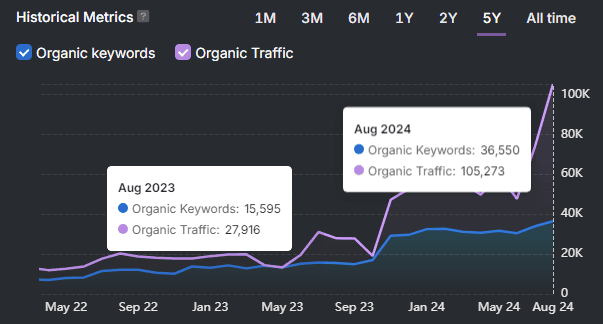
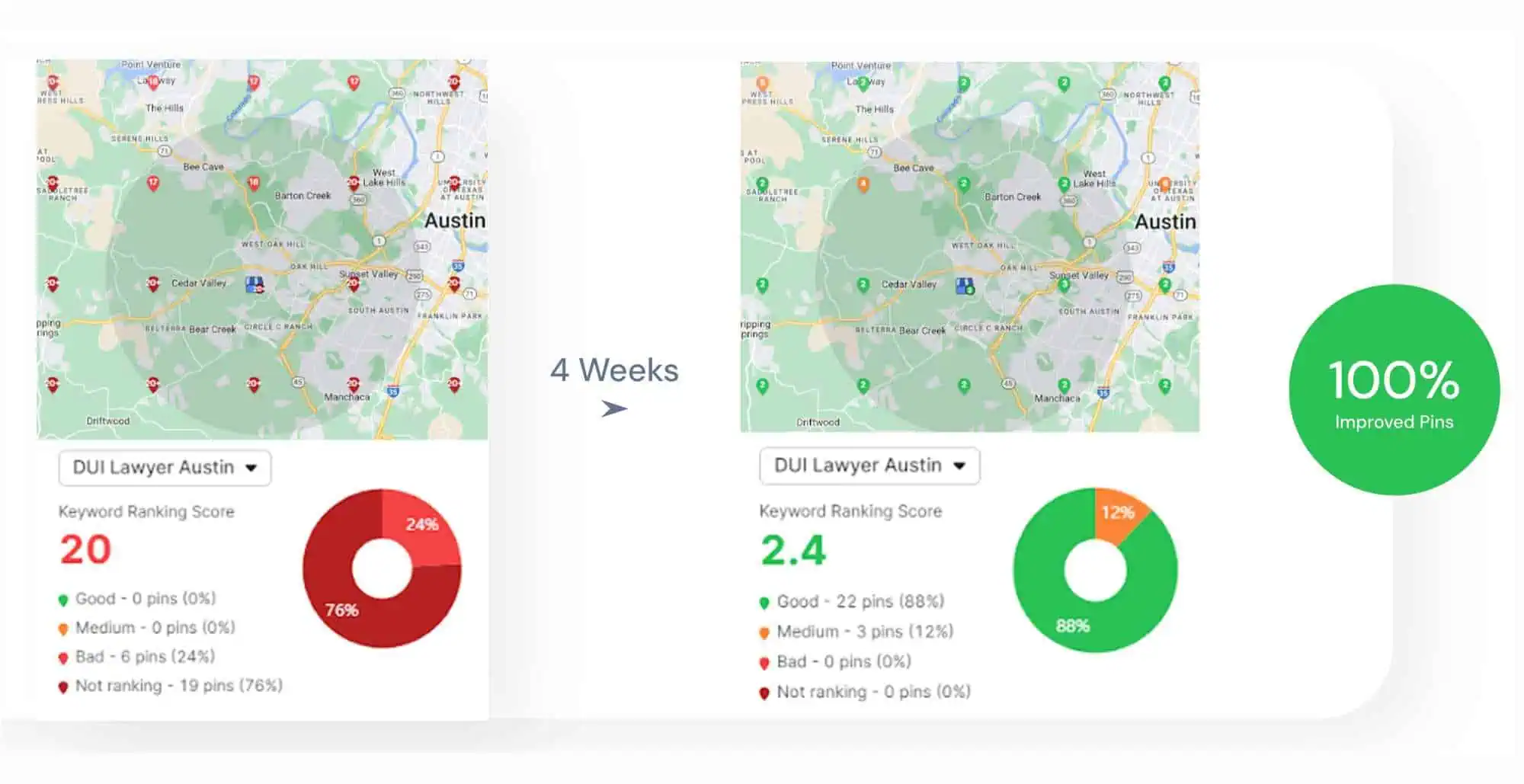
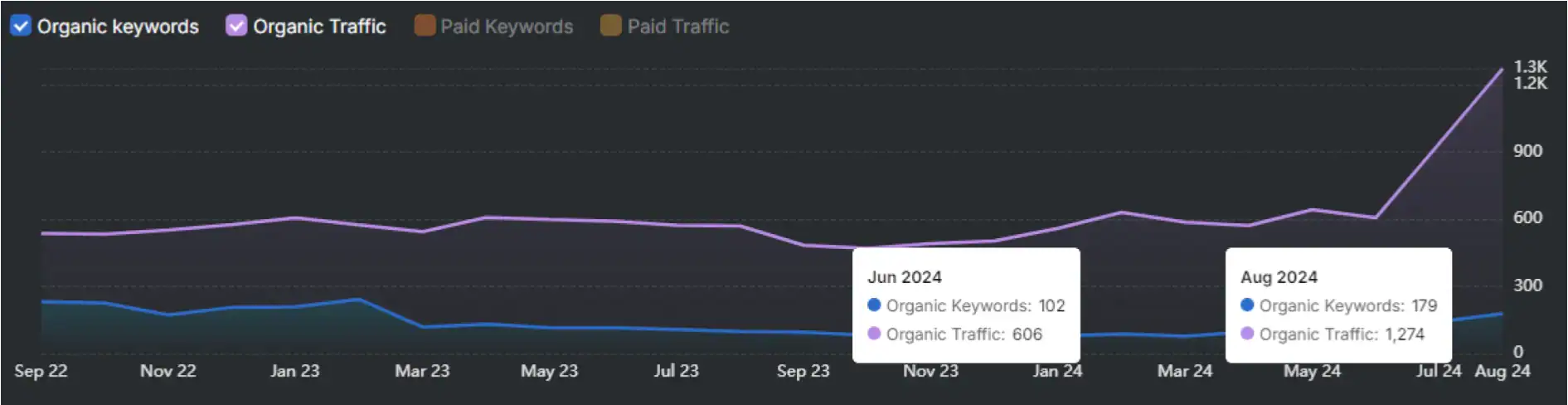
Automated technical SEO is central to scalable growth. Technical SEO is the practice of fixing metadata, canonicals, schema, and crawl signals. Technical SEO matters because these signals determine how search engines index and rank pages.
SEO professionals often describe technical SEO fixes as routine hygiene tasks. Others position automation as a growth lever that compounds visibility across entire websites. The missing piece is large-scale evidence that confirms which view is correct.
This study analyzes the impact of automated technical SEO fixes across 39,486 websites. The websites are clustered into Small, Medium, and Large segments. Automated fixes improved impressions, traffic, keyword coverage, average position (ranking), and click-through rate (CTR).
Methodology – How Did We Test Automation?
This experiment is a structured analysis of automated SEO fixes. This experiment is important because it isolates the real performance impact of technical improvements. This experiment matters because it shows how automation scales across different website sizes.
The dataset combines three core sources. Firstly, Content Assistant provided technical issue breakdowns for metadata, schema, and canonicals. Secondly, OTTO PPC supplied performance data such as impressions and click behavior. Thirdly, Google Search Console (GSC) delivered impressions, clicks, CTR, and average position.
The preprocessing steps are listed below.
- Unify identifiers and standardize timestamps.
- Extract issue percentages from structured fields.
- Filter for quality and exclude invalid records.
- Label each record as “before” or “after” optimization.
- Segment sites into Small, Medium, and Large clusters using k-means on log-transformed metrics.
The analytical methods are listed below.
- Run linear regressions on impressions and traffic.
- Add interaction terms to measure before/after changes.
- Translate coefficients into interpretable performance deltas.
- Test statistical significance with p-values and R².
- Separate models for short-term and long-term effects.
- Exclude outliers with IQR and Z-score thresholds.
The target variables are 5 SEO metrics. They are impressions, traffic, keyword coverage, average position, and CTR.
What Is the Final Takeaway?
The study run by Search Atlas proves that automation is effective at scale and over time. The study shows that all 5 SEO metrics improve after fixes, confirming that automation delivers measurable and statistically significant outcomes. Impressions and keyword coverage produced the largest lifts, while CTR emerged as the strongest long-term predictor of visibility.
Small sites gain from coverage and structured fixes. Medium sites gain from heading hierarchy and canonical links. Large sites gain from canonical consolidation and schema at scale, compounding gains across thousands of URLs.
The evidence confirms that site size matters, but the direction of growth is consistent across clusters. Impressions expanded, keywords grew, CTR rose, and positions improved. Traffic moved upward modestly but demonstrated statistical significance, showing that automation drives both reach and engagement.
Businesses need to treat automation as a baseline for technical SEO. Businesses that adopt automation as part of their strategy achieve predictable visibility, competitive strength, and sustained growth.
How Do Core Metrics Respond to Automation?
I, Manick Bhan, together with the Search Atlas research team, analyzed automated technical SEO fixes across 39,486 websites to measure shifts in performance. The breakdown to show how automation impacts impressions, keywords, traffic, CTR, and average position is listed below.
Impressions
Impressions measure how often a website appears in search results. Impressions represent visibility before clicks or engagement. Impressions matter because they reveal how technical SEO fixes expand indexation and search reach.
The headline results are shown below.
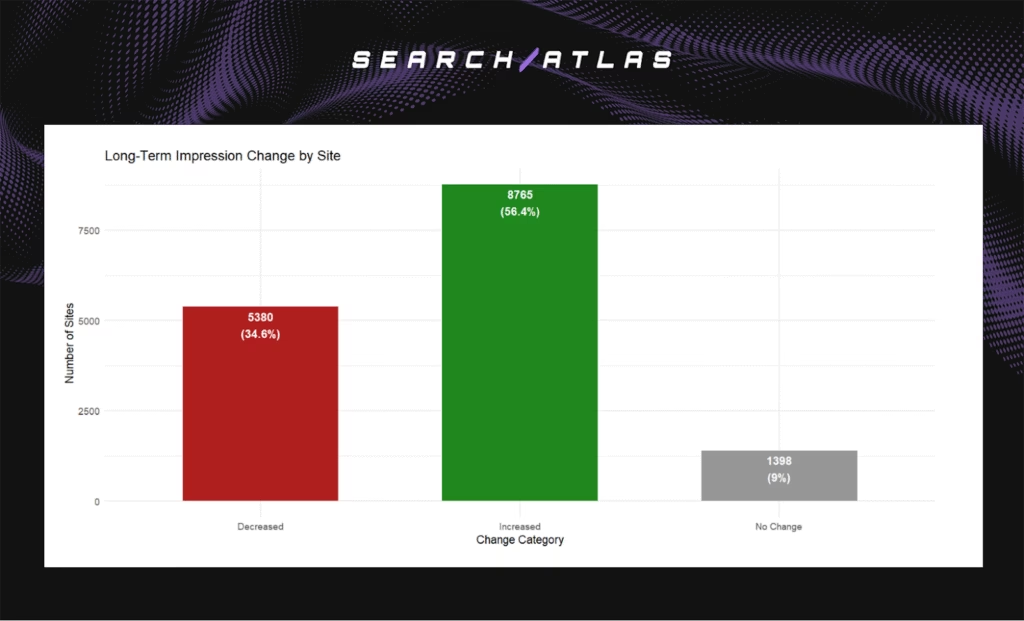
- Increase of 146 long-term impressions per site (high statistical certainty).
- Increase of 2 short-term impressions per site (small but reliable).
- Improve of 56.4% of the impressions of the sites, 34.6% declined, 9% stayed stable.
The changes for different site sizes are listed below.
- Small sites showed almost no long-term change, with only slight short-term lifts.
- Medium sites gained +123 impressions, confirming meaningful visibility growth.
- Big sites gained over 2,370 impressions, the largest absolute increase.
Structural fixes delivered the strongest gains.
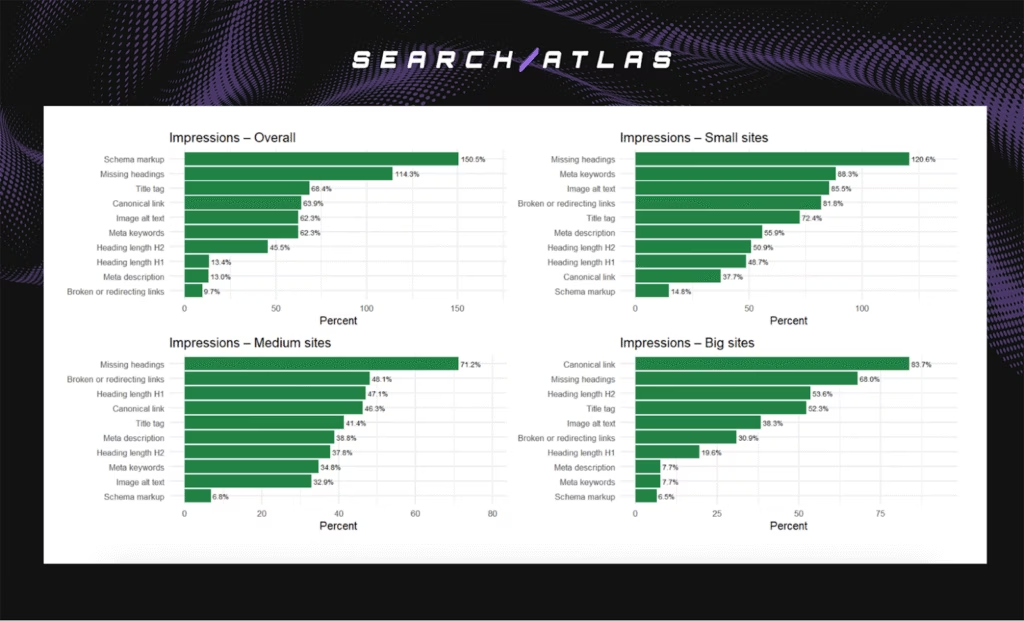
- Schema markup (+150.5%) and Missing headings (+114.3%) led overall.
- Small sites benefited most from headings, alt text, and link hygiene.
- Medium sites gained from headings, canonicals, and links.
- Big sites compounded growth through canonical consolidation and heading hierarchy.
Impression gains confirm that automation improves discoverability across scales. Smaller sites grow through hygiene fixes, while larger properties compound improvements through structural consolidation.
Traffic
Traffic measures how many visits a website receives from organic search. Traffic matters because it reflects how visibility translates into actual reach and user activity. Growth in traffic shows that technical SEO fixes expand indexation and generate engagement.
The headline results are shown below.
- Increase of 2 long-term traffic units per site.
- Increase of 0.5 short-term traffic units per site.
- 46.5% of the sites improved, 34.5% declined, 18.9% stayed stable.
The changes for different site sizes varied in their impact.
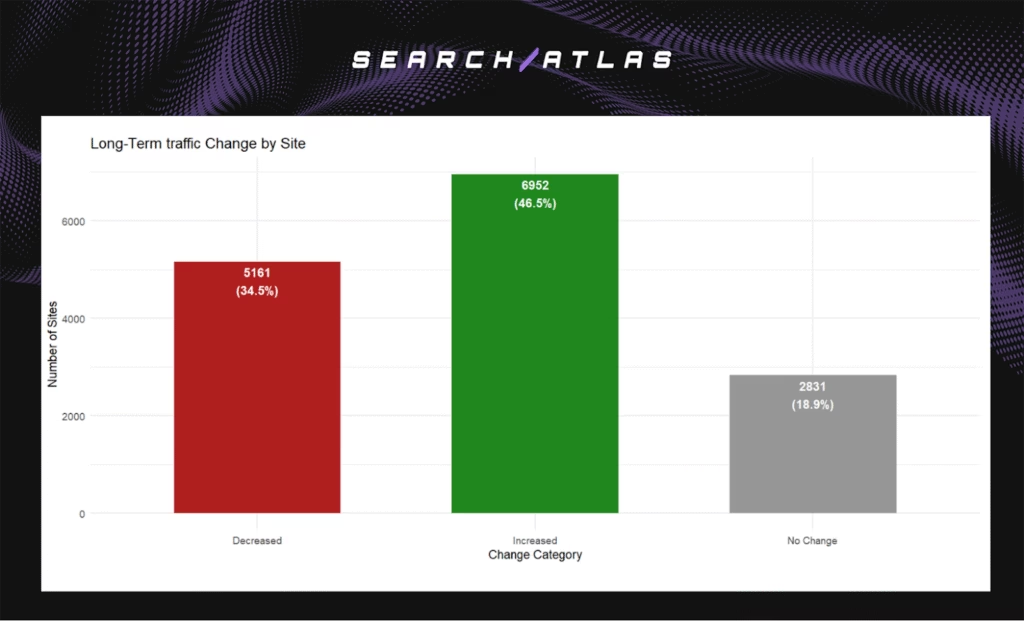
Small sites showed no significant long-term change, with stable but modest short-term lifts. Medium sites showed no net long-term change, though weekly gains were statistically significant. Big sites gained +2 units short term but declined -6 units long term, reflecting volatility at scale.
Structural fixes most strongly associated with traffic growth are listed below.
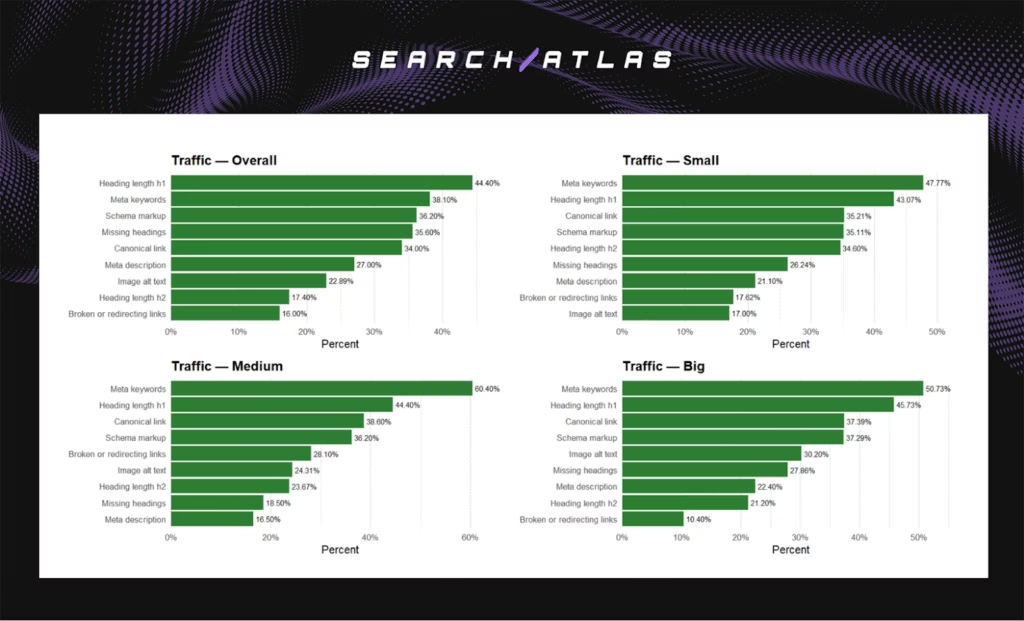
- Overall leaders were H1 length (+44.4%), Meta keywords (+38.1%), Schema markup (+36.2%), Missing headings (+35.6%), and Canonical links (+34.0%).
- Small sites grew most from Meta keywords (+47.8%) and H1 optimization (+43.1%), reinforced by Canonicals and Schema.
- Medium sites benefited most from Meta keywords (+60.4%) and H1 optimization (+44.4%), supported by Canonicals and Schema.
- Big sites again relied on Meta keywords (+50.7%) and H1 optimization (+45.7%), with Canonicals and Schema stabilizing structure but delivering diminishing returns.
Traffic gains confirm that automation strengthens engagement, but effects differ by scale. Smaller and medium sites gain stability through metadata and heading structure, while big sites face volatility that requires ongoing refinements.
Click-Through Rate
CTR measures how often a search impression converts into a click. CTR matters because it reflects both discoverability and user alignment. CTR improvements show that technical SEO fixes expand visibility, and enhance engagement with search snippets.
The headline results are shown below.
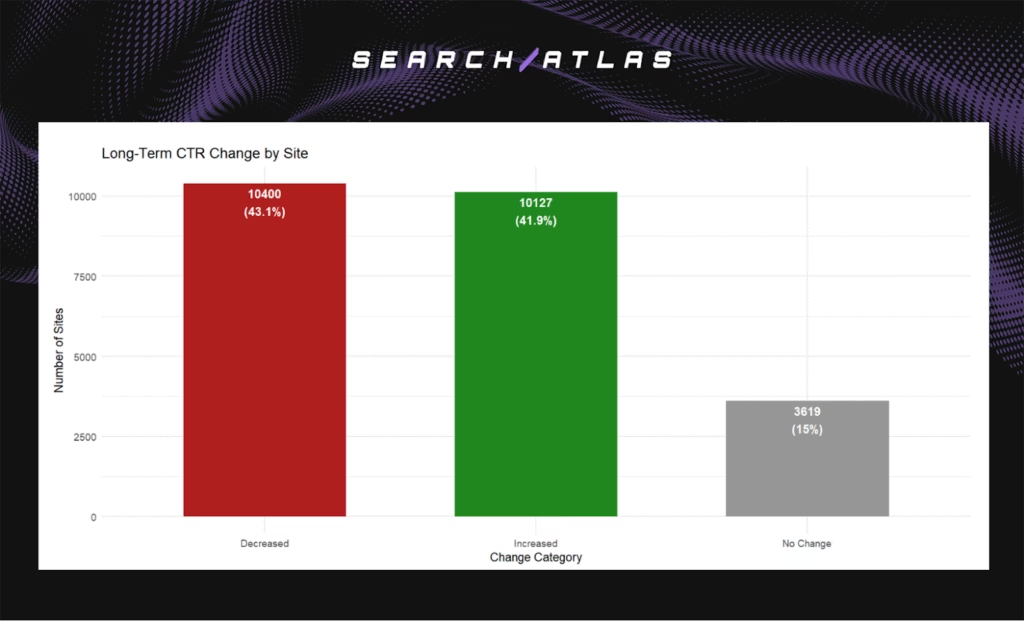
- Increase of 0.02 percentage points short-term.
- Increase of 0.03 percentage points long-term.
- 41.9% of the sites improved, 43.1% declined, 15.0% stayed stable.
The impact of site size differed over time.
Small sites saw only a slight short-term increase of +0.13 percentage points, with no lasting effect. Medium sites experienced stronger gains, rising +2.04 points in the short term and +6.53 points over the long term. Big sites showed the most pronounced growth, with short-term gains of +4.40 points and long-term gains of +24.90 points.
Structural fixes most strongly associated with CTR gains are listed below.
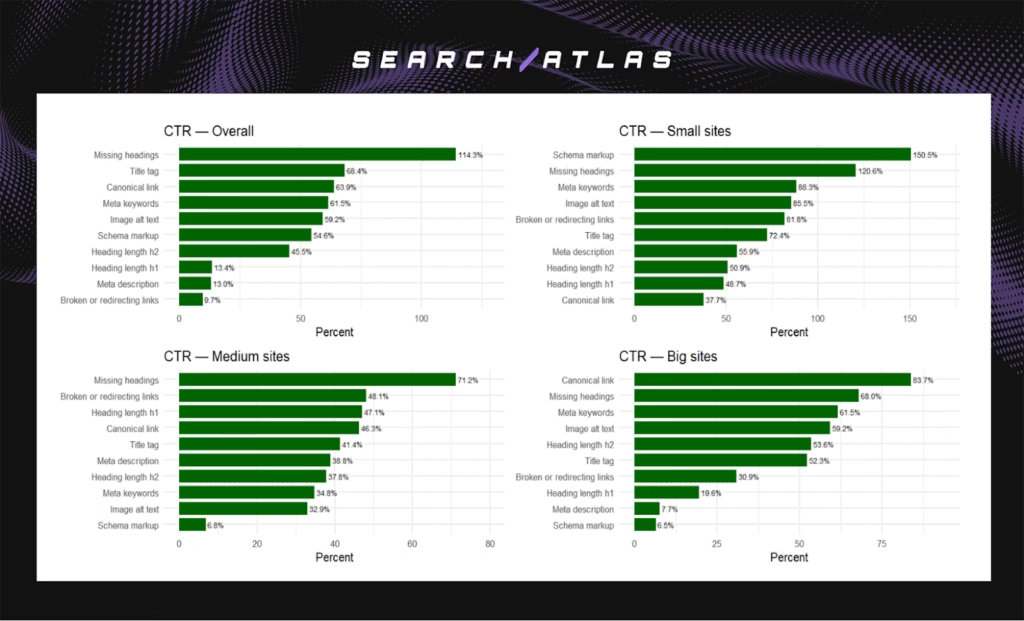
- Overall leaders. Missing headings (+114.3%), Titles (+68.4%), Canonicals (+63.9%), Meta keywords (+61.5%), Image alt (+59.2%), Schema (+54.6%).
- Small sites. Schema markup (+150.5%) and Missing headings (+120.6%) led, followed by Meta keywords (+88.3%), Image alt (+85.5%), and Link hygiene (+81.8%).
- Medium sites. Missing headings (+71.2%), Links (+48.1%), H1 (+47.1%), Canonicals (+46.3%), Titles (+41.4%) provided the largest lifts.
- Big sites. Canonical consolidation (+83.7%) and Missing headings (+68.0%) stood out, supported by Meta keywords (+61.5%), Image alt (+59.2%), H2 (+53.6%), and Titles (+52.3%).
CTR gains confirm that automation strengthens engagement through improved structure and discoverability.
Keywords
Keywords measure how many distinct queries a website ranks for. Keywords matter because they reveal the breadth of visibility and determine how widely content reaches potential audiences. Growth in keyword coverage shows that technical SEO fixes expand discoverability into new search terms and segments.
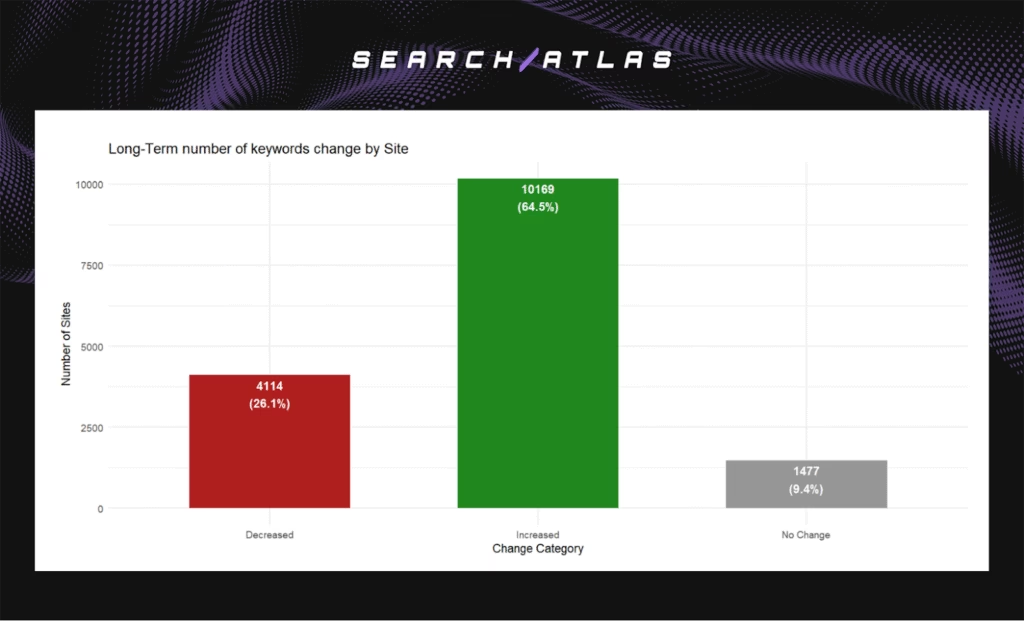
The headline results are shown below.
- Increase of 67 long-term keywords per site (statistically significant).
- Decrease of 2.8 short-term keywords per site (temporary decline).
- 64.5% of the sites improved, 26.1% declined, 9.4% stayed stable.
The impact of site size revealed different growth patterns.
Small sites showed steady but modest increases, reflecting gradual visibility gains. Medium sites fluctuated mid-period but finished with meaningful upward growth. Big sites produced the largest absolute increases, confirming that scale compounds keyword expansion.
Structural fixes most strongly associated with keyword growth are listed below.
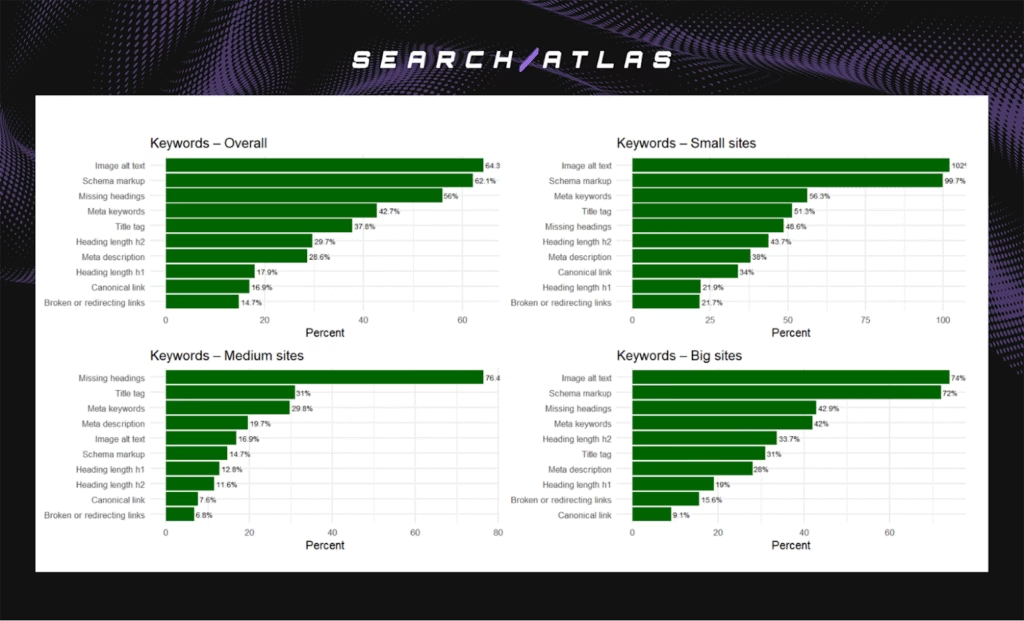
- Overall leaders. Image alt text (+64.3%), Schema markup (+62.1%), Missing headings (+56%), Meta keywords (+42.7%), Title tags (+37.8%).
- Small sites. Image alt text (+102%) and Schema markup (+99.7%) dominated, followed by Meta keywords (+56.3%) and Title tags (+51.3%).
- Medium sites. Missing headings (+76.4%) delivered the strongest lifts, supported by Title tags (+31%) and Meta keywords (+29.8%).
- Big sites. Image alt text (+74%) and Schema markup (+72%) led, with Missing headings (+42.9%) and Meta keywords (+42%) adding additional gains.
Average Position
Average position measures where a website ranks in search results. Average position matters because even small improvements compound visibility and click potential. Gains in position show that technical SEO fixes, expand indexation and improve ranking strength.
The headline results are shown below.
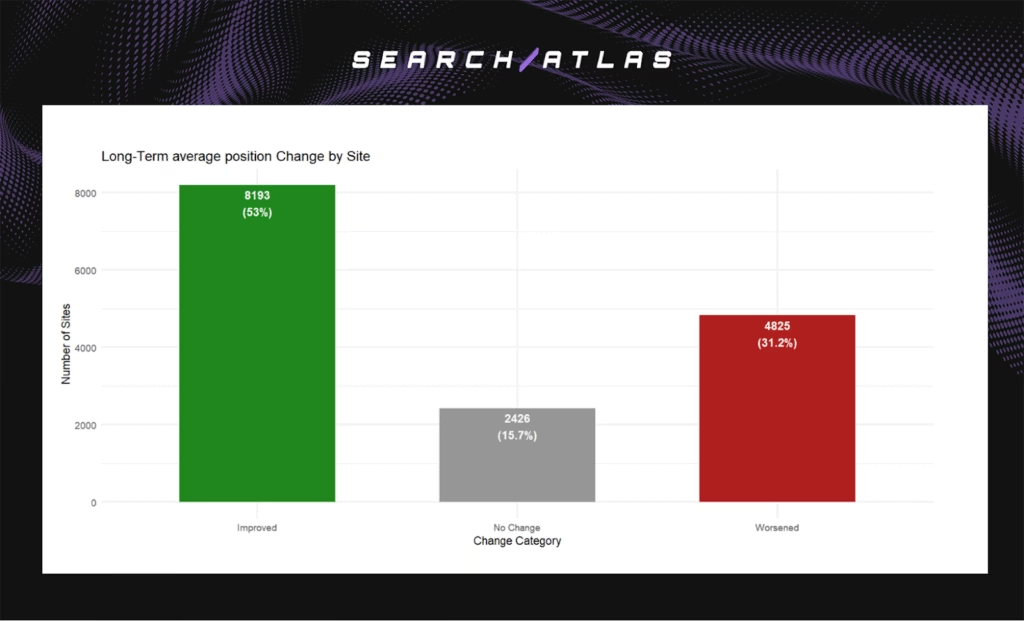
- Decrease in 0.33 positions short-term.
- Decrease of 2 positions long-term.
- 53% of the sites improved, 31% declined, 16% stayed stable.
The impact of site size revealed asymmetric benefits.
Small sites remained flat overall, with only marginal improvements. Medium sites gained around –1 position, a steady but modest lift. Big sites gained –2 positions, the largest absolute movement, stabilizing around the mid-teens on the SERP.
Structural fixes most strongly associated with ranking improvements are listed below.
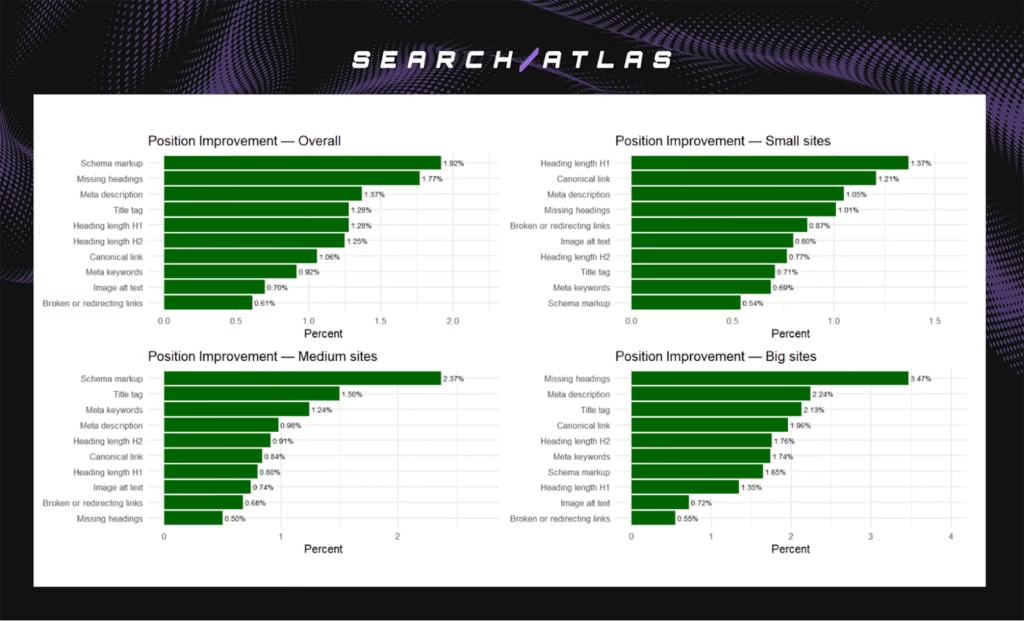
- Overall leaders. Schema markup (+1.92%), Missing headings (+1.77%), Meta description (+1.37%), Title tags (+1.28%), H1/H2 (~+1.25%).
- Small sites. H1 optimization (+1.37%) and Canonicals (+1.21%) led, supported by Meta descriptions (+1.05%) and Missing headings (+1.01%).
- Medium sites. Schema markup (+2.37%) and Titles (+1.50%) delivered the strongest lifts, followed by Meta keywords (+1.24%) and Meta descriptions (+0.98%).
- Big sites. Missing headings (+3.47%) dominated, with Meta descriptions (+2.24%), Titles (+2.13%), Canonicals (+1.96%), and H2 (+1.76%) adding meaningful impact.
Average position gains confirm that automation consistently improves rankings. Even modest improvements compounded across URLs translate into stronger discoverability and CTR.
Which Metrics Best Predict Outcomes?
The 5 core metrics analyzed are impressions, traffic, keywords, CTR, and average position. They capture different stages of the SEO funnel and reveal how automation expands reach, strengthens visibility, and improves engagement.
The headline results are shown below.
- Increase of 146 impressions long-term, increase of 2 short-term
- Increase of 67 keywords gained per site long-term
- Increase of 2 traffic units in long-term, increase of 0.5 short-term
- Increase of 0.03 percentage points CTR long-term
- 2 positions higher on average long-term
Each metric contributes differently. Impressions and keywords confirm expansion into new queries and broader indexation. Average position reflects ranking momentum. Traffic shows realized visits, although results were more volatile on larger properties.
CTR is the strongest predictor of outcomes. It connects visibility to engagement and improves the most consistently over time, especially for medium and large sites. CTR gains confirm that structural fixes such as headings, titles, canonicals, and schema transform technical stability into clicks.
What Should SEO Teams Do with These Findings?
The analysis confirms that automation drives measurable gains across impressions, keywords, traffic, and CTR. To turn these results into practice, SEO teams should align their efforts with the levers that consistently delivered the highest returns. The recommendations are organized by site scale, with each metric addressed directly.
1. All Sites
Impressions rely on schema markup, headings, canonicals, and titles. These fixes create the strongest visibility gains across all clusters.
Keywords expand when indexability improves through schema, canonicals, and headings as the baseline for discoverability.
Traffic grows most consistently with H1 structure, meta keywords, schema, and canonicals. These elements ensure both crawlability and relevance.
CTR lifts come from resolving missing headings, refining titles, consolidating canonicals, and applying schema or image alt tags.
2. Small Sites
Impressions improve when missing headings, image alt tags, and link hygiene are addressed, reinforced by titles and meta descriptions.
Keywords grow fastest when foundations are clean, with heading fixes, alt text, and schema coverage acting as the most effective levers.
Traffic gains are strongest from meta keyword optimization and H1/H2 alignment, with canonicals and schema adding stability.
CTR growth depends on schema coverage, heading completion, alt text, and link hygiene, with titles tuned afterward.
3. Medium Sites
Impressions increase through heading hierarchy, canonicals, and links, with titles providing additional reach.
Keywords expand when H1/H2 and canonical clarity scale across the site, supported by metadata refinements.
Traffic responds most to meta keywords and H1 optimization, reinforced by schema and canonicals.
CTR gains are driven by H1/H2, links, canonicals, and titles, with meta descriptions and alt text adding secondary lift.
4. Big Sites
Impressions compound through canonical consolidation and heading hierarchy, with titles and meta fields applied as polishing passes at scale.
Keywords remain strongest when consolidation prevents cannibalization, supported by canonical clarity and heading optimization.
Traffic stabilizes through large-scale keyword and heading programs, with canonicals and schema acting as structural anchors.
CTR lifts are largest when canonical consolidation and heading hierarchy are systematized, while titles and meta descriptions applied across thousands of URLs ensure alignment.
What Could be the Limitations of the Study?
Every model has limitations. The limitations of this study are listed below.
- The dataset was limited to sites in Content Assistant, OTTO PPC, and GSC.
- Temporal variation affects outcomes because the study window overlaps with seasonal shifts or algorithm updates.
- Confounding factors exist, including competitor actions or concurrent marketing campaigns.
- Statistical associations were strong, but causality is not guaranteed without controlled experimentation.
Despite these limits, automated fixes deliver measurable lifts in impressions, keywords, CTR, and ranking. Automation is not a replacement for strategy. It is a scalable foundation for sustainable growth.