Publishing regular content without results often points to thin content as the problem. Pages with little depth, duplicated copy, or generic filler rarely earn visibility or build trust.
Google rewards relevance and originality. Content loses ranking power if it lacks both, which weakens authority and blocks visibility.
But this issue runs deeper than rankings. Thin content signals low quality across your site and makes it harder to attract and retain visitors. ⚠️
In this guide, you’ll learn how to identify thin content, understand its impact, and take practical steps to improve or replace it with high-value content.
Read on to upgrade your content strategy and make every page count.
What Is Thin Content?
Thin content refers to webpages that lack useful or original information. These pages often contain only a few brief sentences, cover topics in a vague or superficial way, or reuse existing material without offering new insights or using a content rephraser.
They usually have poor structure, limited clarity, and little depth, which makes it hard for users to find meaningful answers or accomplish a specific goal. Thin content is common in automatically generated pages, low-effort blog posts, or content created solely to include keywords without a clear informational purpose.

Why Thin Content Hurts Your SEO
Thin content weakens your SEO strategy because it offers little or no value to users or search engines. Google algorithms prioritize relevance, clarity, and purpose, so shallow pages rarely meet the standards for strong performance.
In January 2025, Google updated its Search Quality Rater Guidelines to spotlight deceptive content practices. That includes exaggerated claims of expertise, misleading design elements, and pages with minimal useful information.
Users who land on vague or repetitive content tend to leave quickly because they expect practical and complete answers. That behavior signals low relevance and unmet intent, prompting Google to demote or ignore the page.
Thin pages waste crawl budgets, disrupt internal ranking signals, and weaken how Google evaluates your site, which means valuable content will be missed and overall search visibility drop.
What Are the Types of Thin Content?
Let’s look at specific examples of thin content that often go unnoticed on many sites. Identifying them improves depth, relevance, and overall quality.
Plagiarized Content: Copied Material Without Original Input
Plagiarized content includes any material copied from another source without proper credit or unique contribution. This be word-for-word duplication or slightly reworded text that still mirrors the original. These pages fail to add new ideas or context, which offers no reason for readers or search engines to trust or engage.
Low-Quality Content: Wordy Pages With No Substance
Low-quality content fills space without delivering real information. It often includes vague claims, repeated phrases, awkward grammar, or keyword stuffing. Even product pages or blog posts fall short if they rely on empty wording instead of useful details.
Content That Lacks E-E-A-T: Pages Without Credibility or Depth
Content that doesn’t meet Google E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) guidelines often appears thin. These pages deliver surface-level insights, lack credible sources, or fail to show firsthand knowledge. This is especially critical for YMYL (Your Money or Your Life) topics, where trust and expertise influence both user confidence and search visibility.
Duplicate Content: Repeated Material Across Pages or Sites
Duplicate content appears when identical or near-identical text exists across multiple URLs. This happens within one site or across different domains. Search engines aim to avoid showing the same material more than once, so duplicated pages risk being ignored or filtered out.
Doorway Pages: Low-Value Pages Built to Manipulate Search
Doorway pages are created to rank for specific keywords but offer no meaningful content. These pages often redirect users, use aggressive keyword placement, or link to unrelated destinations.
Instead of answering a question or providing useful information, they push traffic toward other parts of the site without adding value.
Keyword Stuffing: Overloaded Text That Lacks Clarity
Keyword stuffing happens when you repeat the same words or phrases unnaturally to influence rankings. This tactic prioritizes manipulation over value. Pages packed with repetitive terms confuse readers and reduce clarity.
Ad-Heavy or Popup-Filled Pages: Disrupted Reading Experience
Pages that overload the screen with ads, popups, or unnecessary clicks push the real content out of focus. Distractions block access to useful content and cluttered layouts bury the main message. These distractions slow page speed, frustrate readers, and send clear signals to search engines that the content doesn’t take priority.
How to Identify Thin Content That Hurts Your Rankings
It’s possible to identify thin content in many ways, but we’ll focus on simple, effective methods that quickly highlight weak areas and guide improvement.
Review Your Pages From a Reader’s Viewpoint
Set aside time to read your content carefully from the perspective of your audience. Many website owners do not know what appears on their own site, creating blind spots. Evaluate how clearly each page answers questions and meets user needs.
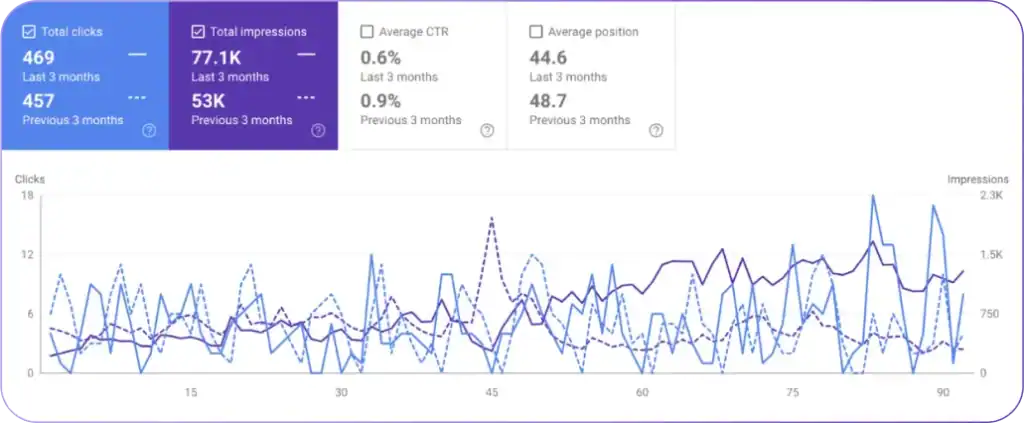
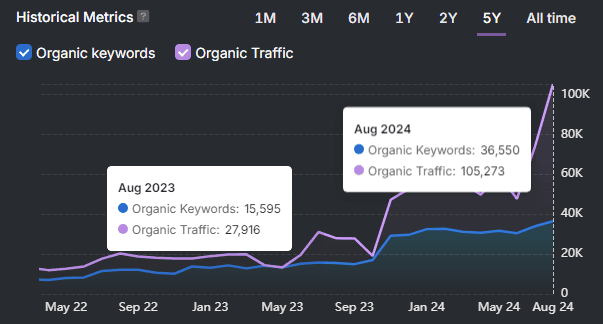
Analyze Your Google Search Console and GA4 Data
Check Google Search Console’s “Security & Manual Actions” tab for any manual penalties. Address any problems and request a review afterward. Use Google Analytics 4 to examine organic traffic trends. Look for pages with sudden drops or consistently low traffic.
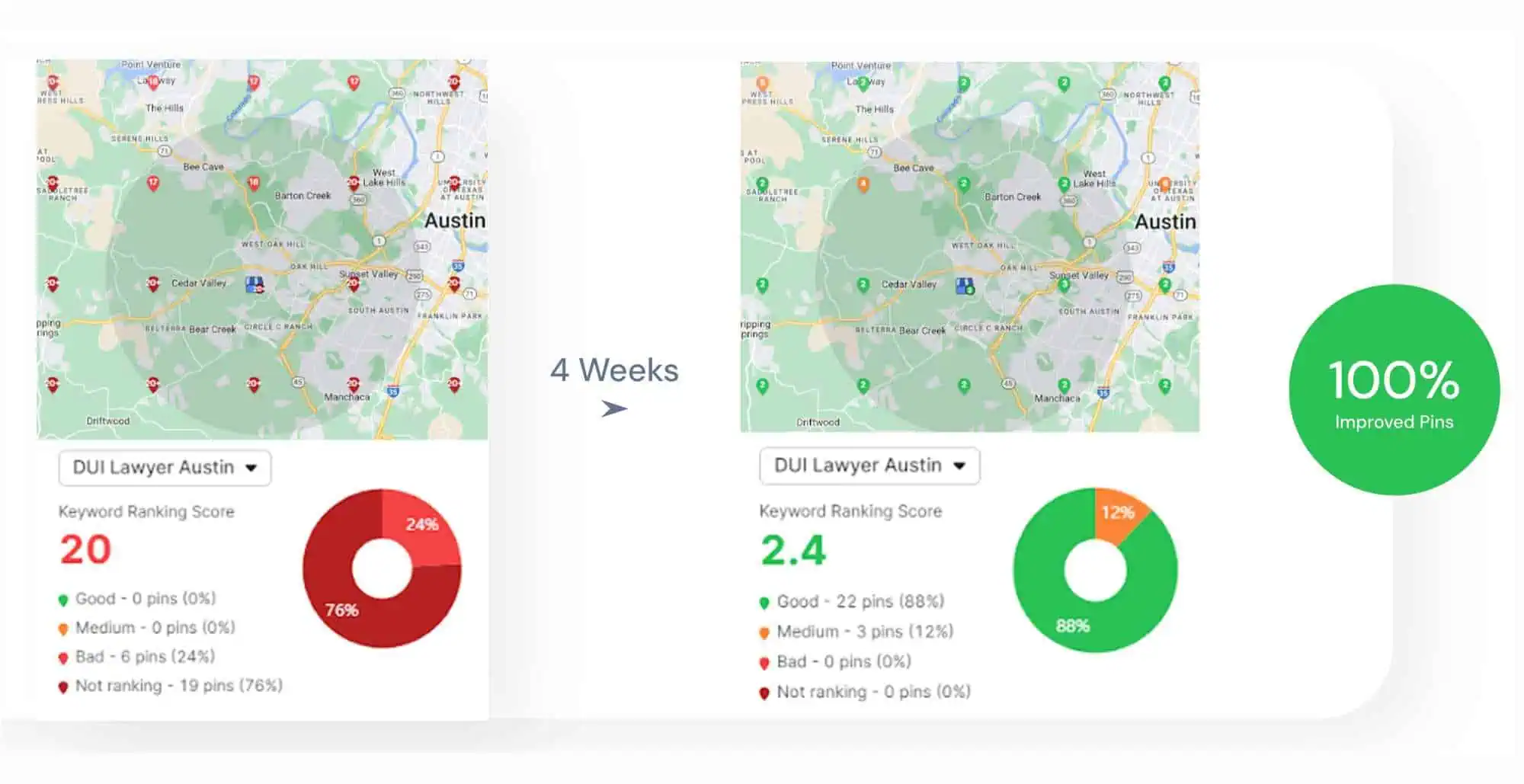
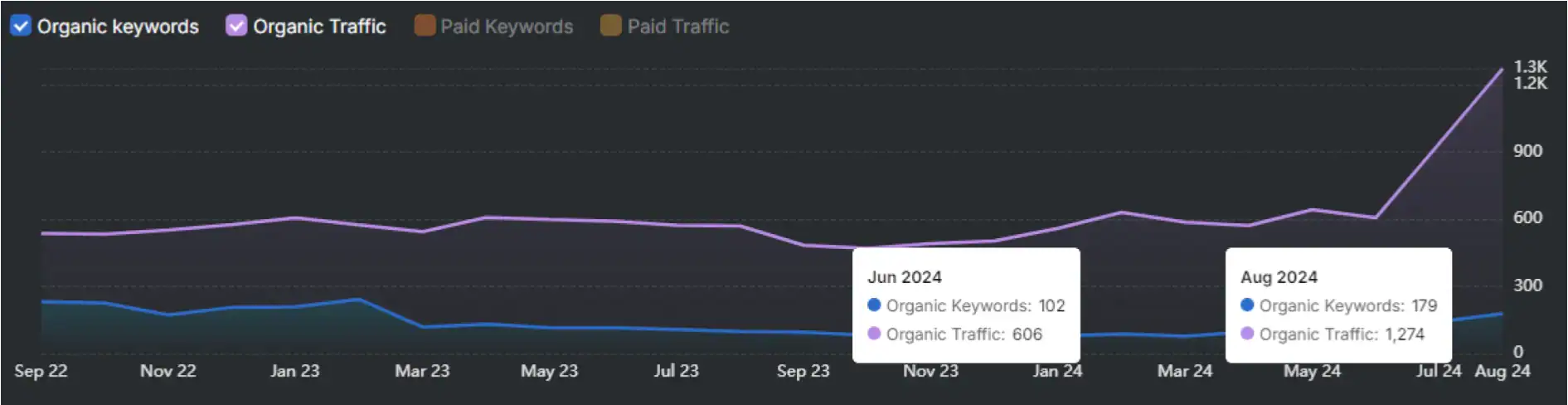
Use tools that combine GSC and GA4 data to identify pages with low or no traffic despite regular crawling and indexing. These tools reveal how Google views your website and quickly highlight thin content. Reporting tools provide this combined insight efficiently.
Run a Site Audit to Identify Issues
Run a full website crawl to uncover pages with duplicate, overly similar content, opportunities and any signs of thin content. Focus audits on content uniqueness, broken pages, and technical SEO problems.
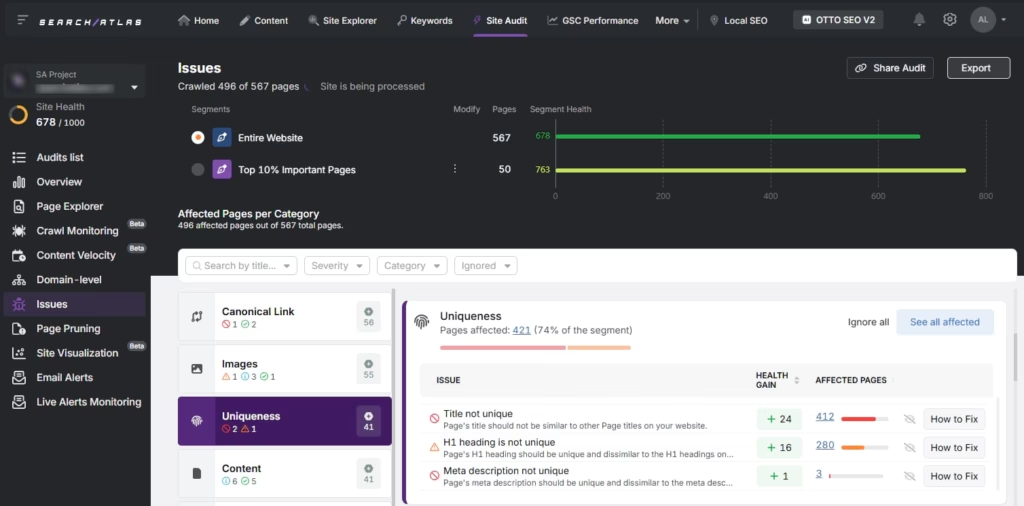
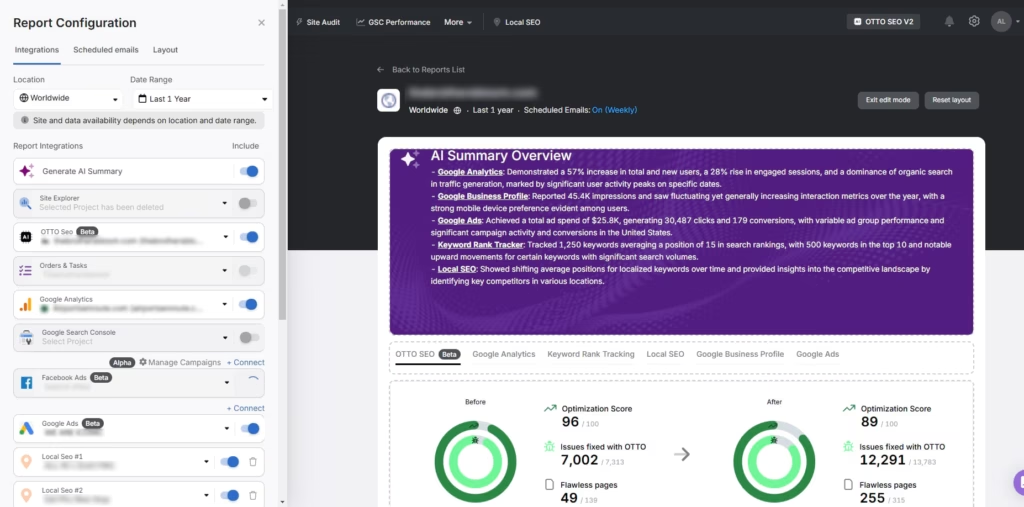
Search Atlas offers a site audit tool that detects issues in headings, meta tags, duplicate page titles, meta descriptions, and overlapping content. The system flags technical issues across performance, structure, and indexing, which helps you keep each page original and clearly differentiated.
Use a Rank Tracker to Monitor Content Health
Set up a rank tracker to receive immediate alerts about ranking drops or indexing issues. This approach helps detect thin content problems and keyword cannibalization early. Rank tracking provides crucial insights when search engines misinterpret your content or make indexing errors.
Use Scholar to Identify Content Problems
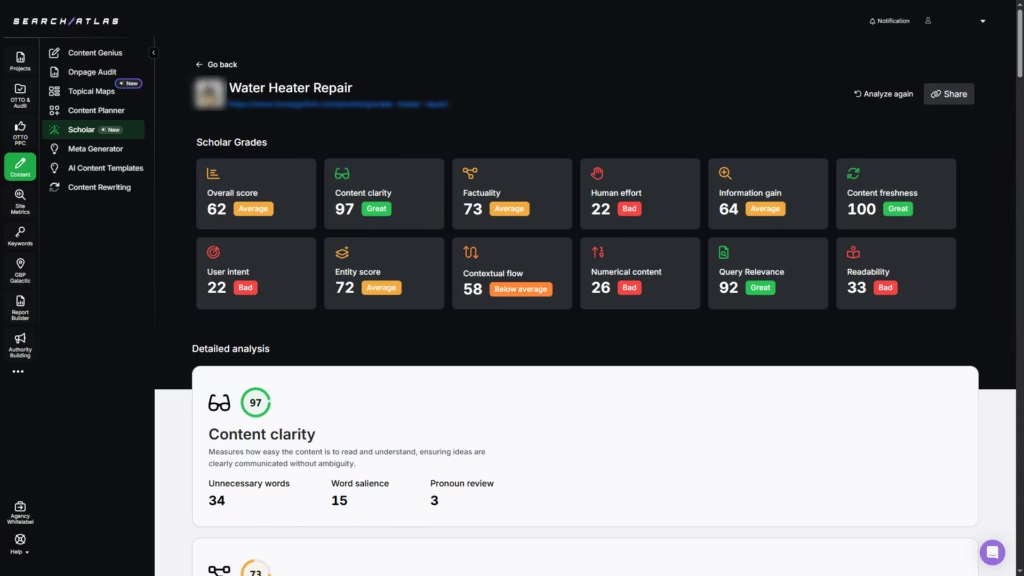
Thin content weakens rankings even if the page looks complete. Scholar, an advanced evaluation tool that helps you detect and fix these issues using clear, data-driven analysis.
With scores content quality from 0 to 100, it reflects how well your content aligns with Google’s expectations for clarity, accuracy, depth, and intent match. This tool breaks down your content using metrics listed below.
- Content Clarity. Flags wordy or vague phrasing that reduces readability.
- Factuality. Checks for relevant, accurate, and query-specific facts.
- Human Effort. Looks for original structure, visuals, and schema that show manual input.
- Information Gain. Highlights missing insights not covered in current top results.
- User Intent Alignment. Ensures your content format matches what users expect.
- Contextual Flow. Analyzes topic order and logic between sections.
For users who want a deeper understanding of their content quality, Scholar offers a clear approach to improvement. It reveals content gaps, flags low-value pages, and provides the insight needed to boost search visibility.
8 Most Efficient Ways to Fix Thin Content to Boost User Experience
These tips enrich content with valuable information using strategies like improving accuracy, clarity, and relevance. Explore 8 top strategies below.
1. Find Keywords For Your Content Strategy
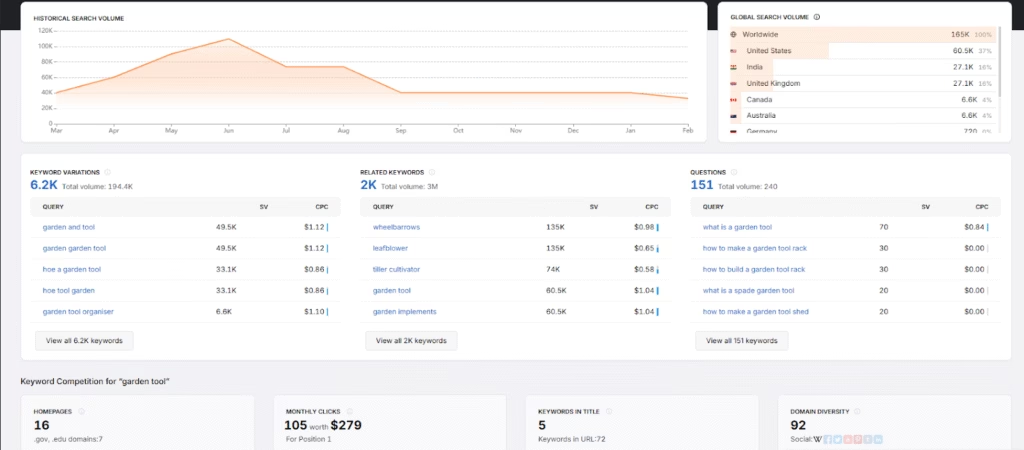
Target specific phrases that show real demand and improve ranking opportunities. Through keyword research you restore content value and set a clear focus. These steps create a practical path to improve your content.
- Use a keyword tool to explore related terms. Begin with a specific phrase, then analyze what people actually search within that theme.
- Check metrics like search volume and competition. Look for keywords that show interest but don’t require high authority to rank.
- Avoid generic keywords that attract broad, unfocused traffic. Prioritize specific searches that reflect real questions or local needs.
- Group related keywords into clusters. These clusters help shape structure, support relevance, and reduce overlap in your topic coverage.
Continue testing keyword ideas as search trends shift. Regular refinement keeps your content aligned with intent and audience demand.
2. Expand on the Topic to Dive Deeper Into the Subject
To create a meaningful experience, every page must offer clarity, depth, and relevance. Use the following steps to expand content without adding fluff.
- Add Specific Details. Go beyond surface explanations with examples, case studies, or unique scenarios.
- Include Relevant Data. Use statistics or findings to support claims and strengthen authority.
- Answer Follow-up Questions. Think about what readers would ask next and address those points directly.
- Bring in Expert Insight. Quote professionals or link to trusted sources to add credibility and context.
- Structure for Readability. Use headers, short paragraphs, and logical flow to keep attention on the page.
- Prioritize clarity over length. A focused 500-word piece with useful insights delivers more impact than 2,000 words of scattered content.
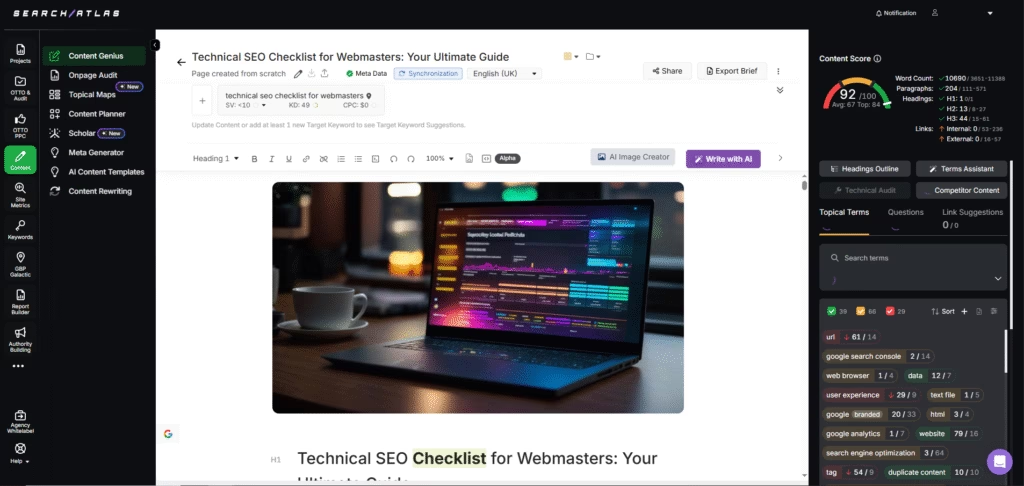
For sharper content refinement, use Content Genius. This AI assistant provides real-time support as you write and edit. It reviews top-ranking pages to suggest improvements based on proven patterns, which includes keyword use, logical structure, natural language processing, and internal linking.
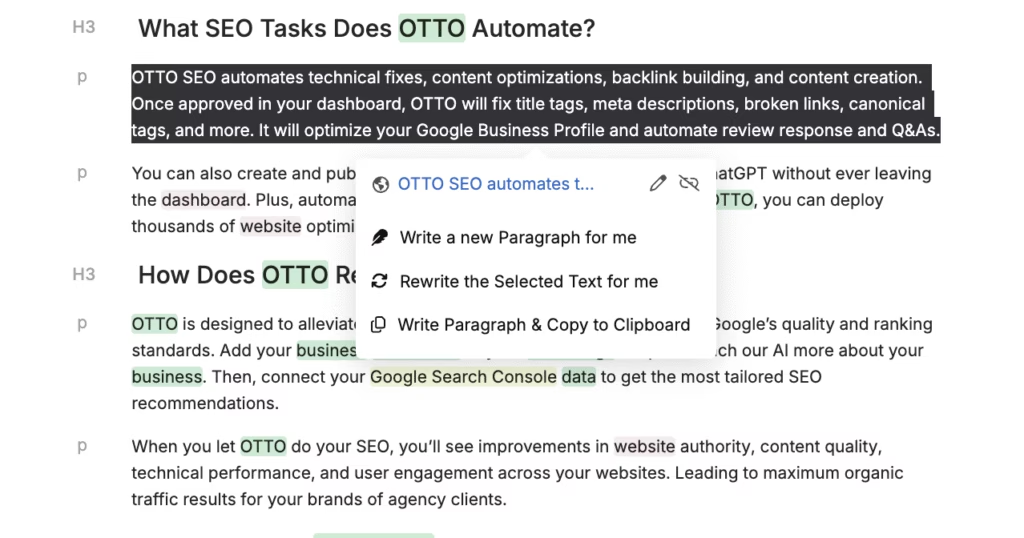
Content Genius includes a rephraser that rewrites text in your own words while keeping the original meaning. This helps you avoid plagiarism and improves clarity without changing intent.
The tool adjusts to your writing style and intent, which makes it easier to produce original, readable content that fits your audience.
3. Answer the User Intent to Provide Relevant Solutions
Understand your audience’s questions and tailor your content to their search intent. For instance, if someone searches “how fast do cheetahs run,” they likely don’t want information on “cheetah hunting habits.” Instead, focus on sub-topics like “top speeds of different big cats” or “factors affecting cheetah speed” to stay relevant.
Use structured data like FAQs or how-to markup to surface your answers in rich results. Break content into short, focused sections so readers find answers quickly. Aligning with intent reduces bounce rates and improves performance in search.
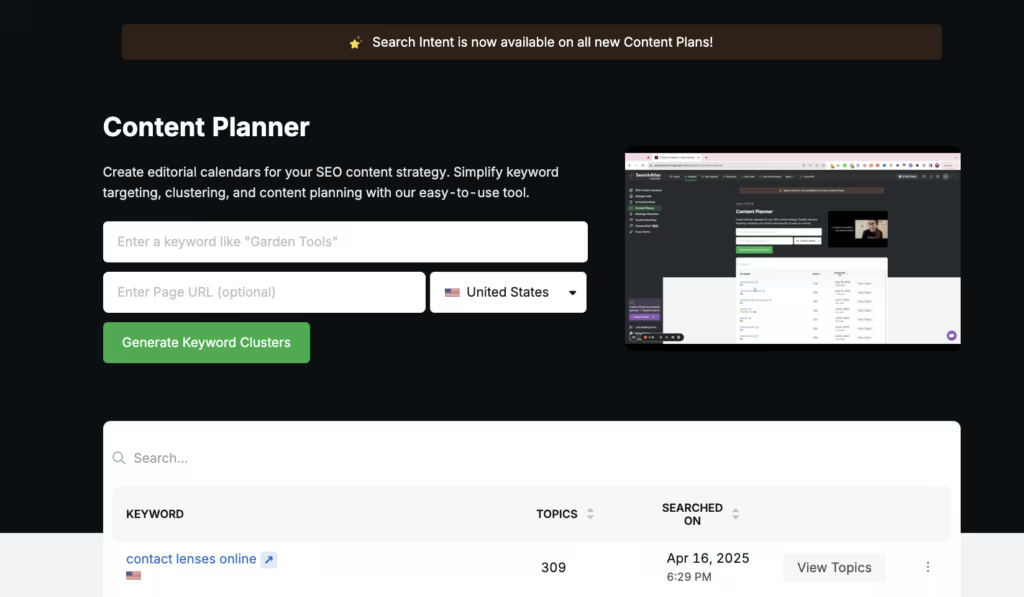
Speed up this process using the Search Atlas Content Planner. Identify the right keywords, build topic clusters, outline articles, and create full drafts from a single dashboard. The planner helps you connect intent to execution without jumping between tools, so you build content that ranks and answers real questions.
4. Update Outdated Information to Ensure Freshness
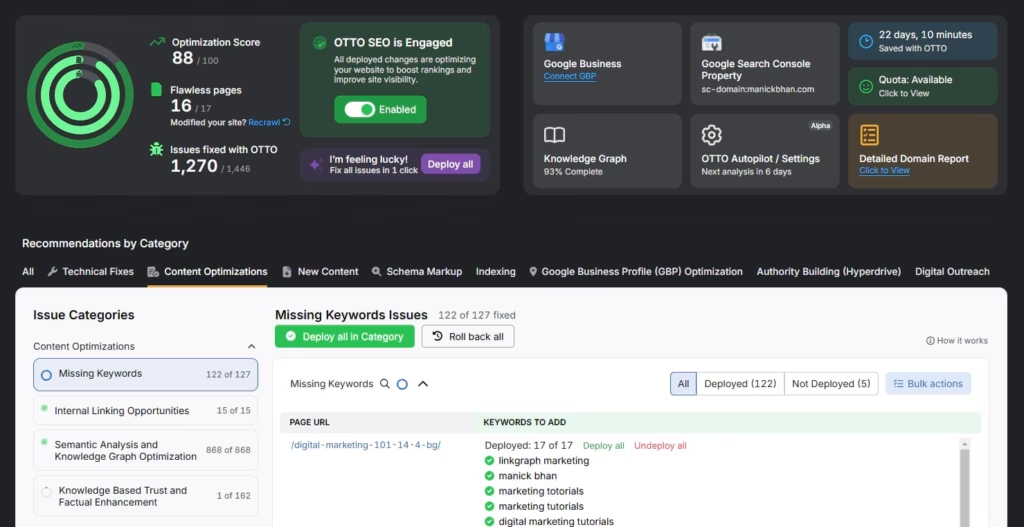
Outdated pages lower relevance and authority. Conduct a content SEO analysis with Scholar to spot outdated material, then refresh it with the most current industry data, trends, and developments. Run this review regularly to keep high-value pages accurate, visible, and aligned with evolving search expectations.
5. Ensure the Visuals are Appealing to Capture Attention
Visual design plays a direct role in how users experience your content. Break long sections of text into digestible chunks using charts, custom images, or short videos. Use alt text and descriptive captions to support accessibility and SEO.
Check that your layout works on both desktop and mobile, as poor formatting on small screens reduce readability. Choose fonts and color schemes that enhance clarity without straining the eyes.
For pages that use outdated design elements or lack consistency, update the theme or visual hierarchy to reflect modern standards. Effective visuals help users stay longer, engage more, and trust your content as a reliable source.
6. Meet Googles E-E-A-T to Strengthen Your Reputation
Thin content fails to meet Googles E-E-A-T standards. To achieve this, build content that delivers unique value and stands out in your field. Ensure your content.
- Includes original insights or unique research unavailable elsewhere.
- Clearly shows the author’s expertise and credibility.
- Relies on trustworthy and reputable sources.
- Is well-written, accurate, and free of errors.
- Provides clearer or more useful information than competing pages.
These practices improve your site’s trustworthiness and authority in the eyes of both users and search engines. For more details, check out our blog where we explain what Google E-E-A-T is and teach you how to write for it with minimal effort.
7. Redirect Shallow Pages to a Relevant Blog
Pages with thin or duplicate content lower your site’s overall quality. Evaluate their performance using metrics like impressions, clicks, and engagement. Strengthen pages with potential by updating content and aligning with user intent. Redirect those that offer little value, attract low traffic, or duplicate stronger content.
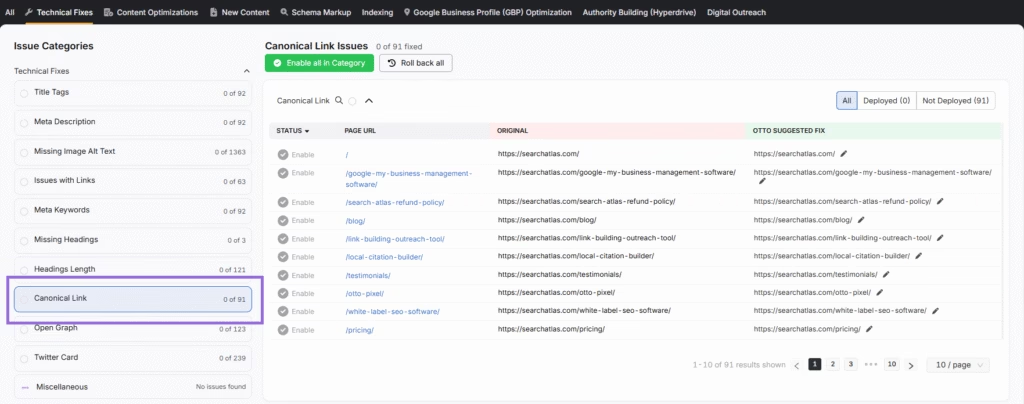
A 301 redirect guides users and search engines to a more relevant blog post or topic cluster, preserving link equity and improving indexing. For intentional duplicates, apply canonical tags to indicate the preferred version and consolidate ranking signals. Combining redirects and canonicals creates a cleaner site structure, improves user experience, and ensures search engines focus on your most valuable content.
8. Repurpose Your Content to a New Format
Thin content doesn’t always need deletion. Reshape pages that still align with your goals, into something more valuable. Repurposing lets you build on the existing structure, adapt it for new formats, and reach audiences through multiple channels. Instead of rewriting everything from scratch, preserve core insights and give them new impact with better delivery.
- Evaluate Fit. Confirm the content still supports your funnel, aligns with current goals, and draws some traffic.
- Optimize First. Strengthen the original with fresh data, updated sources, and improved formatting.
- Choose a Format. Convert articles into infographics, slides, or carousels that simplify and highlight the main points.
- Expand Reach. Turn core ideas into video formats like tutorials, webinars, or short interviews to offer more depth.
- Distribute Widely. Share repurposed versions across social media, email, or third-party sites to increase visibility.
- Track Results. Measure performance across formats to learn which types generate the most engagement or conversions.
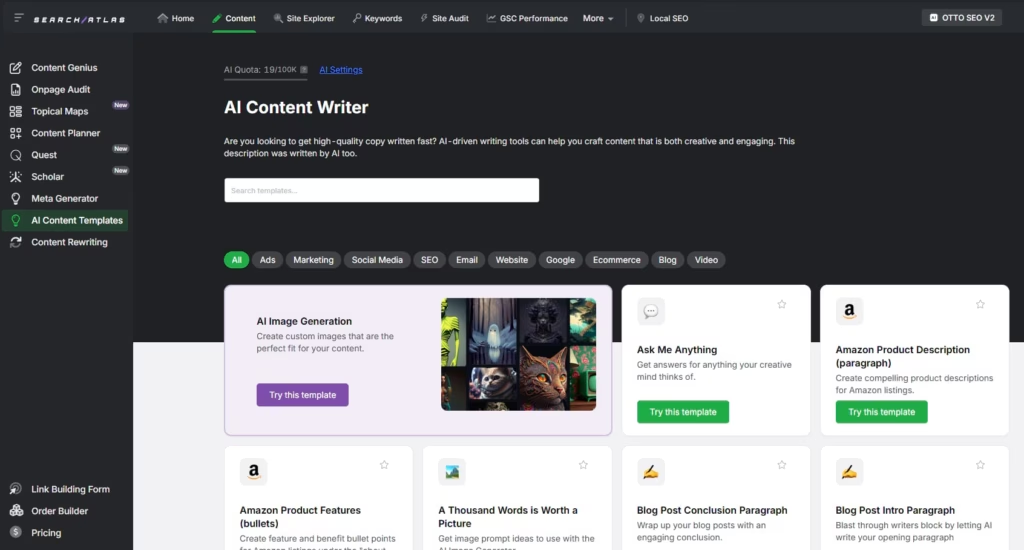
Repurposing helps you scale content creation without starting from scratch. Use Search Atlas to simplify content transformation. Its content templates help you rewrite for different formats like blog posts, product pages, or emails with NLP terms.
Search Atlas: Your Tool for Faster Thin Content Elimination
High-quality content builds trust, engages users, and boosts rankings. While finding and improving thin content takes effort, the long-term impact on visibility, conversions, and brand authority makes it worthwhile.
Search Atlas simplifies this journey. 💪🏻
With advanced tools for keyword research, AI-assisted content creation, and exclusive features like OTTO SEO, it offers a complete solution for content-driven SEO.
With the right tools, optimizing content becomes a strategic advantage. Start refining your content with Search Atlas and experience the impact. Try it free for 7 days! Cancel anytime.