near me” searches.
- Review volume (19.4%) and review keyword relevance (13.1%) remain strong, but slightly less so compared to the full set.
- Interestingly, domain power (9.1%) and profile keyword relevance (7.0%) gain prominence, possibly reflecting more competitive intent.
- Traditional features like ratings (6.7%) and Google’s algo score (5.7%) still play a minor role.
The model’s fit score declines slightly in this range to R² = 0.74, again suggesting greater variability in what drives top-10 success, potentially including off-page factors or user engagement not captured in structured features.
Strategic Takeaways
- Review strategy is critical: healthcare businesses should actively request reviews that mention key services and conditions, while complying with ethical and regulatory constraints.
- Location and mobile optimization are vital, especially for practices relying on local walk-in traffic.
- The relatively lower R² values hint at hidden signals (e.g., click behavior, authority citations, brand trust) that may be disproportionately important in this regulated industry.
The takeaway: for healthcare, local relevance and detailed reviews are not just helpful—they’re essential—but deeper authority and behavioral factors likely contribute behind the scenes.
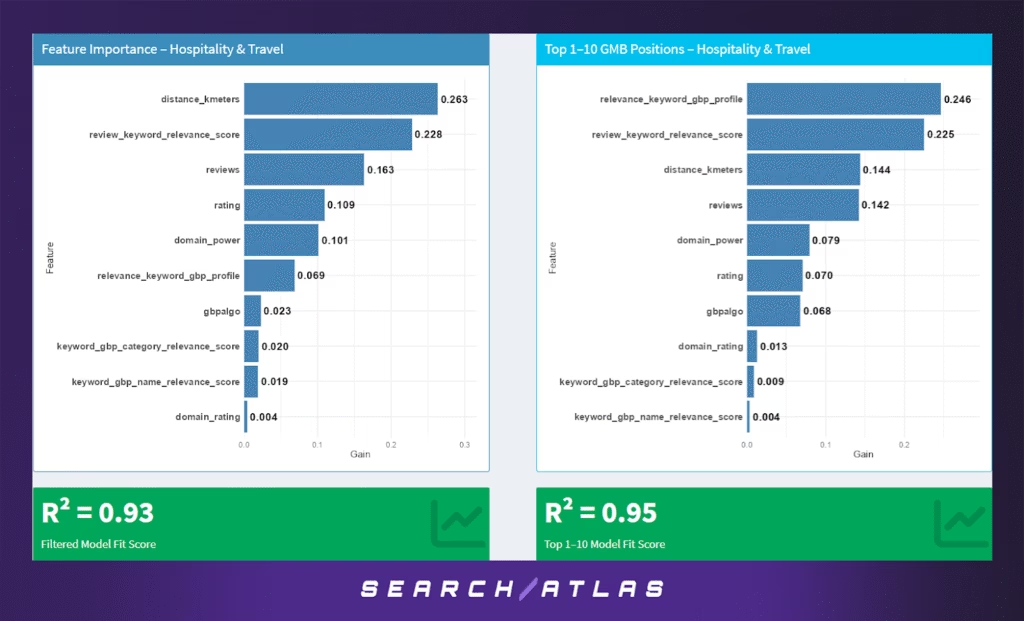
j. Hospitality & Travel GBP Ranking Factors
The Hospitality & Travel industry operates in an intensely competitive environment, where location, brand perception, and relevance all play major roles in shaping Google visibility. Hotels, resorts, tour operators, and related businesses often compete in saturated local markets, where online reputation and proximity directly affect consumer decisions.
Model Results (All GBP Positions)
In the full ranking range:
- Distance to search centroid (26.3%) is the leading feature, underscoring the importance of geographic relevance, especially for location-based services like accommodations or travel experiences.
- Review keyword relevance (22.8%) and review volume (16.3%) also play large roles, suggesting that semantically rich customer feedback helps GBP profiles stand out.
- Rating (10.9%) and domain power (10.1%) are both solid secondary signals, reflecting the dual importance of reputation and off-site authority (e.g., well-known booking platforms).
- GBP profile relevance and Google’s internal score (gbpalgo) contribute modestly.
The model’s performance is strong, with R² = 0.93, indicating that the selected features explain most of the observed ranking behavior.
Model Results (Top 1–10 GBP Positions)
For the top 10:
- The strongest predictor is profile-level keyword relevance (24.6%), highlighting that optimizing GBP descriptions and services for search terms is key to elite placement.
- Review keyword alignment (22.5%) remains highly influential, further emphasizing user-generated content optimization.
- Proximity (14.4%) and review volume (14.2%) are still important, but slightly diminished compared to the full set.
- Domain power (7.9%), rating (7.0%), and Google’s algo score (6.8%) remain modest contributors.
The top pack model achieves R² = 0.95, the highest observed in our study. This suggests that businesses ranking in the top 10 in Hospitality & Travel follow a predictable and replicable pattern, driven by GBP content optimization, proximity, and reviews.
Strategic Takeaways
- GBP profile keyword tuning is critical: Businesses must ensure their GBP description and category listings reflect key commercial queries (“luxury hotel,” “family resort,” “city center”).
- Leverage reviews as SEO assets: Encouraging reviews that reference amenities, locations, and niche terms can directly enhance visibility.
- Proximity remains powerful, but high-ranking businesses also rely on relevant, structured content and domain-level authority, especially when competing on brand trust (e.g., chains vs. local).
In short, for Hospitality & Travel, precision in content and relevance at both the business and customer voice levels is what elevates visibility from average to elite.
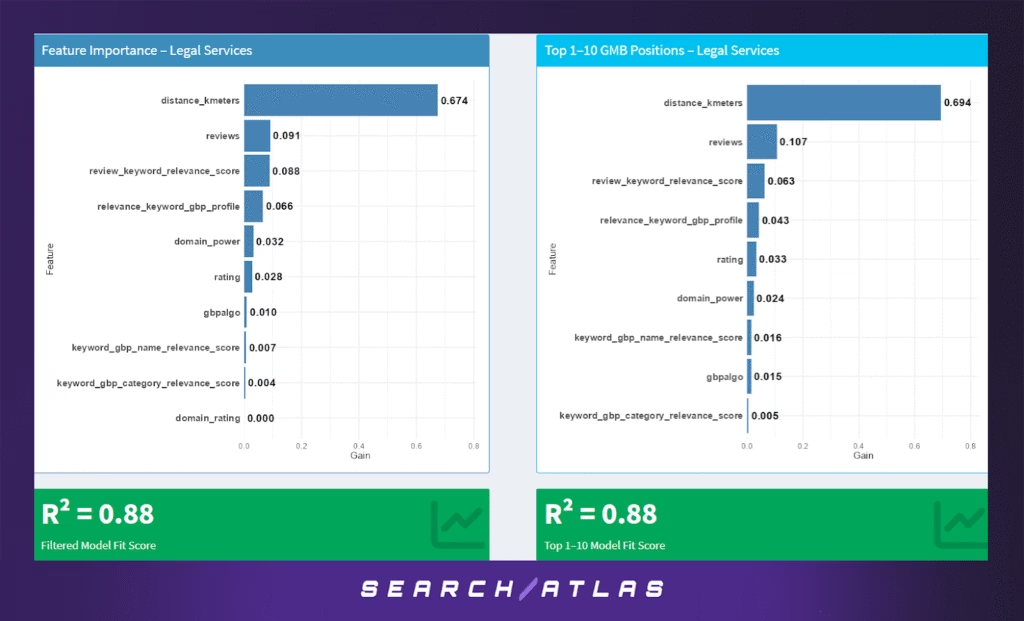
k. Legal Services GBP Ranking Factors
The Legal Services sector demonstrates a unique ranking behavior compared to other industries analyzed. Law firms and legal professionals typically operate within strict geographic licensing zones, and their services are often hyper-localized, leading to strong geographic weighting in search rankings.
Model Results (All GBP Positions)
In the general ranking model:
- Distance to search centroid dominates the model (67.4%), making it by far the most critical factor. This confirms that proximity is overwhelmingly important in determining visibility for legal queries.
- Secondary features include review volume (9.1%) and review-keyword relevance (8.8%), indicating that social proof and semantically aligned testimonials still support rankings.
- GBP profile relevance (6.6%) and domain authority (3.2%) provide minor incremental gains.
- Rating, Google’s internal algo score (gbpalgo), and name/category keyword matches play minimal roles.
The model performs well with R² = 0.88, showing consistent prediction accuracy despite the heavy reliance on a single dominant variable.
Model Results (Top 1–10 GBP Positions)
For top-pack rankings:
- Distance remains even more important (69.4%), further reinforcing that being physically close to the search centroid is a prerequisite for top rankings in legal searches.
- Reviews (10.7%), review-keyword relevance (6.3%), and profile relevance (4.3%) trail distantly but still matter.
- Other features like rating, domain power, and GBP name relevance remain low-weight, consistent with the general model.
Again, the top 10 model maintains R² = 0.88, reflecting the same tight dependence on physical proximity.
Strategic Takeaways
- Location optimization is paramount: Law firms must ensure that their GBP location is accurate, centered within target service areas, and aligned with where searchers are located.
- Review content still matters, especially when it includes specific legal terms like “personal injury,” “immigration lawyer,” or “contract review.”
- Other traditional SEO or GBP optimizations (e.g., category tuning, backlink strength) play a reduced role compared to other industries.
In essence, Legal Services exhibit one of the most proximity-sensitive ranking dynamics of any sector in our study. Firms that rank well are typically those that are not only relevant and reputable, but most importantly, nearby.
l. Logistics GBP Ranking Factors
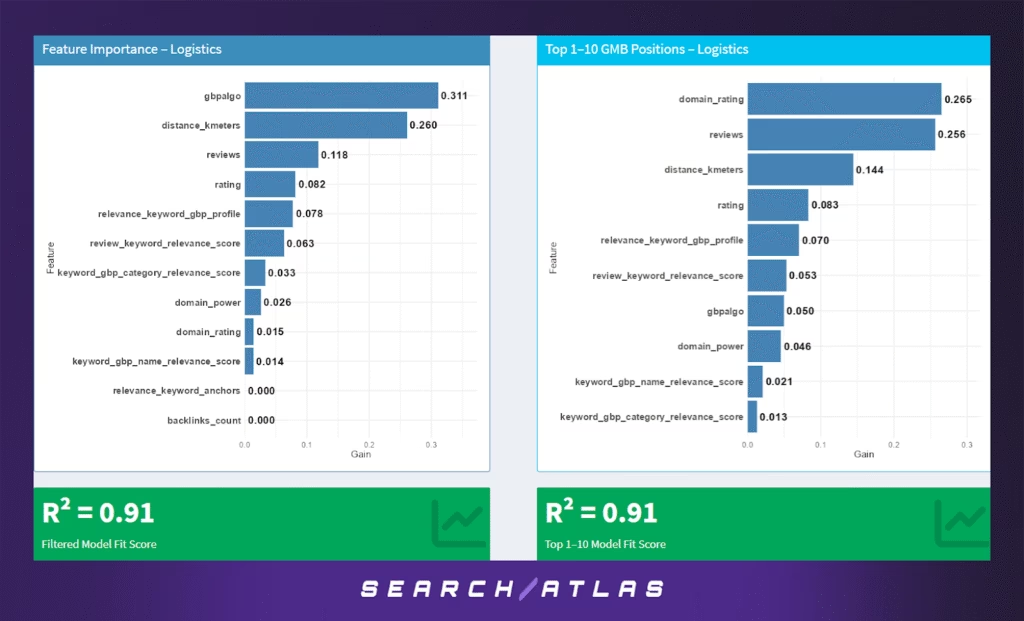
The Logistics sector reflects a hybrid ranking profile that values both local presence and domain-level authority. As a service industry with operational footprints across multiple cities or regions, logistics providers benefit from both physical proximity and strong off-site SEO signals, especially among top-ranking businesses.
Model Results (All GBP Positions)
In the general model that includes all ranking positions:
- Google’s internal GBP algorithm score (gbpalgo) is the most influential factor (31.1%), suggesting that behavioral and engagement-based signals — likely reflecting listing activity, clicks, or other proprietary measures — heavily influence rankings across the board.
- Proximity to the search centroid (26.0%) is the second most important feature, reinforcing that location relevance is critical in logistics, even when companies have broader service coverage.
- Review count (11.8%) and average rating (8.2%) contribute meaningfully, indicating that user trust and satisfaction continue to play a central role in visibility.
- GBP keyword relevance scores across profile, review, and category fields range from 7.8% to 3.3%, reflecting moderate importance of semantic alignment with query intent.
- Domain-level SEO signals such as domain power (2.6%) and domain rating (1.5%) rank low overall but still contribute marginally.
- The model achieves strong explanatory power with R² = 0.91, indicating a highly predictive feature set across the full range of rankings.
Model Results (Top 1–10 GBP Positions)
For top-ranking positions only:
- Domain rating becomes the most dominant signal (26.5%), highlighting the growing importance of authority and backlink strength among high-ranking logistics providers.
- Review count (25.6%) remains critical, with proximity dropping to 14.4%, reflecting how top-pack visibility is less about location alone and more about trust and perceived authority.
- Rating (8.3%), GBP profile relevance (7.0%), and review-keyword relevance (5.3%) still play supporting roles.
- Interestingly, gbpalgo drops to 5.0%, suggesting that Google’s internal engagement signals play a bigger role in general visibility than in differentiating the elite.
- Other GBP semantic fields and domain power each contribute under 5%.
- The model retains excellent performance in this subset with R² = 0.91, showing that top rankings are shaped by a more nuanced mix of trust and authority signals.
Strategic Takeaways
- Authoritativeness is critical at the top: To secure and maintain top-pack positions, logistics providers must invest in off-site SEO (link-building, digital PR) to boost domain authority and trustworthiness.
- Review generation and quality matter throughout: From mid-pack to top 3, review quantity is consistently impactful. Strategies should include customer feedback loops, automated review requests, and integration of logistics-related keywords in testimonials.
- Local presence is still necessary: While not the top factor in elite rankings, proximity remains influential and should be optimized via precise GBP location targeting and local landing pages.
- GBP engagement optimization (gbpalgo) is uniquely important for general rankings, making it worthwhile to encourage listing interactions, post updates, and manage Q&A actively.
In summary, Logistics rankings are shaped by a balanced mix of local relevance, user trust, and web authority. Unlike sectors dominated by a single variable (e.g., proximity in Legal Services), top logistics performers win by being trustworthy, visible, and nearby — in that order.
m. Manufacturing GBP Ranking Factors
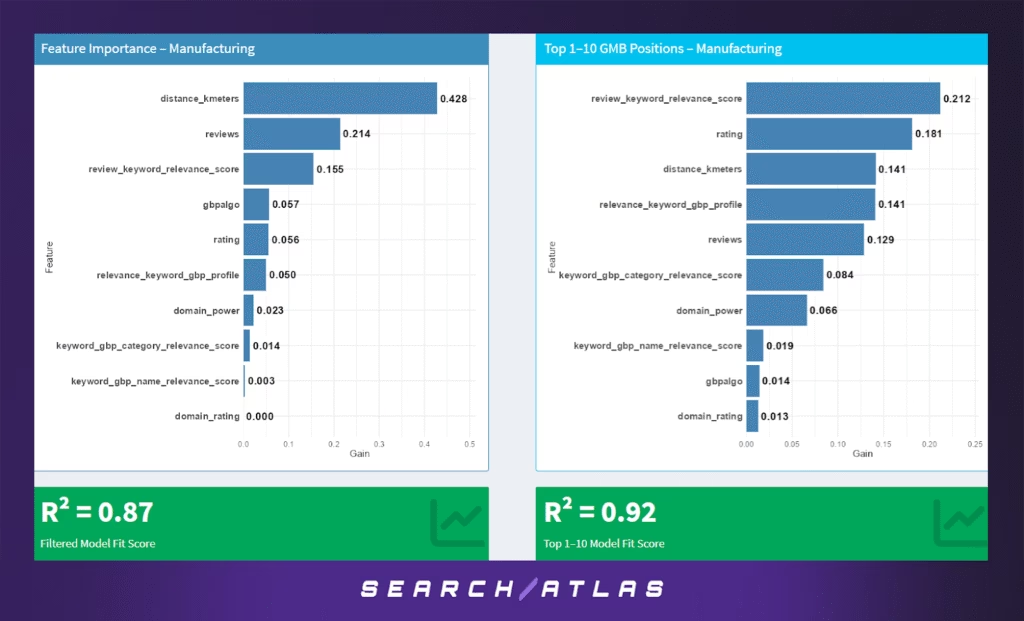
The Manufacturing sector exhibits a unique blend of local and reputation-based ranking factors. While often perceived as B2B and less consumer-facing, many manufacturers rely heavily on local visibility to attract contractors, resellers, and industrial partners.
Model Results (All GBP Positions)
In the full dataset model:
- Proximity is the top ranking factor by far (42.8%), emphasizing that local manufacturers still depend heavily on being physically close to their customers — even in a business-to-business setting.
- Reviews (21.4%) and review-keyword relevance (15.5%) play significant roles, suggesting that social proof and keyword-laden feedback are important even for industrial categories.
- Google’s proprietary engagement score (gbpalgo – 5.7%) and rating (5.6%) contribute moderately.
- GBP profile keyword relevance (5.0%) is notable, but other relevance fields — such as category or name alignment — have very small contributions.
- Website authority metrics (domain_power, domain_rating) play minimal roles overall, consistent with lower reliance on traditional SEO in the sector.
- Model fit remains strong at R² = 0.87, suggesting a reliable understanding of visibility drivers across all ranks.
Model Results (Top 1–10 GBP Positions)
Within the top 10 rankings:
- Review-keyword relevance becomes the dominant factor (21.2%), indicating that what customers say — and how well it matches the query — is key to breaking into the top pack.
- Average rating (18.1%) and proximity (14.1%) follow closely, reflecting a shift from general proximity to quality and sentiment among the top listings.
- GBP profile relevance (14.1%) also rises in importance, suggesting manufacturers who describe their offerings more precisely in their profiles have better odds of ranking highly.
- Review volume (12.9%) maintains its impact but is less dominant than in the full model.
- Lesser factors include category relevance (8.4%), domain authority (6.6%), and various other relevance and engagement scores below 2%.
- Notably, R² improves to 0.92, indicating that top pack rankings are more systematically influenced by specific features than general rankings are.
Strategic Takeaways
- Proximity remains a strong baseline, but to rise above competitors in the top results, manufacturers must focus on review quality and semantic keyword alignment in reviews.
- High average ratings are critical — low ratings are likely disqualifying for top-pack inclusion, even when other signals are strong.
- Detailed, keyword-rich GBP profiles should be a strategic priority for manufacturing companies, especially those with specialized or niche production capabilities.
- Traditional SEO indicators like domain rating and backlink count play a much smaller role than in other B2B sectors (e.g., Logistics).
In essence, Manufacturing rankings balance geographic accessibility with strong review signals and precise profile content. Businesses that succeed are both relevant and well-reviewed, with enough local proximity to fulfill expectations around accessibility and service coverage.
n. Personal Care Services GBP Ranking Factors
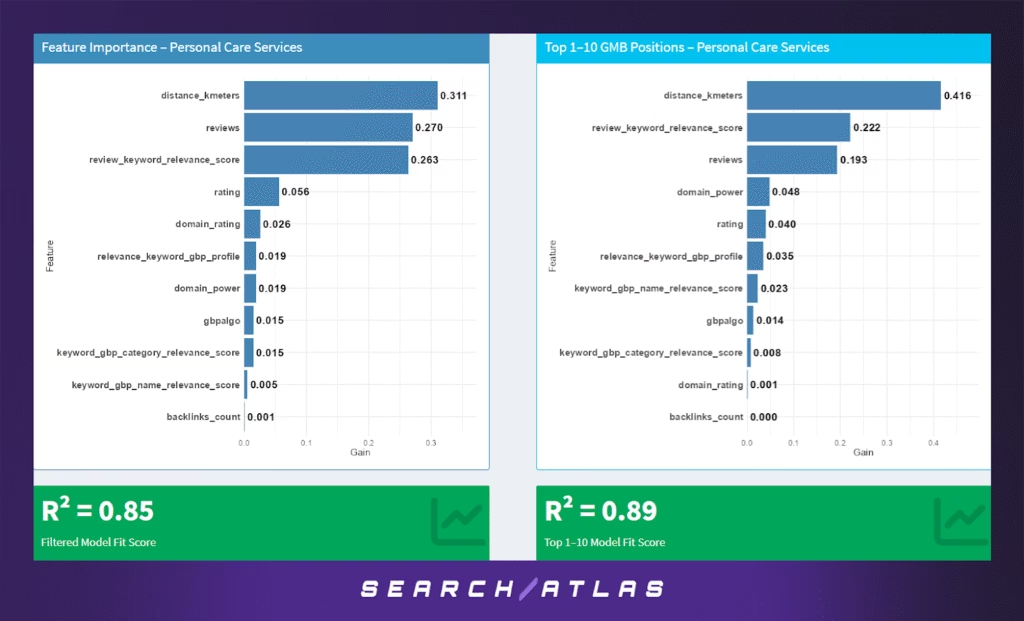
The Personal Care Services sector (including salons, spas, and wellness providers) is highly localized and reputation-sensitive. Consumers often choose providers based on a combination of proximity, reviews, and relevance — making this sector a blend of service quality and discoverability.
Model Results (All GBP Positions)
In the full model across all GBP positions:
- Proximity is the most influential factor (31.1%), indicating that consumers tend to choose care services close to them, often for convenience or immediacy.
- Review volume (27.0%) and review-keyword relevance (26.3%) follow closely, showing that both quantity and keyword-rich content in reviews heavily impact rankings.
- Rating (5.6%) plays a moderate role, suggesting that while star scores matter, volume and relevance of reviews outweigh raw ratings.
- Website authority signals (domain_rating 2.6%, domain_power 1.9%) have marginal influence, hinting that traditional SEO metrics matter less in this hyper-local space.
- Other factors like GBP profile relevance, category match, and backlink count contribute minimally.
- The model achieves R² = 0.85, indicating solid predictability based on the available features.
Model Results (Top 1–10 GBP Positions)
In the top-pack model for ranks 1–10:
- Distance to the search centroid becomes even more dominant (41.6%), confirming that top results skew heavily toward the closest providers.
- Review-keyword relevance (22.2%) and review volume (19.3%) are still highly influential, emphasizing that consumer feedback with relevant terms boosts visibility.
- Secondary factors include domain_power (4.8%), rating (4.0%), and profile relevance (3.5%) — all showing slight but meaningful impact.
- GBP name/category relevance, gbpalgo, and SEO metrics play a small role in differentiating businesses within the top 10.
- The model performs even better here, with R² = 0.89, indicating a strong and consistent pattern among top-ranked listings.
Strategic Takeaways
- Location optimization is critical — ensure GBP address information is accurate and centered in high-traffic or target service zones.
- Review strategy should go beyond volume — encourage customers to mention specific services (e.g., “hair coloring,” “deep tissue massage”) to boost review-keyword relevance.
- Star ratings do matter, but they’re secondary to proximity and content-rich reviews.
- Off-page SEO signals (e.g., domain authority, backlinks) play a very limited role — this is a people-driven, location-centric space.
In summary, Personal Care Services rankings are driven by local presence and authentic, keyword-relevant customer reviews. Businesses can succeed by being both nearby and well-reviewed, especially with feedback that aligns semantically with user intent.
o. Points of Interest (POI) GBP Ranking Factors
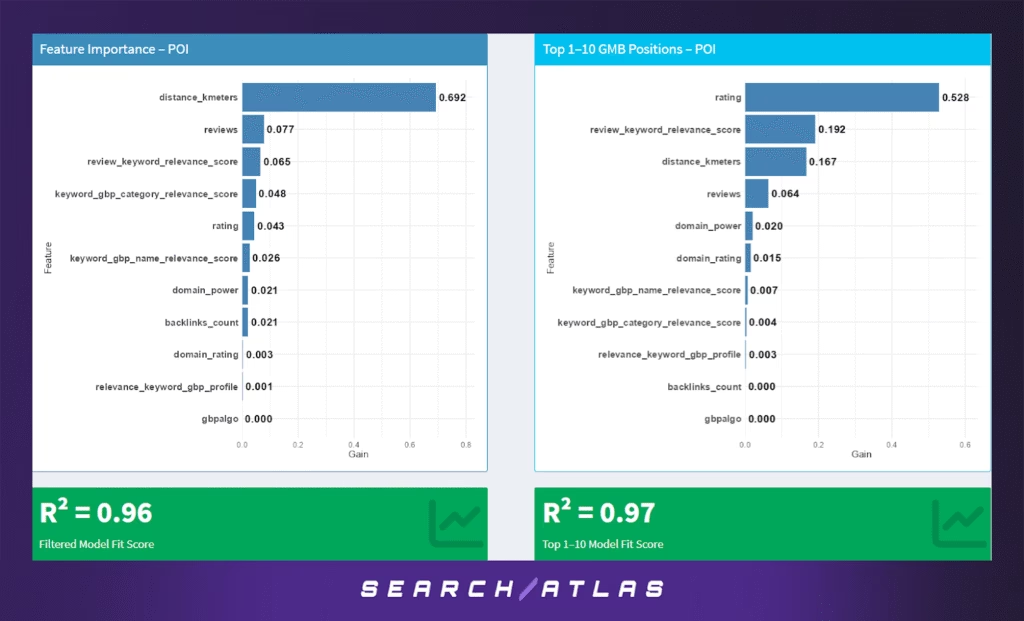
The POI category includes local landmarks, attractions, parks, and other public venues. Unlike commercial businesses, POIs rely heavily on user-generated content and intrinsic visibility within maps and guides. Their ranking behavior is shaped more by physical location and perceived public interest than by traditional SEO or GBP optimization.
Model Results (All GBP Positions)
In the full GBP rankings model:
- Distance to search centroid is overwhelmingly dominant (69.2%), suggesting that visibility for POIs is almost entirely proximity-based. Users are often looking for the nearest point of interest, and Google’s results reflect that intent.
- Review volume (7.7%) and review-keyword relevance (6.5%) contribute modestly, implying that social proof still plays a secondary role — especially if the POI is well-known or culturally significant.
- Category and name relevance (4.8%, 2.6%) show slight influence, meaning that clear naming and category tagging still help discoverability.
- Rating (4.3%), domain authority, and backlinks have minor impact, underscoring that off-site SEO is largely irrelevant for public POIs.
- The model achieves a remarkably high R² = 0.96, reflecting the consistency of proximity-dominated rankings across POIs.
Model Results (Top 1–10 GBP Positions)
For the top local pack positions:
- Rating dominates the model (52.8%), a stark contrast to the all-position model — indicating that once POIs are “in range,” user satisfaction plays the biggest role in determining who ranks at the top.
- Review-keyword relevance (19.2%) and distance (16.7%) still contribute meaningfully, but are clearly outpaced by overall rating.
- Review count (6.4%), domain signals, and profile features play only minor roles.
- The top-10 model performs exceptionally well with R² = 0.97, highlighting Google’s precision in ranking POIs by user quality signals at the top tier.
Strategic Takeaways
- Proximity remains the entry ticket, but to get into the top local pack, maintaining high star ratings is key. This includes good visitor experiences, accessibility, and amenities.
- Encourage keyword-rich reviews that describe experiences (e.g., “great walking trail,” “perfect for sunset pics”) to boost semantic alignment.
- Category tagging and proper naming still help, especially in distinguishing between similar nearby POIs.
- Traditional digital marketing strategies (e.g., backlinks, domain authority) are nearly irrelevant here — focus efforts on on-platform optimization.
POIs represent a unique case in local SEO where location gets you visibility, but public sentiment secures top rankings.
p. Professional Services GBP Ranking Factors
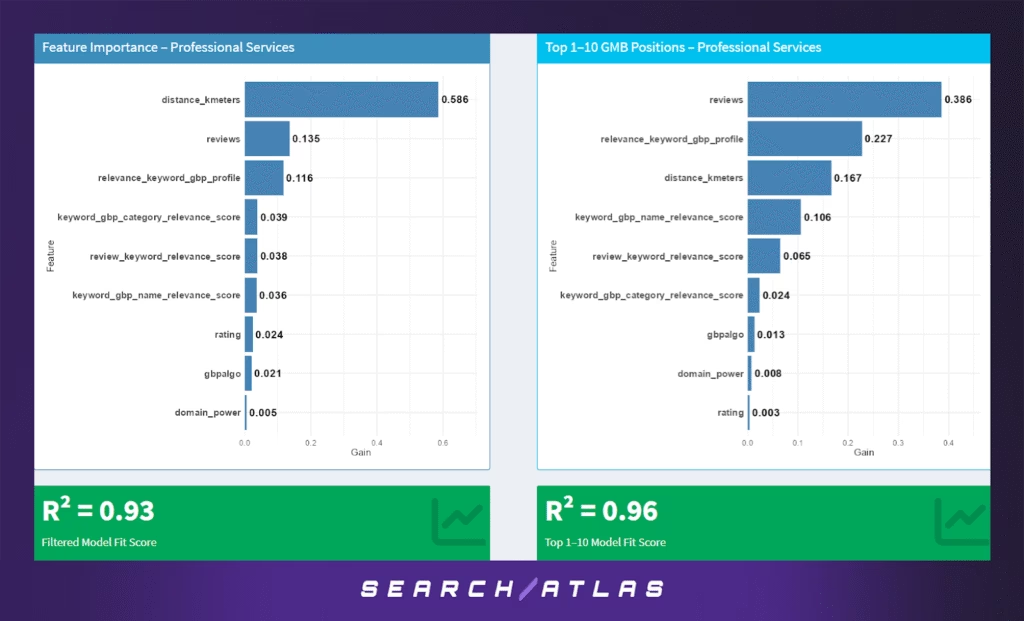
The Professional Services category includes consultants, accountants, architects, and other credential-based experts. These providers often serve a mix of local and regional clients, making proximity relevant but not always decisive. Branding, trust signals, and semantic relevance all contribute to local visibility.
Model Results (All GBP Positions)
In the overall ranking model:
- Distance to the search centroid dominates (58.6%), confirming that geography is a major driver of visibility — especially for queries with implicit local intent like “tax advisor near me” or “business consultant downtown.”
- Review volume (13.5%) and GBP profile-keyword relevance (11.6%) are strong secondary factors, showing that social proof and well-optimized business profiles matter significantly.
- Other meaningful signals include category relevance (3.9%), review-keyword relevance (3.8%), and name-keyword relevance (3.6%) — highlighting the importance of both GBP optimization and semantic alignment.
- Factors like rating, Google’s internal algo score (gbpalgo), and domain authority are relatively weak contributors in this sector.
- The model achieves strong performance with R² = 0.93, suggesting a high degree of predictability in ranking behavior.
Model Results (Top 1–10 GBP Positions)
For businesses at the top of the local pack:
- Review volume becomes the top predictor (38.6%), suggesting that once proximity and basic profile optimization are satisfied, social proof drives differentiation among top-ranked providers.
- Profile-keyword relevance (22.7%) and distance (16.7%) follow, indicating that content alignment and geographic closeness still matter, but are no longer overwhelming.
- GBP name relevance (10.6%) and review-keyword alignment (6.5%) show the importance of semantic cues in both listings and user feedback.
- Lesser factors like category, internal algorithmic scoring, and domain power contribute marginally.
- The model’s R² = 0.96 reflects excellent predictive accuracy in the top-tier results.
Strategic Takeaways
- Proximity is crucial but not exclusive. Professionals must be located reasonably close to their target clients but can stand out even if slightly farther away if their profile is strong.
- Reviews are crucial to appear in the local pack. Encourage volume and relevance — clients should mention specific services, credentials, or problems solved.
- Semantic relevance across GBP content (name, categories, profile text) enhances keyword match quality, particularly for top rankings.
- While traditional domain-based SEO plays a minor role, GBP optimization and user feedback are highly influential in this category.
Professional Services show a balanced local ranking structure, where location gives visibility, and reviews and relevance win trust.
q. Real Estate GBP Ranking Factors
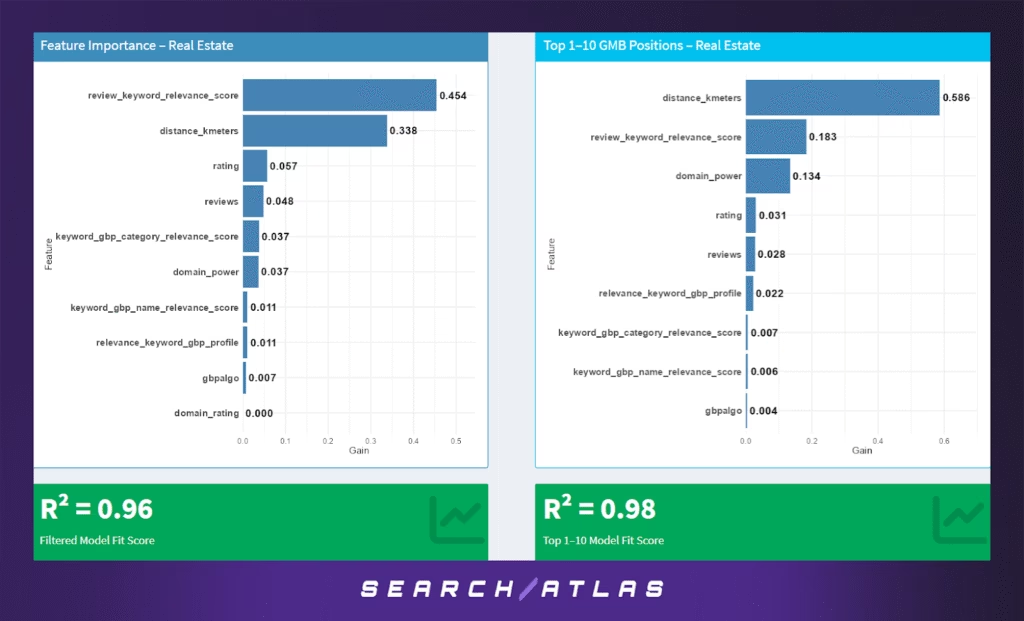
The Real Estate sector exhibits a unique local search behavior due to the inherently location-sensitive nature of property searches. Agents and firms are evaluated based on proximity, credibility, and how well their reputations align with buyer or seller needs in specific geographic areas.
Model Results (All GBP Positions)
In the overall model across all local pack positions:
- Review-keyword relevance is the dominant signal (45.4%), indicating that user-generated content (e.g., reviews mentioning phrases like “home sale,” “condo,” or “open house”) carries significant weight in determining rankings.
- Distance to the search centroid (33.8%) remains highly influential, consistent with the hyper-local nature of real estate.
- Ratings (5.7%) and review count (4.8%) are also relevant, though less than in other service sectors, suggesting that quality and presence of reviews are slightly secondary to their semantic alignment.
- GBP category relevance and domain power (both at 3.7%) offer moderate support, helping businesses reinforce the topical match to real estate queries.
- Other GBP text features and SEO signals (e.g., name relevance, backlinks, domain rating) contribute minimally.
- The model performs robustly with R² = 0.96, indicating high predictive strength in real estate search rankings.
Model Results (Top 1–10 GBP Positions)
For top-pack visibility:
- Distance becomes the most influential factor (58.6%), underscoring that appearing near the user’s target location is a prerequisite for top visibility.
- Review-keyword relevance (18.3%) still holds significant sway, reinforcing that semantic content in reviews matters even among the top-ranked.
- Domain power (13.4%) rises in influence, suggesting that stronger websites may help push realtors into premium ranking zones.
- Traditional metrics like rating (3.1%) and review count (2.8%) are modest contributors.
- Text relevance across the GBP (profile, categories, names) and SEO features play only a minor role, further supporting the dominance of location and semantically rich review content.
- The top 10 model yields R² = 0.98, indicating near-perfect prediction of ranking order in this sector.
Strategic Takeaways
- Review content is powerful: Encourage clients to write reviews that mention real estate services and neighborhood names. Relevance drives performance more than volume alone.
- Local proximity is critical: Businesses need precise GBP locations near key neighborhoods or zip codes to rank prominently for nearby real estate searches.
- Domain strength and SEO presence still matter in the upper echelons of the rankings, but their influence is limited relative to other industries.
- Fine-tuning GBP categories and profile descriptions helps support visibility, though they’re secondary to user-generated signals.
In summary, Real Estate is both proximity-driven and review-sensitive. To rank, agents must be local. To win top spots, they must also have reviews that speak the language of property buyers and sellers.
r. Retail GBP Ranking Factors
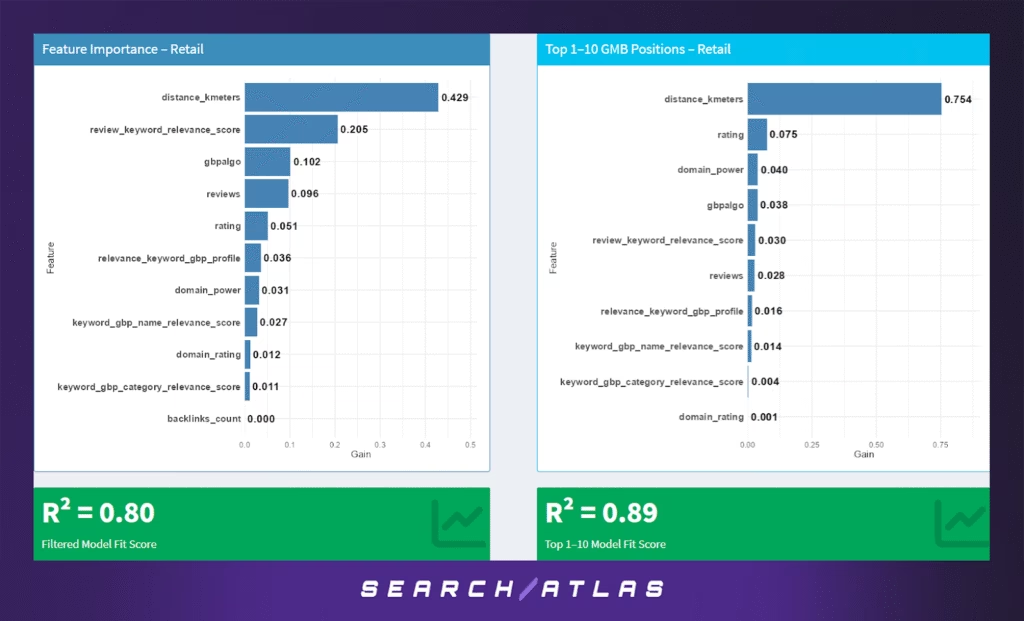
The Retail sector reflects a hybrid behavior in local SEO, where both proximity and digital presence contribute to visibility. Unlike service sectors, retail often benefits from higher foot traffic and in-person visits, making physical location a major factor in search rankings.
Model Results (All GBP Positions)
In the general model across all GBP positions:
- Distance to search centroid (42.9%) is the leading factor, consistent with location-based intent of shoppers looking for stores nearby.
- Review-keyword relevance (20.5%) is also a strong signal, suggesting that when customers mention specific products or services in their reviews (e.g., “shoe repair,” “electronics section”), rankings benefit.
- Google’s internal algo score (gbpalgo, 10.2%) and review volume (9.6%) offer additional influence, capturing general trustworthiness and social proof.
- Rating (5.1%) contributes modestly, showing that star quality matters but doesn’t dominate.
- GBP and SEO features such as profile relevance (3.6%), domain power (3.1%), and GBP name relevance (2.7%) are minor contributors.
- The model performance at R² = 0.80 indicates moderate predictability, slightly lower than other industries due to the mixed behavior of consumer foot traffic and online signals.
Model Results (Top 1–10 GBP Positions)
For top-pack rankings:
- Distance is overwhelmingly dominant (75.4%), reinforcing that being nearby is crucial for breaking into the top 10 spots.
- Rating (7.5%), domain power (4.0%), and gbpalgo (3.8%) follow distantly, emphasizing that while proximity leads, brand credibility and trust metrics can still assist in top-tier placement.
- Review-keyword relevance (3.0%) and review count (2.8%) play supportive roles, much lower than in other sectors like Real Estate or Personal Care.
- Textual relevance across the GBP profile, name, and categories contributes negligibly (1–2%), and domain rating and backlinks are almost irrelevant.
- This model improves in predictive power with R² = 0.89, suggesting higher consistency among top-performing retailers.
Strategic Takeaways
- Location is everything: Ensure accurate, hyperlocal GBP pins—especially for chain stores or franchises operating in dense commercial areas.
- Keyword-rich reviews still help, but their value is reduced relative to other industries. Retailers should still encourage reviews that mention products and services by name.
- Star rating and reputation matter more for top visibility, but not as much as proximity.
- SEO and GBP profile optimization (name, category, backlinks) matter less than physical presence, especially for consumers doing quick “near me” lookups.
In conclusion, Retail visibility is strongly proximity-led. Retailers should optimize GBP placement and local signage first, and consider review and domain authority optimization as secondary levers.
s. Technology / Creative GBP Ranking Factors
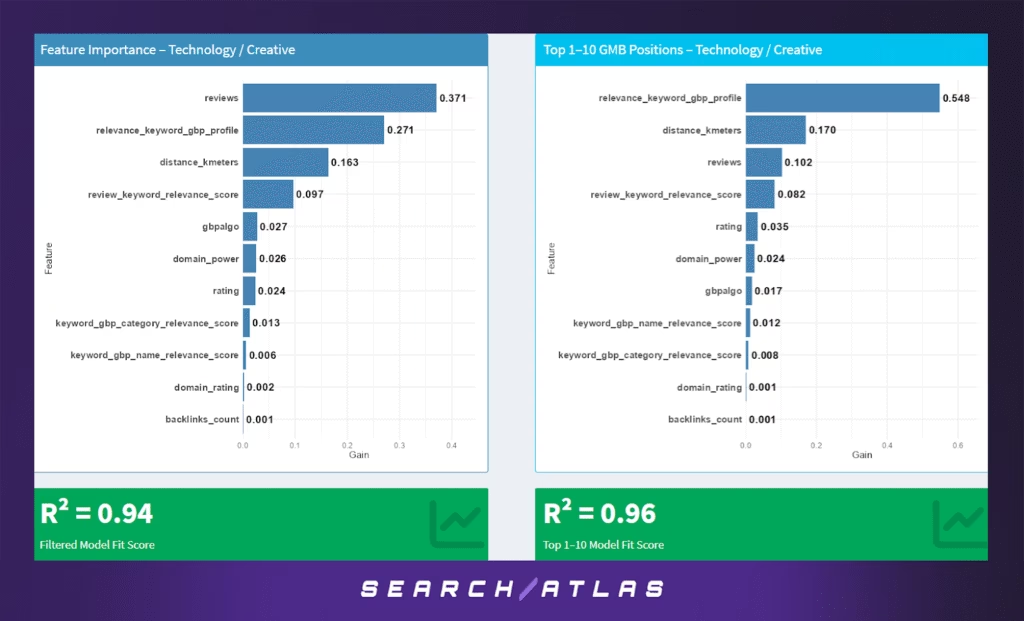
The Technology and Creative Services sector—encompassing agencies, developers, digital marketers, designers, and related firms—shows a distinct ranking pattern that prioritizes content relevance and brand reputation over strict geographic proximity.
Model Results (All GBP Positions)
In the broader model across all GBP rankings:
- Reviews (37.1%) are the most important factor, reflecting how essential social proof is in tech/creative spaces where client trust is paramount.
- GBP profile relevance to the keyword (27.1%) plays a substantial role, indicating the importance of aligning business descriptions and services with the specific search intent (e.g., “web design,” “branding,” “IT consulting”).
- Proximity (16.3%) still matters, but much less than in more location-sensitive sectors, suggesting that service area or national reach softens the need to be physically near the searcher.
- Review-keyword relevance (9.7%) also has weight, reinforcing that what clients say (e.g., “responsive support,” “custom logo”) can help reinforce rankings.
- Google’s internal algo score (2.7%), domain power (2.6%), and rating (2.4%) offer minor additional influence.
- SEO-oriented signals such as GBP name/category matching, domain rating, and backlinks are largely negligible.
- The model shows strong predictability with R² = 0.94, suggesting consistent influence from a diverse mix of digital and semantic signals.
Model Results (Top 1–10 GBP Positions)
For businesses ranking in the local pack (positions 1–10):
- GBP profile relevance dominates (54.8%), emphasizing how critical it is for business descriptions and attributes to semantically match the user’s search query.
- Proximity (17.0%) and reviews (10.2%) trail behind, but still matter—especially in cases where local preference still plays a role.
- Review-keyword relevance (8.2%) adds further value, supporting the notion that rich, descriptive client feedback is a strong ranking enhancer.
- Lower importance features include rating (3.5%), domain power (2.4%), Google’s algorithmic score (1.7%), and minor contributions from name/category relevance and backlinks.
- This model shows excellent performance with R² = 0.96, one of the highest among all sectors analyzed.
Strategic Takeaways
- Semantic GBP optimization is vital: Tech/creative firms must meticulously optimize their Google Business Profiles with services, specialties, and terminology that match real user queries.
- Client reviews are a cornerstone, especially when they include keywords related to services, outcomes, and experiences.
- Proximity still matters, but significantly less so than in service or retail sectors—allowing agencies to rank even when serving broader geographies.
- Traditional SEO signals (backlinks, domain rating) are mostly irrelevant in this sector’s local pack context, reinforcing the dominance of GBP and review signals.
In essence, Technology / Creative is a relevance-first, reputation-second, location-third sector. Success hinges on aligning profile content and review narratives with high-intent, service-specific queries.
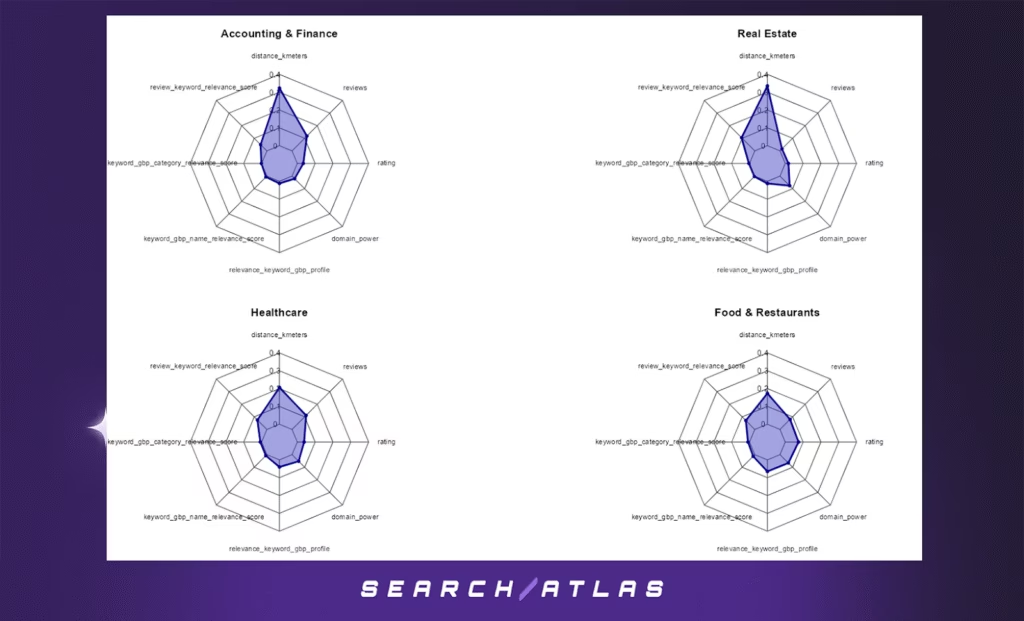
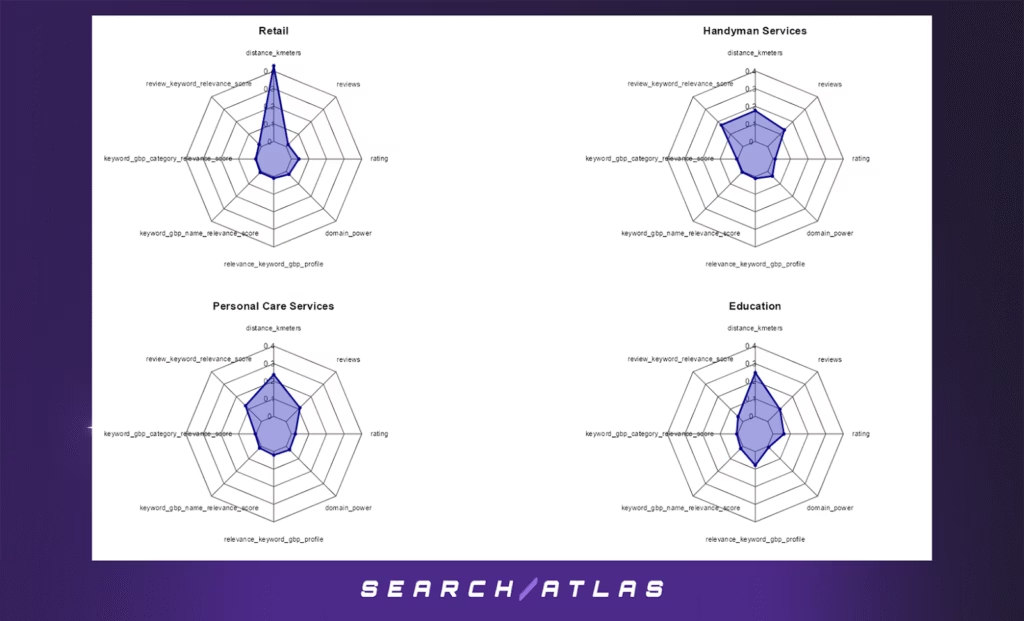
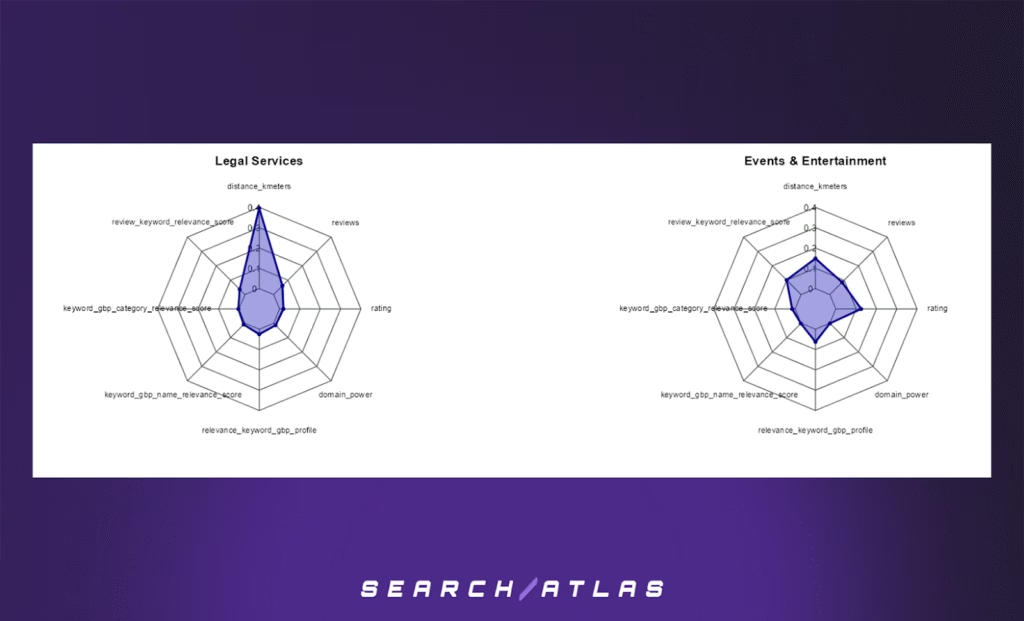
6. Radar Chart Analysis: Top 10 Google Business Profile Ranking Factors by Industry (Distance-Sensitive)
The radar charts below present the top 8 features influencing Google Business Profile (GBP) rankings in the top 10 positions, across ten selected distance-sensitive industries:
- Accounting & Finance
- Real Estate
- Healthcare
- Food & Restaurants
- Retail
- Handyman Services
- Personal Care Services
- Education
- Legal Services
- Events & Entertainment
Each chart displays the relative importance (gain) of key features in an XGBoost ranking model, based on business-level data filtered for top 10 local map rankings.
Key Insights:
- Distance (distance_kmeters) is consistently the most important factor across nearly all industries, reaffirming the role of geographical proximity in local search visibility.
- In sectors such as Retail, Legal Services, and Real Estate, the dominance of distance is even more pronounced, indicating that users are especially likely to choose nearby results in these contexts.
- Relevance signals, like keyword_gbp_name_relevance_score and review_keyword_relevance_score, also appear frequently, highlighting the interplay between proximity and content/keyword relevance.
- Reputation metrics (e.g., reviews, rating, domain_power) have secondary but varying influence across industries. For example, Personal Care Services and Education show more balanced distributions, suggesting that credibility and content quality may partially offset distance effects.
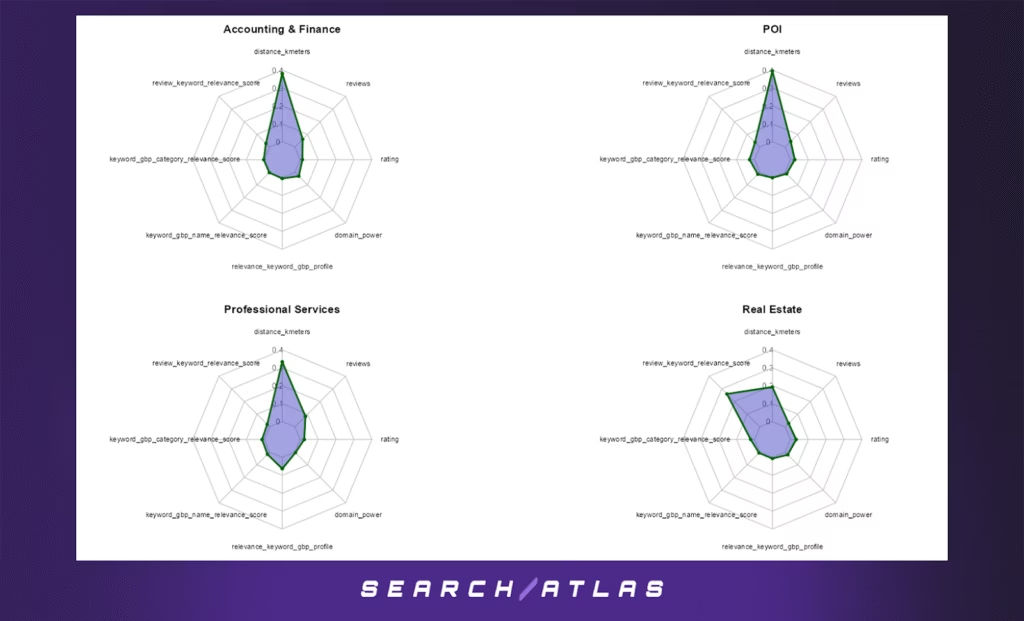
a. Feature Importance Analysis Across All Google Business Rankings
Overview
The radar charts presented here visualize the average feature importances from XGBoost models trained across all Google Business Profile (GBP) rankings — not just the top 10 — for a selection of distance-sensitive industries. Each polygon in the radar plots represents the relative influence of a ranking factor in a specific industry.
Key Distance-Sensitive Factors
One variable clearly dominates across nearly all industries:
🔹 distance_kmeters — This feature consistently holds the highest importance, reinforcing that proximity remains a central factor in determining visibility on local search results, regardless of rank.
However, because this analysis includes the entire ranking range, the influence of other features becomes more visible compared to a top-10-only view.
Supporting Signals
Several features consistently show moderate importance across industries:
- review_keyword_relevance_score — The alignment of keywords in customer reviews with user queries remains influential.
- relevance_keyword_gbp_profile — A holistic relevance score between the keyword and business profile contents is regularly weighted.
- keyword_gbp_name_relevance_score and keyword_gbp_category_relevance_score — These also contribute, especially in sectors like Real Estate, Construction, and Legal Services.
- reviews and rating — Engagement and trust signals, while not top predictors, maintain relevance across many service-oriented categories.
Industry Variability
- Retail, Legal Services, and Automotive Services place an even stronger emphasis on distance, suggesting heavy competition and a proximity-first ranking behavior.
- Education, Professional Services, and Hospitality & Travel show a more balanced distribution, suggesting that content and authority signals also play a substantial role in broader ranking positions.
Takeaways
- For industries where distance sensitivity is paramount, location optimization should be the foundation of any local SEO strategy.
- However, for improving rankings beyond the top tier (e.g., from position 30 to 10), businesses should invest in:
- Review optimization (keyword-rich content)
- GBP category and name relevance
- Profile completeness and keyword alignment
- Review optimization (keyword-rich content)
This comprehensive view provides a more nuanced picture of how Google ranks businesses at all visibility levels, enabling more targeted and realistic ranking strategies across industries.
7. Discussion and Implications
a. Interpretation of Results in Context
The primary aim of this study was to understand the local SEO ranking dynamics across various business industries, using feature importance analysis from XGBoost models trained on GBP (Google Business Profile) data. By modeling both general GBP ranking (all positions) and top-pack visibility (positions 1–10), we can uncover which features most influence local rankings and how these dynamics vary by sector.
Across all industries examined, a few consistent themes emerged:
- Distance to centroid was frequently a dominant feature, especially in industries with strong local intent such as Real Estate, Legal Services, Retail, and Personal Care.
- Review-related features, including volume and keyword relevance, were strong predictors across nearly all sectors.
- Relevance signals from the GBP profile (especially semantic alignment with the query) emerged as increasingly important for industries like Technology and Professional Services.
- Traditional SEO signals like domain authority, backlinks, and GBP category matching played a more modest role, often overshadowed by real-time engagement and proximity signals.
The models exhibited high predictive accuracy overall (R² ranging from 0.80 to 0.98), affirming that a small set of structured features can effectively capture local ranking dynamics. Notably, models focused on top 1–10 GBP positions performed as well or better than general models, underscoring their usefulness in optimizing visibility where it matters most.
b. Implications of Findings
The implications are multifaceted:
- Proximity remains a requirement: For industries where the user’s intent is strongly tied to geography (e.g., Real Estate, Legal Services), distance to the search centroid explains up to 70% of ranking variability. This reaffirms that, regardless of brand authority or optimization, being nearby is essential for local pack inclusion.
- Review quality and quantity matter: In every sector, reviews—not just in quantity but in keyword-relevance—consistently rank as high-value signals. Businesses that encourage customer feedback using natural, keyword-rich language are likely to see better rankings.
- Semantic relevance is rising: In sectors like Technology/Creative and Professional Services, semantic match between the query and GBP profile content was more predictive than distance or reviews. This reflects Google’s move toward meaning over metadata, likely due to advances in BERT and local LLMs used in local search.
- Differentiated strategies are essential: A one-size-fits-all local SEO strategy will not work. For example, while Legal and POI rely heavily on location, Technology businesses benefit more from strong GBP descriptions and relevant content alignment.
c. Comparison to Existing Knowledge
These findings largely align with established SEO knowledge but add quantitative clarity:
- Previous qualitative studies (e.g., Whitespark’s annual local ranking factors survey) consistently mention proximity and reviews. This analysis quantifies those observations, showing exactly how dominant those features are in practice.
- Recent academic work on semantic search and local LLMs (e.g., Google’s use of MUM and BERT) helps explain why GBP content relevance and keyword match are rising in importance for less proximity-bound sectors.
However, the lack of importance for backlinks and low scores for domain authority in most models contrasts with traditional SEO emphasis. It suggests a clear divergence between organic ranking and local pack logic, reinforcing that GBP optimization must be treated as a separate discipline.
d. Limitations
While the models demonstrate strong explanatory power, several limitations should be acknowledged:
- Feature scope: The models are based on structured GMB and external SEO data. Unstructured data—such as image content, recent user interactions, or behavioral signals—was not included but may play a significant role.
- Centroid approximation: Proximity is calculated using an assumed centroid, which may differ slightly from Google’s real-time searcher location estimation.
- Causal inference: Feature importance reveals correlations, not causation. Some high-importance features may be proxies for other unmeasured variables.
- Industry variability within sectors: Broad industry categories (e.g., “Professional Services”) may mask intra-sector differences (e.g., accountants vs. consultants).
- Dynamic SERPs: GBP rankings can fluctuate due to algorithm updates, spam filters, or behavioral personalization, which static models may not capture.
e. Recommendations and Future Research
These insights offer concrete guidance:
- Hyperlocal focus: For proximity-sensitive industries, businesses should ensure GBP locations are aligned with target service areas and located as centrally as possible to customer demand.
- Review optimization: Encourage satisfied clients to leave keyword-rich reviews. Tools that guide customers on what to write (without violating policy) can help improve keyword coverage naturally.
- Content relevance: Carefully craft GBP descriptions and business categories using high-intent, semantically relevant language.
- Segmented strategies: Agencies and brands should tailor local SEO strategies based on industry. High-authority sites may not help in Retail but can be decisive in Real Estate or Technology sectors.
- Explore behavioral data: Future work should integrate behavioral signals such as click-through rates, dwell time, and call actions from GBP listings to better approximate user engagement.
- SERP volatility tracking: Incorporating temporal data into future models could help understand ranking shifts over time—especially valuable for businesses impacted by core updates or spam rollouts.
Conclusion
This study enhances our understanding of local SEO by quantifying how specific features drive visibility in the local pack. By segmenting insights by industry and modeling both general and top-10 positions, it provides clear, actionable strategies for businesses aiming to improve their presence in Google’s local results.
8. Conclusion
This white paper set out to uncover the primary factors influencing visibility in Google’s Local Pack (GBP rankings), using data-driven analysis across thousands of businesses in diverse industries. By applying XGBoost modeling to structured GBP, SEO, and business metadata, we evaluated the relative importance of features such as proximity, reviews, profile relevance, and domain authority, both for all positions and for the critical top 1–10 local rankings.
Our analysis revealed several consistent and industry-specific patterns:
- Proximity to the search centroid is the single most important factor in most industries, especially those with a strong local intent (e.g., Real Estate, Retail, Personal Care).
- Review metrics, including both quantity and keyword relevance, are powerful predictors across nearly all sectors.
- Relevance of GBP content to the search query plays an increasingly critical role in industries less bound by location, such as Technology, Creative, and Professional Services.
- Traditional SEO signals like domain authority and backlinks have limited influence in the Local Pack, marking a clear departure from traditional organic SEO strategies.
Across all models, the predictive performance was high (R² ranging from 0.80 to 0.98), confirming that a relatively small set of features can effectively explain local ranking behavior. Moreover, separate modeling of top 1–10 rankings allowed us to isolate factors that differentiate top-performing businesses from the rest.
In conclusion, local SEO success is driven not just by profile optimization, but by alignment with Google’s evolving local relevance model—one that increasingly rewards proximity, user engagement (reviews), and semantic alignment of business profiles. Businesses that understand and respond to these signals at an industry-specific level are more likely to achieve and sustain visibility in competitive local markets.
This work highlights the need for tailored local SEO strategies and provides a data-backed foundation for prioritizing optimization efforts. By focusing on the right levers for their sector, businesses and agencies can make more informed, impactful decisions in the ever-changing local search landscape.
9. References:
Citations
Google. (2023). Improve your local ranking on Google. https://support.google.com/business/answer/7091
SterlingSky. (2024). Local SEO Ranking Factors Study. Retrieved from https://www.sterlingsky.ca
Whitespark. (2023). Local Search Ranking Factors. Retrieved from https://whitespark.ca/local-search-ranking-factors/
Chen, T. & Guestrin, C. (2016). XGBoost: A Scalable Tree Boosting System. Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, 785–794. https://doi.org/10.1145/2939672.2939785
Google My Business API (2025). Structured data collected from publicly available GMB listings and SERP grid services via Search Atlas proprietary crawling infrastructure.