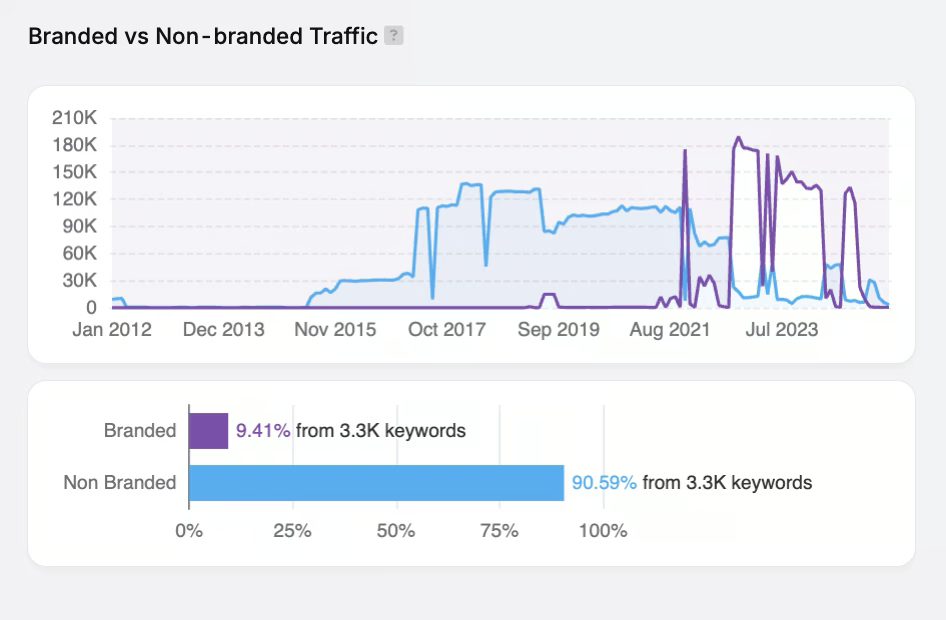
SEO ranking factors are the measurable signals Google uses to evaluate, score, and rank websites in the search engine results page (SERP). SEO ranking factors work together to determine which pages best match user queries and deserve visibility on the first page. Google ranking factors can be organized into four main pillars, known as the XACT framework (as stated by Search Atlas), which are User Experience (X), Authority (A), Content (C), and Technical SEO (T).
The most important SEO ranking factors Google uses to rank results in 2025 include User Experience signals, Backlinks from Authoritative Websites, and High-Quality, Relevant Content. Google uses SEO ranking factors to assess how well a page satisfies user intent, how trustworthy its information is, and how it performs across devices and technical standards. Ranking factors in SEO serve as Google’s way of modeling human preferences and quality expectations into machine-readable signals.
What is an SEO Ranking Factor?
An SEO ranking factor is a specific, quantifiable signal or criterion that search engines like Google use to evaluate and determine a web page’s position in SERP. Search engine ranking factors act as quality indicators that help search engine algorithms assess which pages best answer user queries based on relevance, authority, and user experience.
Google uses SEO ranking factors to filter, prioritize, and order billions of web pages in response to user searches. Factors can be direct (e.g., Core Web Vitals) or indirect (e.g., click-through rate, brand mentions), confirmed by Google or identified through industry consensus.
Each ranking factor in SEO carries a different weight in Google’s algorithm. While Google doesn’t publicly disclose the exact weight of each ranking factor or signal, extensive testing by SEO Scientists reveals patterns in what drives ranking success. Patterns show that ranking factors don’t work in isolation but function as a complex adaptive system where improvements in one area amplify results in others.
What are the Top 10 SEO Ranking Factors in 2025?

The top 10 SEO ranking factors in 2025 represent the most impactful signals Google uses to evaluate and rank websites in search results. Top SEO ranking factors are drawn from Google’s confirmed algorithms, API documentation, and industry-wide consensus.
The most important SEO ranking factors influence visibility by signaling relevance, trust, usability, and quality. SEO ranking factors form the foundation of an SEO strategy. They work best when implemented as part of a holistic SEO approach, not in isolation.
The top 10 SEO ranking factors are listed below.
- User Experience (RankBrain). User Experience measures how users navigate, engage, and respond to a website’s design, layout, and functionality. Google prioritizes websites that deliver positive behavioral signals such as high dwell time, low pogo-sticking, and intuitive navigation.
- Page Load Speed (Core Web Vitals). Page Load Speed reflects how quickly the main content loads and becomes interactive. Page Load Speed is measured by Core Web Vitals (LCP, INP, CLS). Faster-loading websites improve user satisfaction and are rewarded in Google’s ranking system under the Page Experience signal.
- Mobile-Friendly Website. Mobile-Friendly Website ensures a website is fully usable and displays correctly across mobile devices. Google’s Mobile-First Index prioritizes mobile usability as a baseline for ranking. Mobile issues can limit search visibility.
- Backlinks from Authoritative Websites. Backlinks from Authoritative Websites are inbound links from high-trust, topically relevant external sites. Google’s Link Graph algorithm uses backlinks as a primary signal for authority, trust, and external validation.
- Social Signals. Social Signals refer to engagement metrics such as shares, likes, comments, and reposts across platforms like X (Twitter), Facebook, LinkedIn, and Reddit. Social Signals influence search rankings by amplifying visibility, attracting backlinks, and increasing branded search volume. Content with high social engagement generates behavioral signals and external mentions that reinforce authority and topical relevance in Google’s systems.
- Topical Authority. Topical Authority measures a site’s breadth, depth, and consistency in covering a specific subject area. Google’s Helpful Content and Knowledge Graph systems favor websites that demonstrate comprehensive expertise in their domain.
- High-Quality, Relevant Content. High-Quality, Relevant Content refers to content that provides accurate, comprehensive, and helpful answers aligned with user intent and query needs. Google prioritizes content with depth, semantic SEO alignment, and factual accuracy, with keyword use based on query alignment, semantic relationships, and entity coverage across headings, early content, and metadata.
- Structured Data (Schema Markup). Structured Data Markup uses schema.org tags or JSON-LD to define page entities for search engines. Structured data improves Google’s page content understanding and enables enhanced SERP features such as rich results and knowledge panels.
- Secure Website (HTTPS). A Secure Website means a site uses HTTPS encryption to secure data transfer and user privacy. Google confirmed HTTPS as an important ranking factor. Unsecured websites may be deprioritized in search results.
- Internal Linking Structure. Internal Linking Structure refers to how pages within a website are interconnected through hyperlinks. A well-designed internal linking structure helps Google discover pages, pass link equity, and understand content hierarchy.
What are the 250 SEO Ranking Factors that Google uses to Rank Results?
The 250 SEO ranking factors that Google uses to rank results in 2025 are best understood when grouped into four main pillars known as XACT, as characterized by Search Atlas. These 4 pillars (XACT) are User Experience factors, Authority factors, Content factors, and Technical factors.
The 250 Google Ranking Factors are listed below.
User Experience Factors
1. RankBrain & User Interaction Signals
RankBrain and User Interaction Signals are a user experience ranking factor because they help Google understand queries and predict what users will click. RankBrain and User Interaction Signals are considered on-page SEO and user behavior metrics. RankBrain uses machine learning to connect words to concepts and improve results for new or unclear queries. It looks at search result interactions to decide which pages are most helpful.
Since RankBrain is confirmed as one of Google’s three most important ranking signals, optimizing for it involves creating holistic, user-focused content that clearly communicates entities and topics.
2. Core Web Vitals
Core Web Vitals are a user experience ranking factor and one of the top Google ranking factors because they measure how fast and stable a page loads for users. Core Web Vitals are considered on-page SEO and technical performance metrics. Google uses Core Web Vitals metrics to assess loading time (LCP), interactivity (FID → INP), and visual stability (CLS), rewarding sites that offer smooth, responsive experiences.
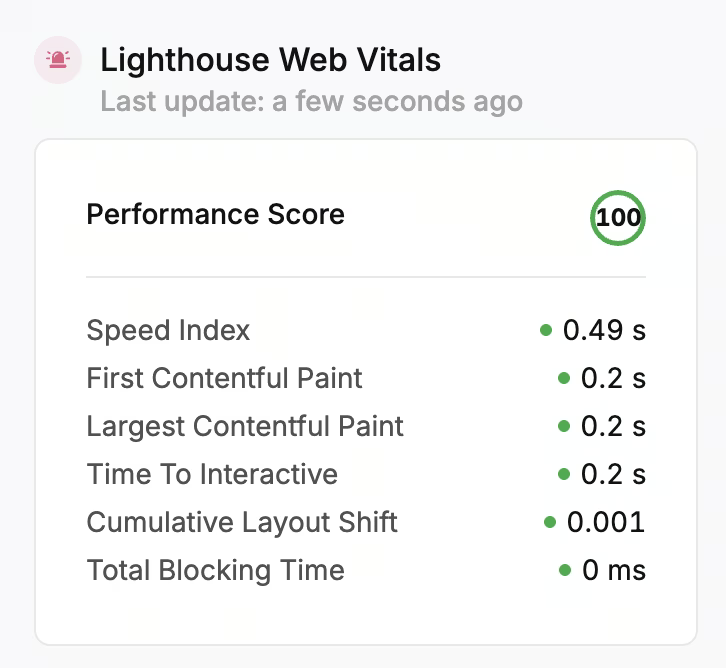
Pages with better Core Web Vitals scores are more likely to rank higher because they keep users engaged and meet Google’s page experience standards.
3. Mobile-Friendliness
Mobile-friendliness is a user experience ranking factor and one of the top Google ranking factors because it checks if pages work well on mobile devices. Mobile-friendliness is considered an on-page SEO and technical performance signal. Google rewards sites that are easy to read and navigate on phones, with responsive design and viewport configuration across devices. A mobile-friendly site improves the user experience and works best when paired with helpful content.
4. Organic Click-Through Rate (CTR) for a Query
Organic Click-Through Rate (CTR) for a Query is a user experience ranking factor that measures how often users click a page in search results for a specific keyword. Organic CTR for a Query is considered on-page SEO and a user behavior metric. Google tracks how many people click a result when it shows for a query. A higher-than-expected CTR signals strong relevance. Google uses CTR in systems like Navboost to adjust rankings based on click patterns. Leaked documents and court evidence confirm that Google uses CTR for a query as a ranking signal.
5. Overall Organic CTR (Site-Wide)
Overall Organic CTR (Site-Wide) is a user experience ranking factor that measures how often users click a site across all search results. Overall Organic CTR is considered an on-page SEO and user behavior metric. Google monitors total click-through rates across keywords. A higher site-wide CTR shows users trust the site and find it relevant. This metric acts like an organic quality score. SEO experts widely accept it as a ranking factor, although Google has not officially confirmed it.
6. Dwell Time (“Long Click” Duration)
Dwell Time is a user experience ranking factor that measures how long users stay on a page before returning to search. Dwell Time is considered an on-page SEO and user behavior metric. Google watches how long users remain on a page after clicking. A longer stay signals that the page answered the query. Google has tried to deny dwell time as a factor, but leaked documents confirm that Google tracks lastLongestClicks as a ranking signal.
7. Bounce-Back Behavior (Short Clicks)
Bounce-Back Behavior is a user experience ranking signal that measures how often users return to search quickly after clicking a result. Bounce-Back Behavior is considered an on-page SEO and user behavior metric. Google watches how fast users leave a page and go back to the results. A high rate of bounce-back signals poor relevance or satisfaction. While Google Analytics bounce rate is not used for rankings, bounce-back behavior in search is connected to pogo-sticking. This behavior is likely used by RankBrain as part of its filtering process to adjust rankings.
8. Pogo-Sticking (Serial Bouncing)
Pogo-Sticking is a user experience ranking factor that measures how often users click a result, return to search, and click another result. Pogo-Sticking is considered an on-page SEO and user behavior metric. Google tracks page-sticking behavior to see if users find what they need on the first click. Frequent pogo-sticking signals that a result failed to satisfy intent. Google has confirmed (via examples and videos) that your ranking will likely suffer if many users immediately leave your page to find an answer elsewhere.
9. “GoodClicks” (Positive Click Satisfaction)
GoodClicks is a user experience ranking factor because it measures when users have a positive interaction after clicking a search result. GoodClicks is considered on-page SEO and user behavior metrics. Leaked Google metrics differentiate goodClicks, clicks where the user had a positive interaction (e.g., stayed long, found what they needed), from others. Pages accumulating goodClicks are rewarded for satisfying users. This internal metric, revealed in 2024’s API leak, confirms Google uses click satisfaction as a relevance signal.
10. BadClicks (Negative Click Satisfaction)
BadClicks is a user experience ranking factor because it measures when users have a negative interaction after clicking a search result. BadClicks is considered on-page SEO and user behavior metrics. Google tracks clicks where users bounce back or show signs of dissatisfaction. A high number of BadClicks signals poor relevance and low satisfaction. Leaked internal documents confirm that Google uses BadClicks to demote pages in rankings, aligning with long-held industry assumptions.

11. Time on Site
Time on Site is a user experience ranking signal that measures how long users stay and interact with a website during a visit. Time on Site is considered on-page SEO and user behavior metrics. Longer visits suggest deeper engagement and stronger relevance. While Google has not officially confirmed using this metric, SEO experts believe Chrome telemetry and behavior signals influence ranking. It is likely evaluated as part of user engagement modeling in RankBrain.
12. Chrome Usage Data
Chrome Usage Data is a user experience ranking factor because it provides Google with direct signals about how users engage with web pages. Chrome Usage Data is considered on-page SEO and user behavior metrics. Google uses data from its Chrome browser to observe behavior like scroll depth, time spent, and site interactions. Chrom data helps refine ranking systems such as RankBrain. Google has confirmed using Chrome data as part of its ranking systems.
13. Intrusive Interstitials
Intrusive Interstitials are a negative user experience ranking signal because they block content and disrupt the user’s ability to access information. Intrusive Interstitials are considered on-page SEO and page experience violations. Google penalizes pages that display pop-ups or overlays that obstruct the main content, especially on mobile. This ranking signal is confirmed and part of Google’s Page Experience evaluation.
14. Above-the-Fold Content
Above-the-Fold Content is a user experience ranking factor that reflects how quickly and clearly users see the main content after loading a page. Above-the-Fold Content is a part of on-page SEO and layout structure. Google favors pages that show key content without scrolling. This is confirmed by Google’s Quality Rater Guidelines, which emphasize visible, immediately accessible information as a sign of quality.
15. User-Friendly Layout
User-Friendly Layout is a user experience ranking factor because it measures how clearly a page organizes content with a visible hierarchy. User-Friendly Layout is a part of on-page SEO and layout structure. Google favors pages that are easy to scan and read. This ranking signal is confirmed in Google’s Quality Rater Guidelines, which highlight clear structure as a sign of quality.
16. Presence of Ads
Presence of Ads is a user experience ranking signal because it evaluates how advertising affects the ability to access content. Presence of Ads is a part of on-page SEO and page layout evaluation. Google filters pages with excessive, misleading, or disruptive ads. This ranking signal is confirmed through Google’s Page Layout Algorithm, which demotes sites where ads harm the user experience.
17. Ad Placement Above Fold
Ad Placement Above Fold is a user experience ranking factor that measures how much ad content appears before users can see the main content. Ad Placement Above Fold is considered an on-page SEO and layout structure signal. Google filters pages that load too many ads before showing meaningful content. This signal is confirmed by Google’s Page Layout Algorithm, which penalizes heavy ad load above the fold.
18. Use of Pop-ups on Mobile
Use of Pop-ups on Mobile is a user experience ranking signal because it checks whether full-screen interstitials block content on mobile devices. Use of Pop-ups on Mobile is considered a part of on-page SEO and mobile user experience. Google penalizes pages that show intrusive pop-ups on mobile. This ranking signal is confirmed through Google’s mobile UX guidelines and Page Experience signals.
19. Chrome Bookmarking Rate
Chrome Bookmarking Rate is a user experience ranking factor that measures how often users bookmark a site in the Chrome browser. Chrome Bookmarking Rate is considered an on-page SEO and user behavior metric. A high bookmarking rate suggests users find the site valuable and want to return. Chrome Bookmarking Rate is likely used within Chrome data sources.
20. Time Between Repeat Visits
Time Between Repeat Visits is a user experience ranking signal that measures how quickly users return to a website after leaving. Time Between Repeat Visits is considered an on-page SEO and user behavior metric. A shorter return time signals high content value or engagement. This metric is likely included in systems like NavBoost.
21. Scroll Depth
Scroll Depth is a user experience ranking signal that measures how far users scroll down a page. Scroll Depth is considered an on-page SEO and user behavior metric. How far users scroll on your page can indicate how much of the content they have consumed.
While Google hasn’t confirmed using scroll depth, it’s easy for browsers to measure. If most users only scroll 10% down and leave, that suggests the page isn’t engaging or front-loaded with the answer. If users scroll all the way or interact with page content (e.g., clicking tabs, playing videos), it’s a sign of deep engagement. Many in the industry believe Chrome UX data could include such metrics (speculative but plausible).
22. Session Duration
Session Duration is a user experience ranking signal that measures the total time users spend across multiple pages during a visit. Session Duration is considered an on-page SEO and user behavior metric. Although search engines do not explicitly consider Session Duration as a ranking factor, it has an impact on SEO. Extended Session Durations suggest higher quality content and a favorable user experience, both of which are elements that search engines evaluate.
23. Direct Traffic
Direct Traffic is a user experience ranking signal that measures how often users visit a site directly without using a search engine. Direct Traffic is considered an off-page SEO and user behavior metric. A site that receives a lot of direct traffic (users typing the URL or using bookmarks) or a high volume of branded searches (people explicitly searching the site or brand name) is seen as popular and trusted by users.
24. Repeat Traffic
Repeat Traffic is a user experience ranking signal that tracks how often users return to a website over time. Repeat Traffic is considered an off-page SEO and user behavior metric. If users repeatedly return to a site (e.g., visiting it multiple times from search or other sources), it indicates the site provides consistent value. Leaked signals suggest Google may even use repeat traffic as a positive factor. In SEO terms, a site that turns one-time search visitors into regular visitors is demonstrating a strong user experience and usefulness.
25. Number of Comments
Number of Comments is a user experience signal because it reflects visible user interaction and engagement on a content page. Number of Comments is considered an on-page SEO signal and likely influences satisfaction signals modeled through Chrome or behavioral data. High comment activity suggests readers found the content engaging enough to respond. While it is not a confirmed ranking factor, comment volume and quality support positive user signals such as dwell time or return visits.
26. Site Usability
Site Usability is a user experience ranking factor that measures how easily users can navigate and use a website. Site Usability is considered on-page SEO and UX heuristics. Google favors sites with clear navigation and intuitive structure. This ranking factor is confirmed in Google’s Quality Rater Guidelines as a key user experience measure.
27. Site Uptime
Site Uptime is a user experience ranking signal that measures whether a website remains consistently available without downtime. Site Uptime is considered a UX and technical SEO signal and is related to infrastructure reliability. Google may reduce rankings for sites that experience frequent outages or server errors. Site Uptime is not explicitly named as a ranking factor, but it is part of site reliability metrics affecting crawlability and indexation.
28. Tabbed Content
Tabbed Content is a user experience ranking factor that measures how hidden content is treated for indexing and ranking. Tabbed Content is considered an on-page factor. Google does not devalue content hidden for mobile usability, but hiding important content to deceive users can lead to penalties. This ranking signal is confirmed through mobile-first indexing guidance.
29. Accessibility Compliance
Accessibility Compliance is a user experience ranking signal because it checks whether a website follows accessibility standards like WCAG. Accessibility Compliance is considered on-page SEO and UX heuristics. Google favors accessible sites, but this signal has not been confirmed as a direct ranking factor.
30. Personalized Experience
Personalized Experience is a user experience ranking signal that evaluates whether a site dynamically adjusts content based on user location or behavior. Personalized Experience is considered an on-page SEO and local SEO signal. Google may favor tailored experiences, though this signal is not confirmed as a direct ranking factor.
31. UX Signals from Other Keywords
UX Signals from Other Keywords is a user experience ranking signal because it measures how user behavior on one query influences ranking adjustments on related queries. UX Signals from Other Keywords is considered an on-page SEO and user behavior metric. Google uses engagement patterns like click-through rate and dwell time across semantically linked keywords to infer content quality and relevance. This signal is likely used within RankBrain and NavBoost systems, though it has not been confirmed as an independent ranking factor.
32. CTA Positioning
CTA Positioning is a user experience ranking signal that measures whether clear calls-to-action appear above the fold to encourage engagement. CTA Positioning is considered on-page SEO and UX heuristics. Google favors pages with well-placed CTAs that improve interaction rates. This signal is widely accepted as influencing user behavior metrics, though it is not confirmed as a direct ranking factor.
33. Autocomplete Prediction Matching
Autocomplete Prediction Matching is a user experience ranking signal that measures how closely content titles match popular autocomplete predictions in search. Autocomplete Prediction Matching is considered an on-page SEO factor relating to SERP behavior optimization. Google’s user behavior models show that titles aligned with autocomplete queries improve click-through rates. This signal is widely accepted for improving CTR, but is not confirmed as a direct ranking factor.
34. Intent Shifting Within Session
Intent Shifting Within Session is a user experience ranking signal because it measures how users refine or pivot their search queries during a single session. Intent Shifting is classified as a session-level on-page SEO and behavioral modeling signal, used by systems like NavBoost and RankBrain. Pages that support query evolution by linking to related topics, offering follow-up resources, or guiding users deeper are more likely to rank higher as they align better with multi-intent search behavior.
35. SERP Engagement Rate
SERP Engagement Rate is a user experience ranking signal that tracks how users engage with search result pages over time. SERP Engagement Rate is considered an on-page SEO signal within RankBrain-related systems. Higher historical engagement rates can improve the result treatment in search. SERP Engagement Rate is supported by indirect evidence but not explicitly confirmed by Google.
36. Scroll-Jacking or Hijack UX
Scroll-Jacking or Hijack UX is a user experience ranking signal that measures manipulative scrolling behaviors that interfere with normal user control. Scroll-Jacking or Hijack UX is an on-page SEO and UX signal. Google’s John Mueller stated that it’s not inherently abusive but noted that it could lead to rendering issues, especially if content isn’t properly displayed during Google’s page rendering process. Such issues might indirectly impact rankings if essential content isn’t visible to Google’s crawlers.
37. Auto-Playing Media Penalty
Auto-Playing Media is a user experience ranking signal because it measures whether videos or audio play automatically and disrupt user interaction. Auto-Playing Media is considered on-page SEO and UX heuristics. Google discourages intrusive auto-play because it lowers satisfaction metrics. Although not a direct ranking factor, such practices can lead to decreased user satisfaction and increased bounce rates, indirectly affecting search rankings.
38. Navigation Demotion (navDemotion)
Navigation Demotion (navDemotion) is a user experience and authority demotion signal that downranks pages with poor navigational structure or weak engagement via nav-based elements. Navigational Demotion is a confirmed demotion filter and likely ties to internal linking, making it a technical and on-page SEO factor.
Authority Factors
39. Quality of Backlinks
Quality of Backlinks is an authority ranking factor and one of the top Google ranking factors because it measures inbound links from trusted and authoritative sites. Quality of Backlinks is an off-page SEO factor, confirmed as part of Google’s Link Graph system. High-quality backlinks from authoritative sources strengthen a website’s authority and search rankings by passing contextual trust and relevance.
40. Topical Authority
Topical Authority is an authority ranking factor and one of the top Google ranking factors because it evaluates how deeply and consistently a website covers a specific subject area. Topical Authority is an on-page SEO signal confirmed through systems like the Knowledge Graph, Helpful Content, and Entity Matching. Google uses topical authority to determine whether a domain or section of a site demonstrates subject-matter expertise by publishing semantically related, high-coverage content over time.
Sites that show strong topical coverage are more likely to be trusted with long-tail queries, informational searches, and future updates in that subject area.
41. Site Authority
Site Authority (siteAuthority) is an authority ranking factor because it measures the overall trustworthiness and quality score. Site Authority is an off-page SEO signal, confirmed by the Google internal docs leak. Site Authority is calculated based on historical performance, link profile, and aggregated signals from Google’s Qstar system.
42. Authority Promotion
Authority Promotion (authorityPromotion) is an authority ranking signal because it represents a boost applied to pages or domains recognized as authoritative. Authority Promotion is a confirmed off-page SEO signal from leaked documentation. Google uses internal scoring systems like QualityBoost.authority.boost to elevate content with strong trust indicators.
43. Homepage Authority
Homepage Authority is an authority boost signal because high-quality links to a homepage increase site-wide trust and ranking potential. Homepage Authority is considered an off-page SEO and link graph signal. Pages that receive authoritative backlinks to their homepage often distribute PageRank more effectively across internal pages. Google’s systems confirm this flow within the Link Graph and treat the homepage SEO as a central hub for equity.
44. Number of Entities per Domain
Number of Entities per Domain is an authority boost signal because it measures how many verified entities a domain covers and connects within its content. Number of Entities per Domain is an on-page SEO and entity graph signal, likely used within Knowledge Graph models. Authority sites often display breadth and depth by covering multiple entities, strengthening semantic relevance and credibility.
45. Domain Age
Domain Age is an authority ranking signal because age contributes to perceived trust over time. Domain Age is considered part of off-page SEO and brand signals. Google has stated that there is no direct ranking boost from age alone, but SEO professionals treat domain longevity as a trust-building heuristic. It aligns with historical trust modeling and supports long-term credibility.
46. Domain History
Domain History is an authority filter signal because history affects how Google evaluates a domain’s trustworthiness. Domain History is confirmed and considered an off-page SEO filter. Domains with a history of spam, ownership churn, or manual actions often retain residual negative signals. Recovery may require disavowal efforts or rebuilding from scratch.
47. Domain Authority (Third-Party Metrics)
Domain Authority (Third-Party Metrics) is an authority heuristic signal that models link equity strength. Domain Authority is considered a third-party off-page SEO metric and does not reflect a direct Google signal. Tools like Moz DA and Ahrefs DR offer estimates, but the Search Atlas Domain Power is more reliable. The Search Atlas Domain Power metric aligns more closely with real Google systems like the Link Graph and topical relevance scoring.
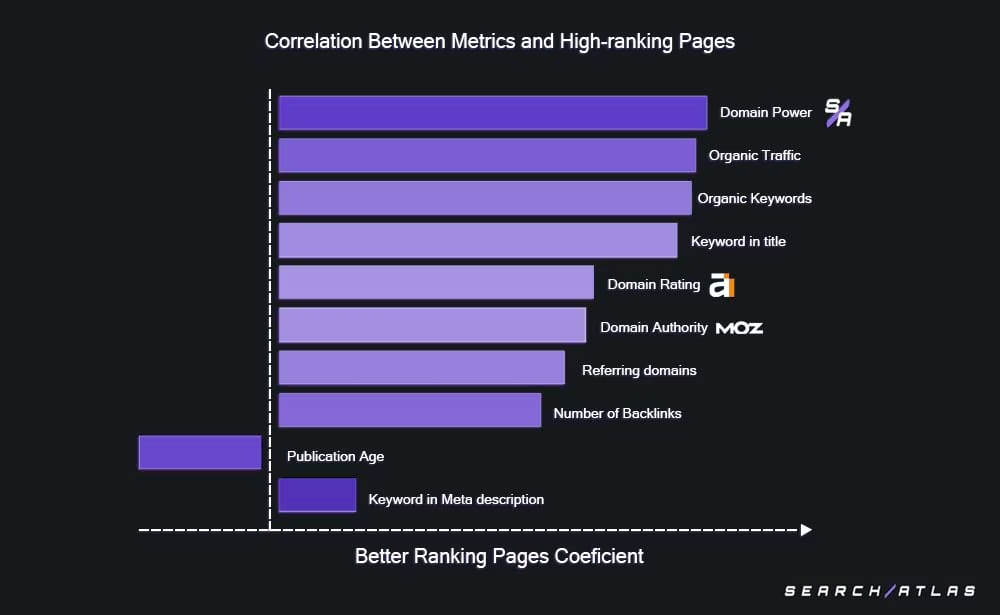
48. Referring Domain Diversity
Referring Domain Diversity is an authority ranking factor that counts the number of unique domains linking to a page or website. Referring Domain Diversity is an off-page SEO factor, and it’s confirmed within Google’s Link Graph. Links from diverse sources reduce dependency on a few domains and signal broader recognition.
49. Referring Domain Authority
Referring Domain Authority is an authority ranking factor because the overall trust and credibility of the domain linking to your site influence the value of that backlink. Referring Domain Authority is classified as an off-page SEO signal, and it is confirmed by the Link Graph system. A link from a trusted, authoritative domain boosts rankings more than one from an obscure site.
50. Referring Page Authority
Referring Page Authority is an authority ranking factor because the strength of the individual page linking to your content directly impacts how much equity is passed. Referring Page Authority is an off-page SEO signal tied to Google’s Link Graph. Links from high-authority pages provide more value than those from low-trust sources.
51. Domain-Level PageRank
Domain-Level PageRank is an authority ranking signal that measures accumulated link equity across a domain. Domain-Level PageRank is an off-page SEO and link graph signal. Google PageRank algorithm distributes link value throughout a domain, which influences how authority flows from high-value pages to deeper content.
52. PageRank Flow Efficiency
PageRank Flow Efficiency is an authority boost signal because it reflects how effectively a website distributes link equity through internal links. PageRank Flow Efficiency is an on-page SEO and technical link structure signal, confirmed through link sculpting systems. Well-executed internal linking boosts the discoverability and ranking of lower-tier pages by maximizing the value passed through navigational paths.
53. Link Relevance
Link Relevance is an authority ranking factor that evaluates whether the context of an inbound link aligns with the content of the target page. Link Relevance is classified as an off-page SEO factor, and it is confirmed within Google’s Link Graph system. Google favors backlinks that are topically relevant, not generic or off-topic.
54. Contextual Links
Contextual Links are an authority ranking factor because links placed within the main body content carry more semantic and editorial weight than those in sidebars or footers. Contextual Links are an off-page SEO factor, confirmed through the Link Graph. Google rewards in-content links that are naturally integrated into paragraphs.
55. Link Placement Priority (First Paragraph Preference)
Link Placement Priority (First Paragraph Preference) is an authority ranking signal because it reflects how Google values the location of links within content. Link Placement Priority is an on-page SEO signal and has been confirmed in SEO patent analysis and testing. Links placed higher in the body, especially in the first paragraph, are treated as more important than those buried in footers or sidebars, as they suggest editorial emphasis and early contextual alignment.
56. Links from Competitor Sites
Links from Competitor Sites are an authority boost signal because editorial references from trusted competitors within the same niche suggest topical credibility. Links from Competitor Sites are an off-page SEO signal likely used within Google’s Link Graph. Backlinks from competitor sites act as strong third-party endorsements of your content’s quality.
57. Links from Hub Pages
Links from Hub Pages are an authority boost signal because authoritative hub or resource pages, often curated and linked to by many, pass stronger link equity. Links from Hub Pages are an off-page SEO signal. Google’s Hilltop algorithm was designed to surface such expert pages.
58. Image Links (Alt Text Anchors)
Image Links (Alt Text Anchors) is an authority ranking signal that measures whether image-based links pass contextual relevance through their alt text attributes. While alt text itself is an on-page element, its role in describing image-based links makes it relevant to off-page SEO by helping Google understand the topic of the destination page. Google uses this alt text to infer topic alignment when traditional anchor text is absent, which is important for how it interprets the relevance of the link.
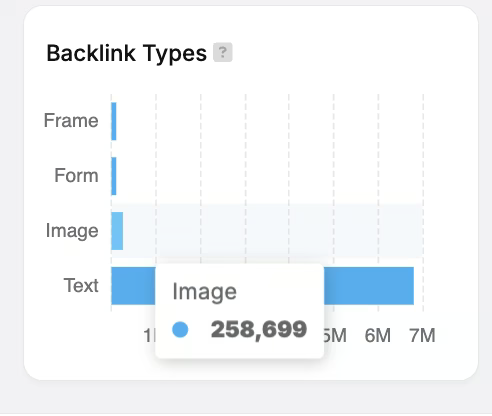
59. Inbound Anchor Text Variation
Inbound Anchor Text Variation is an authority filter signal because natural diversity in anchor text helps avoid spam detection. Inbound Anchor Text Variation functions as an off-page SEO filter, confirmed through the Penguin algorithm. Repetitive, over-optimized anchors can trigger Penguin filters. Google prefers a healthy mix of branded, partial-match, and generic anchors.
60. Branded Anchor Text Ratio
Branded Anchor Text Ratio is an authority filter signal that tracks how often anchor text uses a brand name compared to other terms. Branded Anchor Text Ratio is an off-page SEO signal and was confirmed by Google during Penguin updates as part of spam detection. A healthy ratio that includes branded anchors alongside natural variations indicates editorial authenticity, while excessive use of exact-match anchors can trigger filters.
61. Anchor Text Relevance (External)
Anchor Text Relevance (External) is an authority ranking factor that evaluates how well external anchor text matches the content it links to. Anchor Text Relevance (External) is an off-page SEO signal and is confirmed through link analysis and Penguin updates. Google uses anchor text to understand topical relevance between linked pages, and relevant anchors help reinforce content themes and entity connections in the Link Graph.
62. Anchor Mismatch Demotion
Anchor Mismatch Demotion (anchorMismatchDemotion) is an authority demotion signal that penalizes pages where the anchor text does not match the actual content. Anchor Mismatch Demotion is a confirmed off-page SEO filter, visible in Google’s internal field QualityBoost.mismatched.boost. This mismatch can be interpreted as manipulative or misleading linking behavior.
63. Anchor Spam Velocity Signal
Anchor Spam Velocity Signal is an authority signal because unnatural link spikes trigger demotions based on phrase frequency and velocity. Anchor Spam Velocity Signal is an off-page SEO signal confirmed through the phraseAnchorSpamDays and phraseAnchorSpamFraq features.
64. “Poison” Anchor Text
“Poison” Anchor Text is an authority penalty signal because it often indicates link manipulation or site compromise. “Poison” Anchor Text is an off-page SEO and spam signal, typically associated with terms related to pharmaceuticals, gambling, or adult content. Google uses this pattern in SpamBrain and manual reviews to detect hacked sites or unnatural link profiles, which may result in ranking suppression or security warnings.
65. Selling Links (Outbound Link Penalty)
Selling Links is an authority demotion signal because Google penalizes websites that exchange links for payment without proper disclosure. Selling Links is an off-page SEO and link integrity filter, confirmed through Google’s Link Spam Guidelines and enforced by manual actions or algorithmic suppression.
66. Affiliate Link Disclosure
Affiliate Link Disclosure is an authority filter signal that measures whether outbound affiliate or sponsored links are properly labeled for transparency. Affiliate Link Disclosure is an off-page SEO signal and is confirmed through Google’s enforcement under SpamBrain. Undisclosed affiliate links can be interpreted as deceptive, and sites with excessive or hidden monetized links can face ranking penalties or demotions.
67. User-Generated Link Spam
User-Generated Link Spam is an authority filter signal that evaluates whether spammy or irrelevant links are embedded in user-generated content (UGC) like blog comments or forums. User-Generated Link Spam is an off-page SEO and spam filtering signal, confirmed under SpamBrain. Google may devalue or penalize sites that fail to moderate comment sections or allow link manipulation in forums, reducing their perceived authority.
68. Low-Quality Directory Links
Low-Quality Directory Links is an authority filter signal because Google devalues backlinks from generic or low-moderation web directories. Low-Quality Directory Links is an off-page SEO demotion signal, confirmed in Google’s Link Scheme Guidelines. These links are often seen as manipulative and can trigger Penguin-related filtering or manual actions.
69. Widget Links
Widget Links is an authority penalty signal because links embedded through distributed widgets often lack editorial control and may be over-optimized. Widget Links is an off-page SEO signal, specifically cited by Google as a link scheme when the widget auto-generates dofollow links without proper attribution or disclosure. Such patterns can lead to demotions or complete discounting of the link source.
70. Links from the Same Class C IP
Links from the Same Class C IP is an authority demotion signal because unnatural link patterns from multiple domains hosted on the same server block suggest private blog networks (PBNs). Links from the Same Class C IP is an off-page SEO and infrastructure-level signal, likely used in Penguin and link spam detection systems. A high volume of cross-linked sites on the same IP class, i.e., private blog networks (PBNs), can trigger devaluation or penalties.
71. Bad Neighborhoods
Bad Neighborhoods is an authority penalty that penalizes sites linking to spammy, toxic, or malicious websites. Bad Neighborhoods is considered an off-page SEO filter and confirmed within Google’s SpamBrain system. Links to low-trust sources can harm site authority and trigger penalties.
72. Domain-Level Link Velocity
Domain-Level Link Velocity is an authority filter signal that measures the rate at which a domain gains new backlinks over time. Domain-Level Link Velocity is an off-page SEO signal, confirmed via the Penguin algorithm. Rapid, unnatural spikes in backlink growth can trigger suspicion of manipulative link schemes and result in algorithmic filtering or reduced ranking power.
73. Page-Level Link Growth Pattern
Page-Level Link Growth Pattern is an authority boost signal that measures how steadily a specific page earns backlinks over time. Page-Level Link Growth Pattern is an off-page SEO and link graph signal and is likely used by Google to differentiate between organically growing pages and manipulated link bursts. A natural, consistent backlink profile strengthens long-term trust and authority.
74. URL Change History Signal
URL Change History Signal is an authority ranking signal because only the last 20 indexed versions of a page are considered in scoring. URL Change History Signal is an off-page SEO signal confirmed through the urlHistory field in Google’s docjoin pipeline.
75. Internal Link Drop Signal
Internal Link Drop Signal is an authority ranking signal because irrelevant or excessive internal links may be ignored during ranking. Internal Link Drop Signal is an on-page SEO signal confirmed through Penguin-related fields like droppedLocalAnchorCount.
76. Internal Link Consistency
Internal Link Consistency is an authority boost signal that measures whether key pages are regularly linked across various site sections. Internal Link Consistency is an on-page SEO signal and is confirmed within Google’s Crawl Graph systems. Pages that are well-integrated into the site structure are easier to discover, pass equity more effectively, and are treated as more important in ranking systems.
77. Homepage Link Dilution
Homepage Link Dilution is an authority filter signal that measures the extent to which a homepage passes link equity to external sites instead of distributing it internally. Homepage Link Dilution is an on-page SEO signal and is likely modeled within link equity systems. Excessive outbound linking from the homepage weakens the domain’s ability to circulate PageRank internally, reducing site-wide authority.
78. TrustRank
TrustRank is an authority ranking factor because it propagates trust signals from verified seed sites through linked networks. TrustRank is an off-page SEO factor and is patented by Google. While not publicly confirmed as an active ranking factor, its underlying concept influences link-based trust evaluations.
79. Audience Overlap Signals (Co-Readership Patterns)
Audience Overlap Signals (Co-Readership Patterns) is an authority boost signal that measures shared visitor behavior across different websites. Audience Overlap Signals is an off-page SEO and user behavior signal, likely derived from Chrome Usage Graph data and NavBoost systems. When users frequently visit multiple related domains, Google may interpret this co-visitation pattern as a sign of topical trust and audience relevance between those sites.
80. Content Syndication Control
Content Syndication Control is an authority boost signal because it ensures original content sources retain credit when content is republished elsewhere. Content Syndication Control is an on-page SEO and indexing signal, confirmed through canonical tag guidance. Google prioritizes pages with correctly set canonical tags to avoid dilution of authority across duplicate or content syndication versions.
81. Branded Search Volume
Branded Search Volume is an authority factor that tracks how often users search for a brand name in Google. Branded Search Volume is considered a brand signal under off-page SEO. Google likely uses this factor to evaluate brand strength and user trust, although it’s not officially confirmed.
82. Brand Mentions (Unlinked)
Brand Mentions (Unlinked) is an authority signal that measures recognizable brand mentions in text without hyperlinks. Brand Mentions (Unlinked) is considered a brand signal under off-page SEO. Google likely uses brand mentions in its NavBoost system to infer entity authority, but it has not formally confirmed their impact.
83. SERP Brand Presence (Site Name Displayed)
SERP Brand Presence (Site Name Displayed) is an authority ranking signal because it reflects whether Google includes a brand name next to the page title in search results. SERP Brand Presence is an off-page SEO and entity trust signal, confirmed through Google’s branding display systems. When a site earns enough trust and recognition, Google automatically displays the brand name in SERPs, indicating entity-level authority and improved perceived legitimacy.
84. Knowledge Panel Presence
Knowledge Panel Presence is an authority ranking signal that indicates that a brand, person, or organization has been verified and indexed within Google’s Knowledge Graph. Knowledge Panel Presence is an off-page SEO and entity validation signal, confirmed by Google. Entities that appear in knowledge panels gain prominence and trust signals across multiple search verticals, including featured snippets and branded queries.
85. Entity Cross-Linking
Entity Cross-Linking is an authority boost signal because it evaluates how well related entities (brands, products, services) are semantically connected across websites owned by the same organization. Entity Cross-Linking is an off-page SEO and semantic validation signal, likely utilized within Google’s Knowledge Graph systems. Linking verified entities across domains reinforces their association and helps Google disambiguate brand identity.
86. Real-World Brand Activity (Aggregated Brand Trust)
Real-World Brand Activity (Aggregated Brand Trust) is an authority boost signal that reflects whether a business or brand has a verified presence in physical or third-party digital ecosystems, such as event listings, press mentions, or map integrations. Real-World Brand Activity is an off-page SEO and entity validation signal, likely used within entity-based ranking models. These signals support credibility by connecting online presence to verifiable offline activity.
87. Social Authority
Social Authority is an authority boost signal that reflects brand visibility and user engagement across major platforms. Social Authority is considered an off-page SEO and entity co-occurrence signal. Strong interaction on platforms like X, LinkedIn, Facebook and YouTube helps validate a brand’s real-world presence and trustworthiness. While Google does not confirm using social signals directly, leaked guidelines and patents support the use of entity-related social activity for ranking evaluation.

88. Verified Social Profiles (Schema/Markups)
Verified Social Profiles (Schema/Markups) is an authority boost signal because verification confirms the ownership and authenticity of brand-affiliated social media accounts. Verified Social Profiles is an off-page SEO and schema-based entity trust signal, backed by industry consensus and structured data implementation (e.g., sameAs, Organization, or Person markup). Verified profiles improve credibility in the Knowledge Graph.
89. Social Profile Consistency
Social Profile Consistency is an authority boost signal that checks whether a brand maintains a consistent identity (name, logo, URL) across major platforms. Social Profile Consistency is an off-page SEO and entity validation signal, likely used in entity matching systems. Brands with a coherent social presence are easier for Google to verify and trust.
90. Employee / Team Page
Employee / Team Page is an authority boost signal because it shows the real individuals behind a business, increasing site credibility and transparency. Employee / Team Page is an on-page SEO and E-E-A-T trust signal, confirmed in Google’s Quality Rater Guidelines. Pages that list team members, founders, or contributors help Google verify organizational legitimacy, especially in YMYL niches.
91. Business Profile Completeness
Business Profile Completeness is an authority boost signal that measures whether a brand’s Google Business Profile (GBP) is fully populated with accurate NAP (Name, Address, Phone), categories, hours, and media. Business Profile Completeness is an off-page SEO and local SEO trust signal, confirmed within Google’s Local Pack ranking systems. A complete GBP boosts visibility in local SERPs and signals credibility to both users and algorithms.
92. Local Citations Consistency
Local Citations Consistency is an authority boost signal that measures how consistently brand information appears across business directories and citation sources. Local Citations Consistency is an off-page SEO and local trust signal, confirmed within Google’s Local SEO ranking systems. Inconsistent NAP information across directories weakens local ranking potential, while strong citation alignment supports location-based authority.
93. Curated List Inclusions
Curated List Inclusions is an authority boost signal that reflects mentions in top tool lists, book guides, or authoritative resource roundups. Curated List Inclusions is an off-page SEO and external validation signal, likely used to identify expert-endorsed content or services. Being featured on trusted editorial lists strengthens perceived domain trust and content credibility, especially in competitive categories.
94. “Expert Roundups” Participation
“Expert Roundups” Participation is an authority boost signal that reflects inclusion in curated lists or collaborative expert content across trusted domains. “Expert Roundups” Participation is an off-page SEO and semantic trust signal, likely modeled through Semantic Networks or entity relationship graphs. Being featured alongside recognized industry professionals enhances entity visibility and reinforces perceived topical authority.
95. Forum Reputation Signals
Forum Reputation is an authority boost signal that evaluates the quality and tone of brand mentions on platforms like Reddit, Quora, and niche communities. Forum Reputation Signals are an off-page SEO and entity-level trust signal, likely used in Entity Graph Expansion systems. Consistent, positive community discussion around a brand or domain strengthens semantic relevance and user-perceived authority.
96. News Media Coverage
News Media Coverage is an authority boost signal that measures brand or website mentions in reputable news publications, even without links. News Media Coverage is an off-page SEO and brand reputation signal, likely used in entity trust scoring. Google’s systems treat coverage from high-authority editorial sources as a signal of legitimacy and public validation.
97. Alumni/Press Citations
Alumni / Press Citations is an authority boost signal because backlinks or mentions from university bios or press features associate the entity with external authority sources. Alumni/Press Citations are an off-page SEO and entity reputation signal, likely modeled within Google’s External Authority Graph. These citations establish credibility through third-party validation, especially when tied to professional or academic institutions.
98. TLD Trust Bias
TLD (Top Level Domain) Trust Bias is an authority perception signal because certain extensions carry institutional or governmental trust. TLD Trust Bias is considered an off-page SEO and domain reputation heuristic. While Google has confirmed it does not explicitly favor .edu or .gov, these domains tend to earn stronger backlinks and editorial trust, indirectly improving authority signals.
99. Patent or Research Citation
Patent or Research Citation is an authority boost signal that measures whether a site or author is cited in academic papers, patents, or scholarly research. Patent or Research Citation is an off-page SEO and entity authority signal, likely used in Knowledge Vault modeling. Citations in trusted intellectual domains help verify expertise and signal a higher level of trustworthiness.
100. Wikipedia Citation (Unlinked)
Wikipedia Citation (Unlinked) is an authority boost signal that measures whether a site or brand is referenced on Wikipedia, even without a direct hyperlink. Wikipedia Citation is an off-page SEO and entity recognition signal, likely used in entity matching and knowledge graph expansion. Mentions in Wikipedia imply editorial trust and inclusion in Google’s broader understanding of verified topics and entities.
101. Review Site Presence
Review Site Presence is an authority boost signal that reflects how often a brand appears in trusted review aggregators like Trustpilot, Yelp, or G2. Review Site Presence is an off-page SEO and reputation signal, likely reflected in Google’s Quality Rater Guidelines (QRG). Brands with a positive presence in verified review platforms earn higher perceived trust and entity-level confidence.
102. Reviewer Transparency
Reviewer Transparency is an authority boost signal that evaluates whether product or content reviewers are identified with credentials and real names. Reviewer Transparency is an on-page SEO and E-E-A-T trust signal, confirmed through systems like the Product Review System and supported by structured data and QRG guidelines. Pages that name and qualify their reviewers help Google verify authenticity and expertise.
103. Fake Review Detection
Fake Review Detection is an authority filter signal that penalizes sites that publish fabricated, templated, or misleading user reviews. Fake Review Detection is an on-page SEO and manual/ML trust signal, confirmed within Google’s SpamBrain and review evaluation systems. Google uses spam detection models and pattern recognition to identify artificial review activity and reduce the visibility of deceptive pages.
104. Review Schema Manipulation
Review Schema Manipulation is an authority filter signal that penalizes websites that misuse structured data to misrepresent review scores. Review Schema Manipulation is an on-page SEO and structured data compliance signal, confirmed by Google’s enforcement of rich result eligibility. Sites that fake or inflate ratings through markup abuse can receive manual actions or be excluded from review-rich snippets.
105. Trust Seals/Certifications
Trust Seals/Certifications is an authority boost signal that measures the presence of recognized third-party validations like SSL, BBB, or ISO badges. Trust Seals/Certifications is an on-page SEO and E-E-A-T signal, likely used to reinforce site legitimacy. While not confirmed as a direct ranking factor, trust seals and badges contribute to perceived trustworthiness, especially on transactional or YMYL pages.

106. WHOIS Visibility
WHOIS Visibility is an authority filter signal because hidden ownership may raise trust concerns. WHOIS Visibility is considered an off-page SEO and spam detection signal. While not confirmed by Google directly, private registration has been cited in manual action cases and may be used in combination with other spam signals in filters like SpamBrain.
107. Public vs. Private WHOIS
Public vs. Private WHOIS is an authority filter signal because hiding domain ownership can raise red flags in Google’s trust evaluation systems. Public vs. Private WHOIS is considered an off-page SEO and ownership transparency signal, widely associated with spam detection and credibility modeling. While not confirmed as a standalone ranking factor, private WHOIS can contribute to reduced trust when combined with other low-quality signals.
108. Author Profile Links
Author Profile Links is an authority boost signal that evaluates whether content includes links to credible author bios or third-party profiles. Author Profile Links is an on-page SEO and E-E-A-T signal, confirmed as part of Google’s authorship and credibility evaluation. Linking content to real, traceable experts supports transparency and helps Google connect expertise to individual contributors.
109. Rich Author History
Rich Author History is an authority boost signal that examines whether an author has a consistent presence across multiple trusted domains over time. Rich Author History is an off-page SEO and entity-level authority signal, confirmed through Author Signals in Google’s documentation and supported by the Quality Rater Guidelines. An established track record of publishing high-quality content helps associate authors with specific topics and improve perceived expertise.
110. Penalized WHOIS Owner
Penalized WHOIS Owner is an authority penalty signal because domains tied to registrants with a history of spam or manipulation may inherit a negative trust profile. Penalized WHOIS Owner is considered an off-page SEO and entity reputation signal, and has been referenced in multiple manual action cases. Google may apply historical trust penalties to new domains if ownership overlaps with previously penalized entities.
111. Author Bio Schema
Author Bio Schema is an authority boost signal because it provides structured data that helps Google understand the identity, credentials, and relevance of an author. Author Bio Schema is an on-page SEO and E-E-A-T trust signal, confirmed through Google’s structured data documentation. Proper implementation of the Person schema with contextual fields (name, job title, affiliation, sameAs) reinforces author credibility and supports entity-level trust.
112. Publisher Schema Usage
Publisher Schema Usage is an authority boost signal because it clarifies the organization responsible for publishing content. Publisher Schema Usage is an on-page SEO and structured data signal, confirmed by Google as part of content classification and entity mapping. When implemented using the Organization schema or publisher markup, it allows Google to associate the content with a verified source, improving visibility in features like Top Stories and Google News.
113. Hacked Website
Hacked Website is an authority penalty signal because compromised sites often distribute spammy links, malicious scripts, or deceptive content that violates Google’s quality guidelines. Hacked Website is an off-page SEO and site trust demotion signal, confirmed in Google’s Search Essentials and via the Safe Browsing system. Once detected, hacked pages may be removed from the index, flagged in SERPs with security warnings, or penalized with visibility loss until the issue is resolved and revalidated in Search Console.
114. GSC Manual Actions
GSC Manual Actions is an authority demotion signal that reflects a human-applied penalty for violating Google’s Webmaster Guidelines. GSC Manual Actions is classified as an off-page SEO and link trust signal, confirmed by Google’s Search Console. When Google issues a manual action (typically for manipulative link schemes, thin content, or spam), the affected site loses ranking power until the issue is resolved and a reconsideration request is approved.
115. Low Quality Score (lowQuality)
Low Quality Score (lowQuality) is an authority demotion signal assigned to pages based on S2V vector analysis and other quality classifiers. Low Quality Score encompasses thin content, spammy link patterns, and weak user satisfaction. This score is applied in Qstar and is confirmed as a cross-category
116. Page Quality Data (pqData)
Page Quality Data (pqData) is an authority composite signal that includes page-level evaluations like expertise, structure, and satisfaction metrics. Although the exact variables are not public, pqData represents an on-page SEO signal that contributes to overall authority and quality assessments. This is confirmed by Google’s leak.
117. Baby Panda Demotion
Baby Panda Demotion (babyPandaDemotion / babyPandaV2Demotion) is an authority demotion filter that reduces visibility for content with low engagement, weak quality signals, or thin content patterns. Baby Panda Demotion evolved from the original Panda system and now runs atop new evaluation layers.

Content Factors
118. High-Quality, Relevant Content
High-Quality, Relevant Content is a content ranking factor and one of the top Google ranking factors because it directly addresses whether a page satisfies the search intent behind a query. High-Quality, Relevant Content is considered an on-page SEO and topical relevance signal. Google’s Helpful Content System, Quality Rater Guidelines, and Knowledge Graph all reinforce that clear, informative, well-structured SEO content, aligned with user needs, outperforms shallow, keyword-stuffed pages.
119. Keyword Optimization (Semantic Targeting)
Keyword Optimization is a content ranking factor that helps the algorithm assess whether a page addresses the concepts behind a search query. Keyword Optimization (Semantic Targeting) is considered an on-page SEO and topical alignment signal. Google no longer rewards keyword repetition but analyzes semantic relevance using NLP systems like RankBrain, Hummingbird, and BERT. Proper keyword usage means covering related entities, synonyms, modifiers, and query variations in natural contexts across titles, headings, and early content zones.
120. Keyword in Title Tag
Keyword in Title Tag is a content ranking factor because it signals page relevance based on the title’s topic focus. Keyword in Title Tag is an on-page SEO factor and part of the content hierarchy. Google has confirmed that keywords in the title tags influence rankings by helping algorithms understand what the page is about.
121. Keyword in H1 Tag
Keyword in H1 Tag is a content ranking factor that reinforces the primary topic of the page. Keyword in H1 Tag is an on-page SEO factor and part of the content hierarchy. Google has confirmed that the H1 tag helps organize information and provides a clear signal about the page’s focus.
122. Keywords in H2/H3 Tags
Keywords in H2/H3 Tags are a content ranking factor because they help search engines understand subtopics and the semantic structure of a page. Keyword in H2/H3 Tags is an on-page SEO signal. While not explicitly confirmed, SEO industry consensus and Google documentation support its relevance.
123. Keyword in URL
Keyword in URL is a content ranking signal that offers additional context for search engines and users. Keyword in URL is an on-page SEO signal and part of the content structure. Google has confirmed that keywords in URLs offer a minor relevancy signal and can aid in click-through rates.
124. Keyword Prominence
Keyword Prominence is a content ranking factor because placing key terms early in sentences or paragraphs gives them more semantic weight. Keyword Prominence is an on-page SEO factor that correlates with higher search result rankings. Keyword Prominence is a consensus-based factor reinforced by Google’s NLP systems.
125. Keyword in First 100 Words
Keyword in First 100 Words is a content ranking signal because early keyword placement helps establish topical relevance quickly. Keyword in First 100 Words is considered an on-page SEO signal and part of the content introduction. This signal is widely supported by industry consensus, though not officially confirmed by Google.
126. Keyword in Description Tag
Keyword in Description Tag is a content CTR signal because meta descriptions influence how content appears in SERPs. Keyword in Description Tag is considered on-page SEO and a CTR optimization factor. Google does not use meta descriptions directly for ranking but uses them to influence click behavior, especially when keywords match query terms.
127. Keyword in Top-Level Domain/Subdomain
Keyword in Top-Level Domain/Subdomain is a weak content relevance signal. Keyword in Top-Level Domain/Subdomain is considered an off-page SEO signal and part of the domain naming strategy. Although the impact is minimal, keywords in domain names may help users understand topic alignment. This signal is based on consensus, not confirmation.
128. Keyword Variants & Synonyms
Keyword Variants & Synonyms is a content ranking factor because semantic alternatives enhance query matching. Keyword Variants & Synonyms are an on-page SEO factor and part of semantic content clarity. Google’s BERT and NLP systems rely on variant detection to interpret meaning, making this a confirmed signal.
129. Entity and Semantic Keyword Usage
Entity and Semantic Keyword Usage is a content ranking factor that helps Google interpret topical clarity and depth through related terms and concepts. Entity and Semantic Keyword Usage is an on-page SEO signal and is likely evaluated through Google’s natural language systems, such as BERT, MUM, and the Knowledge Graph.
Outdated SEO advice still refers to “LSI keywords,” but Google has confirmed that Latent Semantic Indexing is not used in its ranking systems. Google now applies deep learning models that analyze entities, term co-occurrence, and semantic proximity to understand content meaning and topical relationships.
130. Entity Match & Semantic Clarity
Entity Match and Semantic Clarity are content ranking factors that help Google understand exactly what a page is about. Entity Match and Semantic Clarity are on-page SEO signals confirmed through BERT, MUM, and the Knowledge Graph. Google uses entity recognition to disambiguate terms (e.g., “Apple,” the company vs. the fruit) and prefers pages that reference and connect entities through names, attributes, and relationships. Pages that include relevant entities and contextual clarity gain stronger visibility in entity-driven systems.
131. TF-IDF & Co-Occurrence Frequency
TF-IDF & Co-Occurrence Frequency is a content ranking factor that models how important a term is within a document and across documents. TF-IDF & Co-Occurrence Frequency is an on-page SEO signal and a part of semantic relevance modeling. While not directly confirmed, patents and NLP-based ranking systems suggest this signal is actively used.
132. Content Length
Content Length is a content ranking factor because it correlates with how comprehensively a topic is covered. Content Length is an on-page SEO factor supported by industry consensus. While Google does not reward word count directly, longer content tends to include more entities, answer more related questions, and demonstrate topical depth, especially for informational or YMYL queries. Search engines interpret longer pages as more likely to fulfill multiple aspects of user intent when they maintain relevance and clarity.
133. In-Depth Topic Coverage
In-Depth Topic Coverage is a content ranking factor that signals a comprehensive understanding and topical authority. Content Depth is an on-page SEO factor, confirmed through Google’s Helpful Content system. Pages that cover all angles of a topic (definitions, examples, subtopics, objections, and context) are favored in systems designed to rank helpful, expert-level content. In-depth coverage improves a page’s ability to rank across a wide range of long-tail queries related to the same entity.
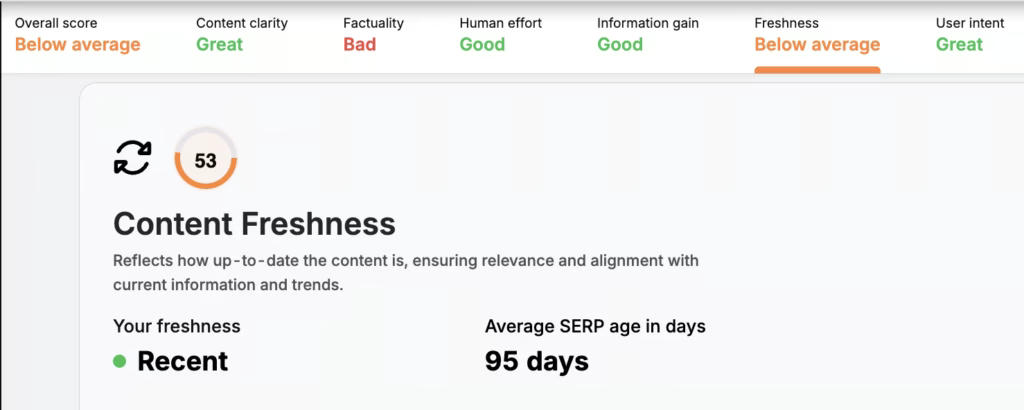
134. Content Freshness
Content Freshness is a content ranking factor that evaluates how recently a page was created or updated, especially for time-sensitive topics. Content Freshness is an on-page SEO factor confirmed through Google’s Caffeine indexing system. Google prefers fresh content that reflects current information for queries related to news, trends, or evolving topics. Updates to older pages can trigger a freshness boost if the content remains relevant.
You can check Content Freshness, along with the other content factors in the Search Atlas SCHOLAR Tool.
135. Content Originality
Originality is a content ranking factor that determines whether a page provides unique value instead of just duplicating existing content. Originality is an on-page SEO factor confirmed through the Panda algorithm and reinforced in the Helpful Content Update (HCU). Google devalues pages that scrape, spin, or lightly reword content without offering new insights. Sites that produce original research, unique perspectives, or firsthand information are more likely to rank well.
136. Grammar and Spelling
Grammar and Spelling is a content ranking signal because clean, professional language improves user comprehension and trust. Grammar and Spelling is an on-page SEO signal likely evaluated through Google’s Quality Rater Guidelines (QRG). While not confirmed as a direct algorithmic factor, poor grammar may contribute to low-quality assessments, particularly in YMYL (Your Money or Your Life) content.
137. Content Hierarchy
Content Hierarchy is a content ranking factor because it uses clear headings (like H2 and H3) to structure content and signal topic relationships. Content Hierarchy is an on-page SEO signal confirmed in Google’s Quality Rater Guidelines (QRG), which highlight the importance of organized formatting. Proper use of subheadings helps Google understand topic segmentation, improves accessibility, and supports semantic interpretation of complex content.
138. Structured Content (Lists, Tables)
Structured Content is a content ranking factor because it enhances readability and comprehension by organizing information into scannable formats like lists, tables, and bullet points. Structured Content is an on-page SEO signal confirmed in Google’s Quality Rater Guidelines (QRG), which emphasizes content clarity and ease of understanding. Pages that use structured formatting help users extract key insights quickly and are more likely to earn featured snippets and higher user engagement.
139. Topical Clustering
Topical Clustering is a content ranking factor that shows how individual pieces of content relate within a larger topical map. Topical Clustering is an on-page factor, confirmed through Google’s systems like the Knowledge Graph and Site Authority. When multiple interlinked pages cover a subject from different angles (e.g., guides, use cases, comparisons), Google better understands the site’s topical focus and ranks pages higher within that domain. Topical clustering is fundamental for building topical authority.
140. Use of Related Questions
Use of Related Questions is a content ranking factor because it improves semantic coverage and user satisfaction. Use of Related Questions is an on-page SEO and content structure signal, confirmed through systems like Featured Snippets and People Also Ask. Including and answering related queries on the page helps cover search intent and increases a page’s chance of ranking for multiple variations of a query.
141. Coverage of “Why” and “How” Queries
Coverage of “Why” and “How” Queries is a content ranking signal because it aligns with explanatory and informational intent. Coverage of “Why” and “How” Queries is an on-page SEO and content intent signal, confirmed via SERP structure and Google’s Helpful Content system. Pages that directly address causal and instructional queries are more likely to appear for long-form searches, featured snippets, and instructional results.
142. Use of Lists and Bullets
Use of Lists and Bullets is a content ranking signal because structured formatting improves scannability and user comprehension. Use of Lists and Bullets is considered an on-page SEO and readability signal, confirmed in Google’s Quality Rater Guidelines (QRG). Google rewards content that presents information clearly, especially when answering intent-driven queries, where bullet points improve usability.
143. Use of Citations and References
Use of Citations and References is a content ranking signal because linking to authoritative sources reinforces factual accuracy and trust. Use of Citations and References is considered an on-page SEO and E-E-A-T signal, likely factored into Google’s evaluation of trustworthiness. While not explicitly confirmed, Google’s guidance around trustworthy content favors properly sourced claims and attribution.
144. Use of FAQs
Use of FAQs is a content ranking signal because structured Q&A formatting aligns with how Google parses and serves featured snippets. Use of FAQs is considered an on-page SEO and structured content signal, confirmed through schema.org markup and the Helpful Content Update. Google surfaces FAQs that match common user queries in position-zero placements and voice results.
145. Multiple Content Formats
Multiple Content Formats is a content ranking signal because offering information through text, video, and audio formats meets varied user intent and accessibility needs. Multiple Content Formats is an on-page SEO and multimedia engagement signal, confirmed through systems like Google Discover and MUM. Google rewards content that serves different learning styles and contexts, especially for broad-topic, evergreen, or experience-rich queries.
146. Media Embeds
Media Embeds is a content ranking signal because embedding visual aids like charts, infographics, and videos strengthens explanation quality and engagement. Media Embeds is an on-page SEO and visual UX signal, confirmed in Google’s Quality Rater Guidelines and user behavior modeling. Pages that illustrate key points with embedded media improve clarity, time on page, and perceived helpfulness, particularly for how-to or data-driven content.
147. Embedded Topic Transitions
Embedded Topic Transitions is a content ranking signal that reflects how smoothly a page shifts between semantically related subtopics. Embedded Topic Transitions is considered an on-page SEO and content structure signal, likely used within Google’s Helpful Content and RankBrain systems. When content answers multi-intent queries through natural progression, without abrupt or disjointed jumps, it increases user satisfaction and topic coverage depth.
148. Author Byline Presence
Author Byline Presence is a content ranking signal because clearly attributing content to a named individual increases trust, especially on sensitive or YMYL topics. Author Byline Presence is an on-page SEO and E-E-A-T trust signal, confirmed in Google’s Quality Rater Guidelines. Pages with transparent authorship are favored when credibility and accountability matter.
149. Author Expertise (E-E-A-T)
Author Expertise is a content ranking factor because Google evaluates whether the author has demonstrable experience or qualifications in the topic area. Author Expertise is an on-page SEO and content credibility signal, confirmed through the Helpful Content System and E-E-A-T guidelines. Proven topical expertise improves rankings for queries that require accuracy or trust.
150. Topical Consistency
Topical Consistency is a content ranking factor because pages that stay tightly focused on one subject are easier for Google to interpret and serve to the right audience. Topical Consistency is an on-page SEO and content quality signal, confirmed by Google’s content scoring systems. Fragmented or off-topic inclusions dilute semantic relevance and reduce ranking potential.
151. Content Accuracy
Content Accuracy is a content ranking filter because Google demotes pages that contradict factual consensus or mislead users. Content Accuracy is an on-page SEO and E-E-A-T trust signal, confirmed in Google’s QRG and misinformation policies. Matching known facts and citing reliable sources improves both snippet eligibility and long-term trust signals.
152. First-Hand Experience
First-Hand Experience is a content ranking signal because original insights or usage-based details enhance authenticity and user value. First-Hand Experience is an on-page SEO and helpfulness signal, confirmed by Google’s Helpful Content System. Google prefers articles with direct observations over generic rewrites, particularly for product reviews or YMYL queries.
153. Sentiment & Tone Appropriateness
Sentiment and Tone Appropriateness is a content ranking filter because emotional exaggeration, clickbait, or irrelevant tone reduces user trust and clarity. Sentiment and Tone Appropriateness is an on-page SEO and quality filter signal, likely part of Google’s Helpful Content Update. Mismatched tone or padded content can lower perceived helpfulness and lead to demotion.
154. Contextual Relevance to Entity
Contextual Relevance to Entity is a content ranking factor because Google favors content that aligns precisely with the search entity’s known attributes. Contextual Relevance to Entity is an on-page SEO and Knowledge Graph signal, confirmed via entity mapping models. Pages that directly match search context and entity scope perform better for named queries.
155. Answering Follow-Up Queries
Answering Follow-Up Queries is a content ranking signal because anticipating next-question intent improves content completeness and engagement. Answering Follow-Up Queries is an on-page SEO and behavioral modeling signal, likely used within systems like NavBoost. Google promotes content that reflects the natural query journey of the user.
156. Clarifying Definitions
Clarifying Definitions is a content ranking signal that helps disambiguate terminology and improve entity understanding. Clarifying Definitions is considered an on-page SEO and NLP signal, confirmed through its influence on featured snippets and Google’s Knowledge Graph parsing. Pages that define terms early and clearly are more likely to rank for “what is” and informational queries.
157. “People Also Ask” (PAA) Alignment
“People Also Ask” Alignment is a content ranking signal because matching the phrasing and structure of PAA questions increases snippet inclusion. “People Also Ask” Alignment is an on-page SEO and SERP features signal, confirmed by testing and SERP behavior analysis. Structuring sections to align with “People Also Ask” (PAA) intent increases visibility for question-based queries.
158. Helpful Supplementary Content
Helpful Supplementary Content is a content ranking signal because it improves user satisfaction by adding context, examples, or supporting modules to core content. Helpful Supplementary Content is an on-page SEO signal and part of user-centric content design. While not explicitly confirmed by Google, it is supported by the Quality Rater Guidelines and aligns with Google’s Helpful Content updates, which reward depth and clarity through additional helpful assets like FAQs, sidebars, and related links.
159. Content Index Saturation
Content Index Saturation is a content filter signal that measures the ratio of indexed pages to total published content, which reflects overall content quality and crawl efficiency. Content Index Saturation is a technical and on-page SEO signal, confirmed through Google’s indexing evaluation systems. A site with low indexation rates may signal thin, duplicate, or low-value content, and potentially trigger site-wide trust demotion.
160. Use of Internal Glossaries
Use of Internal Glossaries is a content enhancement signal because it improves semantic clarity by defining key terms within the page or site structure. Use of Internal Glossaries is considered an on-page SEO and semantic support tactic. While not confirmed as a direct ranking factor by Google, SEO glossaries help Google’s NLP systems (like BERT or MUM) better interpret context and disambiguate entities, especially in technical or YMYL content.
161. Sitelink Inclusion Criteria
Sitelink Inclusion Criteria is a content structure ranking signal that reflects how well a page or site is structured for SERP enhancements. Sitelink Inclusion Criteria is an on-page SEO signal confirmed through Google’s SERP enhancements system. Pages with clean anchor structures, distinct sections, and logical hierarchy are more likely to receive sitelinks, increasing visibility and trust.
162. Scroll-Activated Content
Scroll-Activated Content is a content filter signal because hidden content loaded only during scroll may not be indexed or evaluated properly. Scroll-Activated Content is a content and technical SEO signal confirmed by Google’s rendering and indexing systems. If essential information is hidden in lazy-loaded sections or JavaScript-triggered modules and not visible to bots, it may not count toward ranking.
163. Redundant Topic Pages
Redundant Topic Pages is a content penalty signal because having multiple thin or overlapping pages dilutes canonical authority and confuses Google. Redundant Topic Pages is an on-page SEO filter confirmed in the Panda and Helpful Content systems. Google favors consolidated, authoritative pages over fragmented or near-duplicate entries on the same subject.
164. Clear Content Purpose
Clear Content Purpose is a content filter signal because pages with vague or mixed goals struggle to match user intent. Clear Content Purpose is an on-page SEO signal confirmed through Google’s Helpful Content system. Content that blends too many topics or switches context mid-way may trigger demotion signals due to unclear value.
165. Intro Section Clarity
Intro Section Clarity is a content ranking signal because a clear and relevant introduction improves engagement and reduces bounce rate. Intro Section Clarity is an on-page SEO and UX layer signal, confirmed in Google’s behavior modeling and CTR optimization systems. Pages that summarize purpose and topical focus early help Google and users align expectations.
166. Magnitude of Content Updates
Magnitude of Content Updates is a content ranking signal that evaluates how significantly a page changes during updates. Magnitude of Content Updates is considered an on-page SEO signal tied to Google’s freshness and helpfulness systems. Substantial edits (like adding new sections, revising outdated data, or restructuring content) carry more weight than superficial changes. Industry consensus holds that larger updates are more likely to trigger reindexing and positively affect rankings than trivial tweaks.
167. Historical Page Updates
Historical Page Updates is a content ranking signal that tracks how consistently a page is updated over time. Historical Page Updates is considered an on-page SEO and freshness signal, likely monitored within systems like Caffeine and Helpful Content. Pages that show a pattern of meaningful updates signal editorial oversight and long-term relevance. While not directly confirmed, SEO practitioners agree that Google favors content with a maintenance history over stagnant pages.
168. Content Aging and Decline
Content Aging and Decline is a content filter signal because outdated or underperforming content may lose its ranking over time. Content Aging and Decline is an on-page and temporal SEO signal confirmed within Google’s freshness and decay modeling systems. If content engagement metrics drop or information becomes outdated, its visibility will likely degrade.
169. Content Strategy Signal
Content Strategy Signal is a content ranking signal because consistently publishing in defined topical clusters improves semantic relevance and trust. Content Strategy Signal is an on-page SEO signal confirmed through Google’s Topical Authority system. Google favors sites that build structured topical coverage, reinforcing their expertise across interconnected entities and query themes.
170. Entity Type Matching (User Intent Alignment)
Entity Type Matching (User Intent Alignment) is a content ranking signal that evaluates whether a page’s structure and intent match the expected content type of the target entity (e.g., a recipe page for a food item, a review for a product). Entity Type Matching is an on-page SEO and semantic signal confirmed within Google’s Knowledge Vault and entity understanding systems. Google favors content that conforms to the standard structure and attributes associated with its entity class, which improves content clarity, schema alignment, and SERP eligibility.

171. Visual Content Alignment
Visual Content Alignment is a content ranking signal that measures how well images support the on-page text and reinforce topical clarity. Visual Content Alignment is an on-page SEO and image relevance signal, confirmed through Google’s Image AI systems. Pages where visuals semantically match headings, entities, or product mentions are more likely to be favored in both standard and image search. Aligned visual content improves UX metrics like time-on-page and scroll depth.
172. Conversational Page Tone
Conversational Page Tone is a content ranking signal that measures whether the writing style reflects natural, helpful, and user-friendly language. Conversational Page Tone is considered an on-page SEO and user experience signal, confirmed through systems like BERT and MUM. Pages that mirror real human phrasing (especially in FAQ, how-to, and YMYL content) perform better in mobile and voice search environments where intent matching depends on tone clarity.
173. FAQ Anchor Jump Links
FAQ Anchor Jump Links is a content ranking signal because jump links enable direct navigation from the SERP to a specific FAQ section of a page, improving user experience and CTR. FAQ Anchor Jump Links is an on-page SEO and SERP enhancement signal, confirmed by Google’s implementation of structured FAQ schema. Pages that support FAQ jump links increase visibility in the results and can secure more real estate with expandable answers in rich results.
174. Site-Wide Quality Distribution
Site-Wide Quality Distribution is a content penalty signal that measures how the quality of low-performing pages impacts the overall authority of a domain. Site-Wide Quality Distribution is an on-page SEO and domain-level trust signal, confirmed through the Helpful Content System. Google applies quality classifiers at the domain level, meaning thin, irrelevant, or duplicate content sections can harm rankings site-wide, even for strong pages.
175. Intent-Satisfying Snippet Content
Intent-Satisfying Snippet Content is a content ranking factor that evaluates how well a page snippet meets query intent directly in the SERP. Intent-Satisfying Snippet Content is an on-page SEO and user behavior signal, confirmed through RankBrain. Snippets that directly answer a user’s question improve click-through rate and signal relevance. Over time, these snippets receive preferential treatment in visibility and feature eligibility.
176. Internal Navigation UX
Internal Navigation UX is a content ranking signal that reflects how easily users can move across related pages within a site. Internal Navigation UX is an on-page SEO and entity graph signal, confirmed through Google’s UX modeling systems. Smart use of breadcrumbs, in-line contextual links, and nav menus helps users and bots explore related content, which improves crawl depth, time on site, and semantic connection signals used by Google’s indexers.
177. Query Deserves Freshness (QDF)
Query Deserves Freshness (QDF) is a content ranking signal that prioritizes recently updated or published content for time-sensitive searches. Query Deserves Freshness is an on-page SEO and intent-matching signal, confirmed through Google’s QDF system. For queries related to news, trends, or recent events, fresher content outranks older but otherwise authoritative pages to meet user expectations for recency.
178. Query Deserves Diversity
Query Deserves Diversity is a content ranking signal that triggers Google to display a broader range of perspectives or sources in SERPs. Query Deserves Diversity is an off-page SEO and user behavior signal, confirmed by Google. For ambiguous or controversial queries, Google intentionally surfaces results from varied domains to reflect multiple interpretations and avoid perceived bias.
179. Top Stories Box Eligibility
Top Stories Box Eligibility is a content visibility signal that determines whether a page can appear in Google’s “Top Stories” news carousel. Top Stories Box Eligibility is an on-page SEO and structured data signal, confirmed through Google News SEO and Search documentation. Content must meet quality, recency, and schema requirements to qualify. Eligibility improves visibility dramatically for newsworthy topics.
180. Gibberish Content Filter
Gibberish Content Filter is a content demotion signal that detects low-quality, nonsensical, or machine-generated text with no user value. Gibberish Content Filter is an on-page SEO signal through Panda and the Helpful Content Update. Pages lacking coherence or that appear algorithmically constructed face demotion in rankings.
181. Doorway Pages Penalty
Doorway Pages Penalty is a content demotion signal that penalizes pages created to rank for specific queries that funnel users to a different destination. Doorway Pages Penalty is an on-page SEO and spam signal, confirmed through Google’s Webmaster Guidelines. Doorway pages offer little unique value and violate Google’s goal of surfacing diverse, user-centric results.
182. Fred Penalty
Fred Penalty is a content demotion signal that targets thin, ad-heavy, low-value content primarily designed for monetization. Fred Penalty is an on-page SEO and spam filtering signal, confirmed through Google representatives and community analysis. Pages hit by this filter often prioritize affiliate links or ads over helpful information, resulting in ranking loss.
183. Autogenerated Content Penalty
Autogenerated Content Penalty is a content demotion signal that penalizes pages composed by scripts or tools without adding original value. Autogenerated Content Penalty is an on-page SEO and spam signal, confirmed through Google’s documentation. Content created with the primary intent of manipulating search rankings, without meaningful human review or refinement, is demoted or excluded from results.
184. Redundant Topic Pages Penalty
Redundant Topic Pages Penalty is a content demotion signal that flags websites that publish many low-quality pages on the same topic. Redundant Topic Pages Penalty is an on-page SEO and site structure signal, confirmed through Panda and Helpful Content updates. Google favors consolidated, high-value content over fragmented topic repetition, which can dilute topical authority and harm rankings.
Technical Factors
185. HTTPS Usage (Valid SSL)
HTTPS Usage is a technical SEO ranking factor and one of the top Google ranking factors because it ensures secure data transmission and aligns with Google’s Page Experience system. HTTPS Usage is classified as an on-page technical SEO signal and has been confirmed by Google since 2014. Sites without HTTPS may be flagged as “Not Secure” in Chrome and can be deprioritized in rankings. HTTPS for SEO is a prerequisite for eligibility in features like Top Stories on mobile.
186. Use of Structured Data (Schema Markup)
Use of Structured Data or Schema Markup is a technical SEO boost signal and one of the top Google ranking factors because it helps search engines better interpret page content and enables rich SERP features. Use of Structured Data is a semantic markup and ranking signal, confirmed through Google’s schema markup documentation. JSON-LD or microdata for entities like reviews, products, and FAQs can lead to enhanced visibility and snippet eligibility.
187. Internal Linking
Internal Linking is a technical SEO ranking factor and one of the top Google ranking signals because it shapes crawl behavior, distributes PageRank, and clarifies site structure. Internal Linking is classified as an on-page SEO and crawl optimization signal, confirmed by Google. When internal links are consistently implemented across relevant pages, they help Google understand content hierarchy, pass link equity effectively, and improve the discoverability of high-value pages.
188. XML Sitemap
XML Sitemap is a technical SEO ranking factor that helps search engines discover and index website pages more efficiently. XML Sitemap is a crawl and indexing signal, confirmed by Google. A properly configured sitemap improves crawl coverage and ensures important URLs are seen by Googlebot.

189. Robots.txt File
Robots.txt File is a technical SEO filter signal because it controls crawler access to specific parts of a website. Robots.txt File is a crawl control and indexing signal, confirmed through Google Search Central documentation. Misconfigured directives can block essential pages from being indexed.
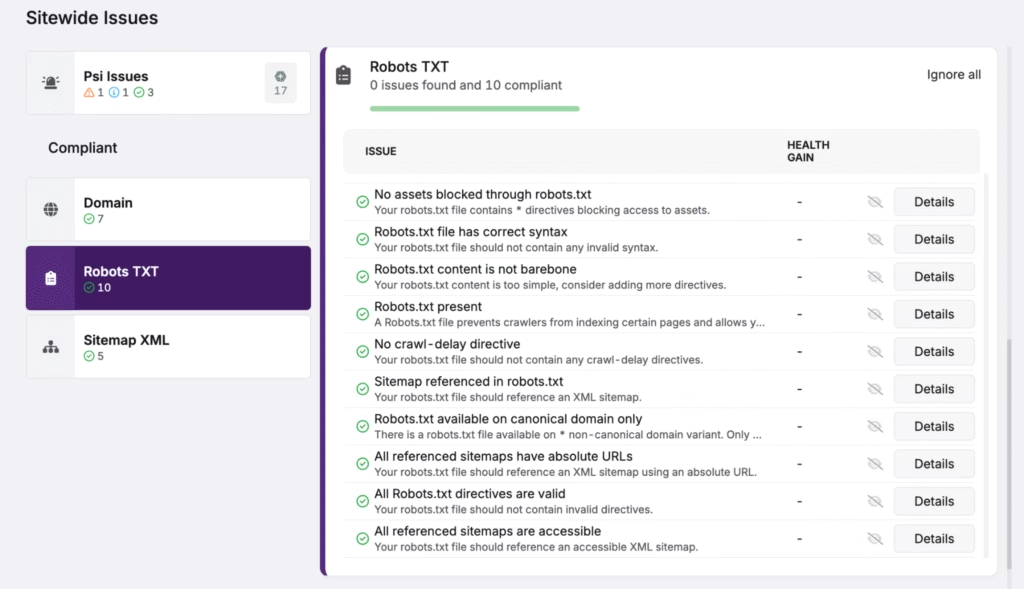
190. Canonical Tags
Canonical Tags are a technical SEO filter signal because they indicate which version of a URL should be considered the original. Canonical Tags are indexing and duplicate management signals, confirmed by Google. Proper use prevents duplicate content issues by consolidating link equity to the preferred page version.
191. Canonical Misuse
Canonical Misuse is a technical SEO filter signal that penalizes sites that implement incorrect, self-referencing, or circular canonical tags. Canonical Misuse is an on-page indexing signal confirmed by Google’s documentation and support threads. Pages with conflicting or broken canonicals may be excluded from the index or lose ranking eligibility, especially in duplicate content scenarios.
192. Mobile-Specific Canonicals
Mobile-Specific Canonicals is a technical SEO filter signal because mobile-specific URLs (e.g., m.example.com) require correct use of rel=canonical and rel=alternate tags to prevent duplication and misindexing. Mobile-Specific Canonicals is an on-page SEO and mobile indexing signal, confirmed in Google’s mobile-first indexing documentation. Improper configuration can lead to split signals or indexing errors across desktop and mobile versions.
193. URL Structure
URL Structure is a technical SEO ranking factor because clean, descriptive URLs are easier for users and search engines to interpret. URL Structure is a crawl and indexing signal, confirmed by Google. Short, keyword-rich URLs with minimal parameters improve crawlability and can enhance CTR in SERPs.
194. Breadcrumbs
Breadcrumbs are a technical SEO boost signal that clarifies site structure for users and search engines. Breadcrumbs are a structured data and UX signal, confirmed through Google’s SERP enhancement systems. Breadcrumbs can appear in search results as rich snippets and improve navigational clarity.
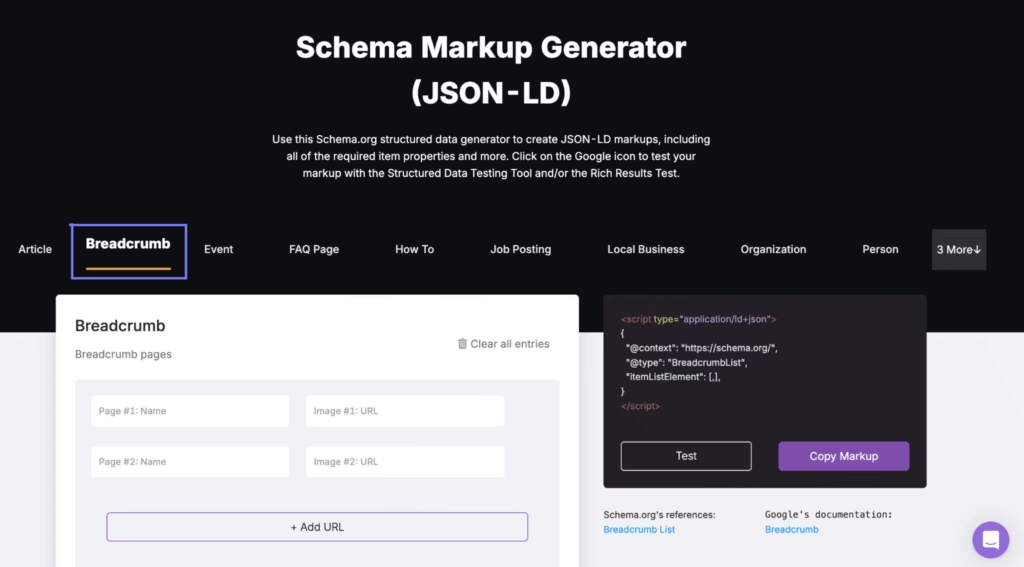
195. Site Architecture
Site Architecture is a technical SEO ranking factor that influences how search engines crawl and understand a website. Site Architecture is a crawl depth and content discoverability signal, confirmed by Google. Flat or logically siloed website structure improves internal equity flow and indexation of deeper pages.
196. Mobile Indexing Priority
Mobile Indexing Priority is a technical SEO ranking signal because Google uses the mobile version of a site as the primary content source for indexing and ranking. Mobile Indexing Priority is an on-page SEO and rendering system signal confirmed through Google’s Mobile-First Indexing rollout. Googlebot evaluates mobile layout, content, and performance first, and that makes mobile optimization critical for visibility across all devices.
197. Site Speed on Mobile Data
Site Speed on Mobile Data is a technical SEO ranking factor that evaluates how quickly a site loads on 3G/4G mobile networks. Site Speed on Mobile Data is a confirmed mobile performance signal used in Google’s Page Experience system. Google prioritizes fast-loading pages on slower mobile connections to improve usability for mobile-first indexing. Poor mobile load performance directly affects rankings, especially on mobile SERPs.
198. Duplicate Meta Tags
Duplicate Meta Tags are a technical SEO filter signal because repeated title and description tags confuse search engines and dilute relevance. Duplicate Meta Tags are an indexing and content clarity signal, confirmed in Google Search Console. Unique meta tags for SEO improve page identification and click-through performance.
199. Meta Robots Tag Usage
Meta Robots Tag Usage is a technical SEO filter signal because it determines whether a page is eligible for indexing or crawling. Meta Robots Tag Usage is classified as an on-page SEO and indexing control signal. When used correctly (e.g., “index, follow”), it grants Google permission to include the page in its index. Misconfigured tags (e.g., “noindex” on valuable pages) can block visibility entirely. Google confirms its use through documentation and indexing guidelines.
200. Disallowed JS/CSS in Robots.txt
Disallowed JS/CSS in Robots.txt is a technical SEO filter signal because it prevents Google from fully rendering and evaluating page content and layout. Disallowed JS/CSS in Robots.txt is an on-page SEO and rendering signal, confirmed by Google. Blocking essential resources in robots.txt can lead to layout and usability misjudgments, harming rankings under the Page Experience and Mobile-First indexing systems.
201. Pagination Markup (rel=next/prev)
Pagination Markup (rel=next/prev) is a technical SEO indexing signal because it historically guided how search engines handled paginated content. Pagination Markup is considered an on-page SEO signal related to crawl structure and indexing behavior. Although officially deprecated by Google in 2019, older implementations may still influence legacy systems or reinforce content sequencing patterns. Pagination SEO is confirmed historically through Google’s prior documentation and algorithm behavior.
202. Faceted Navigation Crawlability
Faceted Navigation Crawlability is a technical SEO filter signal because improperly managed filter and sort parameters can generate near-duplicate URLs and infinite crawl paths. Faceted Navigation Crawlability is classified as an on-page and site architecture signal, especially with big sites. Google confirms that unoptimized faceted navigation (without canonical tags, noindex rules, or parameter handling) can waste crawl budget and harm indexation quality. This is documented in Google’s guidelines for large-scale sites and ecommerce SEO architecture.
203. Crawl Error Rate
Crawl Error Rate is a technical SEO filter signal that reflects how often Googlebot encounters broken or unreachable URLs on a site. Crawl Error Rate is an on-page SEO and crawl trust signal, confirmed via Google Search Console. High crawl error rates reduce crawl efficiency and signal poor maintenance, which may lead to reduced indexation or delayed re-crawling.
204. Redirect Chains
Redirect Chains is a technical SEO filter signal because long chains of redirects degrade crawl efficiency and dilute link equity. Redirect Chains is classified as an on-page SEO and crawl budget factor. Google confirmed that excessive 301/302 redirects slow down crawlers, increase rendering complexity, and reduce the authority passed between pages.
205. Status Code Handling (3xx/4xx/5xx)
Status Code Handling is a technical SEO ranking signal because HTTP status codes influence how search engines crawl, index, and trust pages. Status Code Handling is an on-page SEO and server-side ranking signal, confirmed by Google documentation. Correct use of HTTP status codes like 200 for valid pages, 301/302 for redirects, and 404/410 for removed content maintains crawl efficiency. Repeated 5xx errors or inconsistent status codes lead to crawl demotion and indexing issues.
206. Soft 404 Handling
Soft 404 Handling is a technical SEO filter signal because serving a 200 OK status for pages that no longer exist misleads Googlebot. Soft 404 Handling is a confirmed index quality signal used in Google’s Search Console and indexing systems. When non-existent or low-value pages return 200 instead of 404 or 410, they dilute index quality, reduce crawl efficiency, and signal poor site management.

207. Custom 404 Page (Branded Helpful)
Custom 404 Page (Branded Helpful) is a technical SEO and user experience boost signal because it enhances navigation and retention when a user hits a broken link. Custom 404 Page implementation is an on-page SEO best practice and consensus-backed UX signal. While not a direct ranking factor, branded 404s that offer search boxes, navigation menus, or helpful links reduce bounce rates and help retain user trust.
208. Meta Refresh Redirects
Meta Refresh Redirects is a technical SEO penalty signal because it uses outdated browser-based redirection instead of server-level HTTP redirects. Meta Refresh Redirects are considered an on-page SEO and indexing filter, confirmed by Google’s indexing guidelines. Use of <meta http-equiv=”refresh”> with delay values can be penalized as it may be used to mislead or manipulate users and bots.
209. Robots.txt Redirects or Inaccessibility
Robots.txt Redirects or Inaccessibility is a technical SEO filter signal because redirecting or blocking access to robots.txt prevents Googlebot from understanding crawl rules. Robots.txt Redirects or Inaccessibility is confirmed in Google’s crawling documentation. When robots.txt returns a 3xx redirect, 404 error, or is blocked, Google may skip crawling important parts of the site or apply incorrect directives, hurting indexation and visibility.
210. Server Response Variability
Server Response Variability is a technical SEO filter signal because unstable TTFB (Time to First Byte) damages crawl reliability. Server Response Variability is an infrastructure-level signal confirmed in Google’s documentation on crawl health. Pages with inconsistent or slow server responses are crawled less often and may experience indexation delays.
211. JavaScript Rendering
JavaScript Rendering is a technical SEO filter signal because improperly rendered JavaScript can block Googlebot from accessing or understanding page content. JavaScript Rendering is an on-page SEO and rendering system signal, confirmed by Google. Google uses a second wave of rendering after crawling raw HTML. If essential content is hidden behind deferred JS or rendered too late, it may not be indexed or ranked.
212. JavaScript Content Preloading
JavaScript Content Preloading is a technical SEO boost signal that ensures dynamic or client-rendered content is available for indexing. JavaScript Content Preloading is an on-page SEO and rendering pipeline signal, confirmed through documentation on hydration, SSR, and indexing behavior. Proper preloading techniques help avoid content gaps in rendered HTML, especially for SPAs or JavaScript-heavy frameworks.
213. JavaScript Blocking Critical Content
JavaScript Blocking Critical Content is a technical SEO filter signal because content that fails to render due to JavaScript delays or client-side errors may not be indexed. JavaScript Blocking Critical Content is an on-page SEO and rendering signal, confirmed by Google’s rendering pipeline documentation. Googlebot relies on rendered HTML snapshots. If key elements aren’t loaded in time, they’re ignored.
214. Page Size in KB
Page Size in KB is a technical SEO filter signal because large HTML or resource payloads (>2MB) slow rendering and crawling. Page Size in KB is an on-page SEO and rendering signal, confirmed by Google PageSpeed Insights and Chrome UX reports. Bulky pages delay interaction and can fall outside crawl budget thresholds.
215. Content Compression
Content Compression is a technical SEO boost signal that improves data transfer by reducing file size during delivery. Content Compression (GZIP) is an on-page SEO and performance optimization signal, confirmed by Google. Proper compression (e.g., GZIP or Brotli) speeds up load times and enhances user experience, which indirectly benefits rankings.
216. Caching Headers (HTTP Cache Control)
Caching Headers (HTTP Cache Control) is a technical SEO boost signal that determines how browsers and crawlers store and reuse content. Caching Headers are an on-page SEO and performance control signal, confirmed in Google’s speed optimization guidelines. Well-configured caching reduces server load and improves performance for returning users.
217. Mixed Content Warnings
Mixed Content Warnings is a technical SEO filter signal because it penalizes HTTPS pages that load HTTP resources, undermining page security and user trust. Mixed Content Warnings is an on-page SEO and page experience signal, confirmed by Google’s HTTPS guidelines. Mixed content can prevent indexing, trigger browser warnings, and lower ranking eligibility.
218. Gated Content Handling
Gated Content Handling is a technical SEO filter signal because content hidden behind login walls or paywalls may not be indexed unless structured correctly. Gated Content Handling is considered an on-page SEO and structured content compliance signal, confirmed by Google’s Structured Data Guidelines. Pages that use paywall schema or data-nosnippet attributes transparently can still qualify for indexing and visibility in search results, but failure to implement them properly may lead to exclusion or ranking suppression.
219. Cookie Consent Behavior
Cookie Consent Behavior is a technical and user experience boost signal because cookie banners and consent prompts impact page usability, load speed, and perceived trust. Cookie Consent Behavior is an on-page SEO and UX signal, considered likely to influence user metrics like dwell time and bounce rate. Although not directly penalized, poor cookie implementation (e.g., covering content) can reduce engagement and ranking potential.
220. URL Parameter Handling
URL Parameter Handling is a technical SEO filter signal because improper use of tracking/session parameters can confuse canonicalization, dilute link equity, and inflate crawl budget. URL Parameter Handling is an indexing and canonicalization signal, confirmed in Google’s URL Parameter Handling documentation. Google sometimes overrides developer-defined canonicals when parameter logic is unclear or overly complex. This signal is confirmed by Google’s legacy parameter tool and indexing documentation.
221. TLS Certificate Authority Trust
TLS Certificate Authority Trust is a technical SEO boost signal because HTTPS certificates from reputable authorities support browser and crawler trust. TLS Certificate Authority Trust is an off-page SEO and security infrastructure signal, likely modeled within Chrome and Googlebot validation layers. Certificates from lesser-known or self-signed issuers may result in trust warnings or insecure site designations.
222. Geolocation Accuracy
Geolocation Accuracy is a technical SEO boost signal because Google uses geographic signals like server IP, ccTLDs, and hreflang to serve regionally appropriate results. Geolocation Accuracy is an off-page SEO and localization signal, confirmed by Google’s geo-targeting documentation. Proper geographic signals improve visibility in country-specific SERPs.
223. Hreflang Tags
Hreflang Tags are a technical SEO ranking signal that help Google serve the correct language or regional URL to international users. Hreflang Tags are a local SEO and global targeting signal, confirmed by Google. Proper hreflang tags implementation supports localization strategies and prevents duplicate content across country variants.
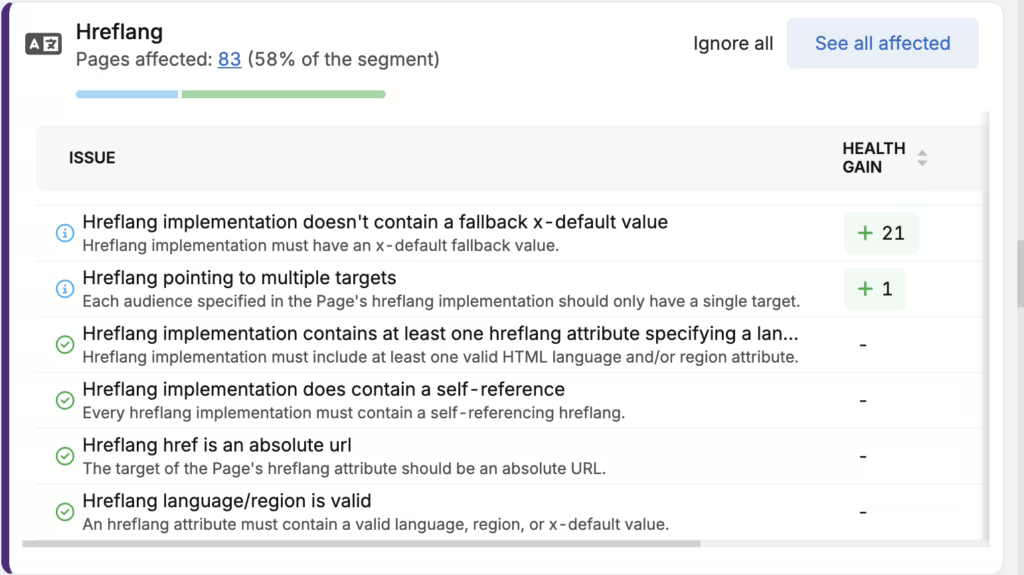
224. Country TLD Extension (ccTLD)
Country TLD Extension (ccTLD) is a technical SEO and authority signal that indicates a site’s regional targeting based on its top-level domain (e.g., .fr, .de, .ca). ccTLD is classified as an off-page SEO and trust localization signal, confirmed through Google’s geo-targeting documentation. While ccTLDs help improve rankings in country-specific SERPs, they can limit global visibility, as Google assumes the site is primarily relevant to users in that specific country unless it is configured otherwise in Search Console.
225. Mixed Language Signals
Mixed Language Signals is a technical SEO filter because Google may demote or misindex pages with multiple languages and no hreflang tags. Mixed Language Signals are part of international SEO and indexing filters. Google requires clear language targeting, and inconsistent language use without proper hreflang implementation can confuse crawling systems and reduce ranking in target regions.
226. Site Speed by Region
Site Speed by Region is a technical SEO filter signal because Google evaluates performance in specific geographies, especially for localized queries. Site Speed by Region is an off-page SEO and crawl distribution signal, confirmed via Google’s geo-distributed data centers and international crawling behavior. Slow response times in specific regions may reduce local ranking potential and limit crawl frequency.
227. Sitemap Indexing Ratio
Sitemap Indexing Ratio is a technical SEO filter signal that measures the proportion of submitted URLs in a sitemap that are actually indexed by Google. Sitemap Indexing Ratio is confirmed through Index Coverage reports in Google Search Console. A low ratio can indicate thin, duplicate, or low-quality content that fails Google’s indexing quality thresholds.
228. Sitemap Update Frequency
Sitemap Update Frequency is a technical SEO boost signal that informs search engines that a site is actively maintained and updated. Sitemap Update Frequency is an on-page SEO and index management signal, likely used within Google’s indexing systems. Regular sitemap refreshes signal to crawlers that content is fresh or changed, leading to more consistent crawling and faster index updates.
229. Critical Rendering Path Optimization
Critical Rendering Path Optimization is a technical SEO performance signal because it accelerates how quickly visible content appears on screen. Critical Rendering Path Optimization is an on-page SEO and performance layer signal, supported by Google’s PageSpeed Insights and developer documentation. Pages that optimize critical resources, such as fonts, CSS, and above-the-fold images, experience faster First Contentful Paint (FCP) and Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), improving UX and Core Web Vitals scores.
230. HTML Validation and Clean Code Structure
HTML Validation is a technical SEO quality signal because it ensures that a page’s source code follows proper syntax and structural rules. HTML Validation and Clean Code Structure is an on-page SEO and parsing signal. Clean HTML enables smoother interpretation by crawlers and reduces the risk of rendering or indexing errors. While not a direct ranking factor, poor code hygiene may disrupt Googlebot’s ability to parse page content or schema, especially in complex layouts or JS-heavy environments.
231. Presence of Performance Budget Enforcement
Performance Budget Enforcement is a technical SEO signal that reflects disciplined control over resource bloat and load times. Presence of Performance Budget Enforcement is an infrastructure and build pipeline optimization signal. Developers who set caps for total JS/CSS size, number of requests, or render-blocking scripts are more likely to produce lightweight, mobile-first websites. While not directly measured by Google, this practice supports better Core Web Vitals and crawl accessibility.
232. Use of HTTP/2 or HTTP/3 Protocols
Use of HTTP/2 or HTTP/3 is a technical SEO boost signal because it improves how data is transmitted between the server and the browser. Use of HTTP/2 or HTTP/3 is classified as an infrastructure-level and performance optimization signal. These modern protocols support multiplexing, header compression, and reduced latency, which enhance page speed and interactivity. While Google has not explicitly confirmed HTTP/2 or HTTP/3 as a direct ranking factor, faster-loading pages that use these protocols benefit indirectly through improved Core Web Vitals and crawl efficiency.
233. Use of Content-Type Headers
Use of Content-Type Headers is a technical SEO boost signal because it ensures that servers correctly label the format of delivered content (e.g., HTML, XML, JSON). Use of Content-Type Headers is a confirmed crawler signal. When content is mislabeled or lacks a proper content type, Googlebot may misinterpret or skip it, leading to rendering or indexing issues.
234. Accessibility Metadata
Accessibility Metadata is a technical SEO boost signal because semantic labels help both users and machines interpret content meaning. Accessibility Metadata is an on-page SEO and accessibility signal, confirmed via Google’s accessibility evaluation systems. Proper use of accessibility and SEO, like ARIA labels, role attributes, and alt text, improves clarity for assistive technologies and supports better semantic parsing by search engines.
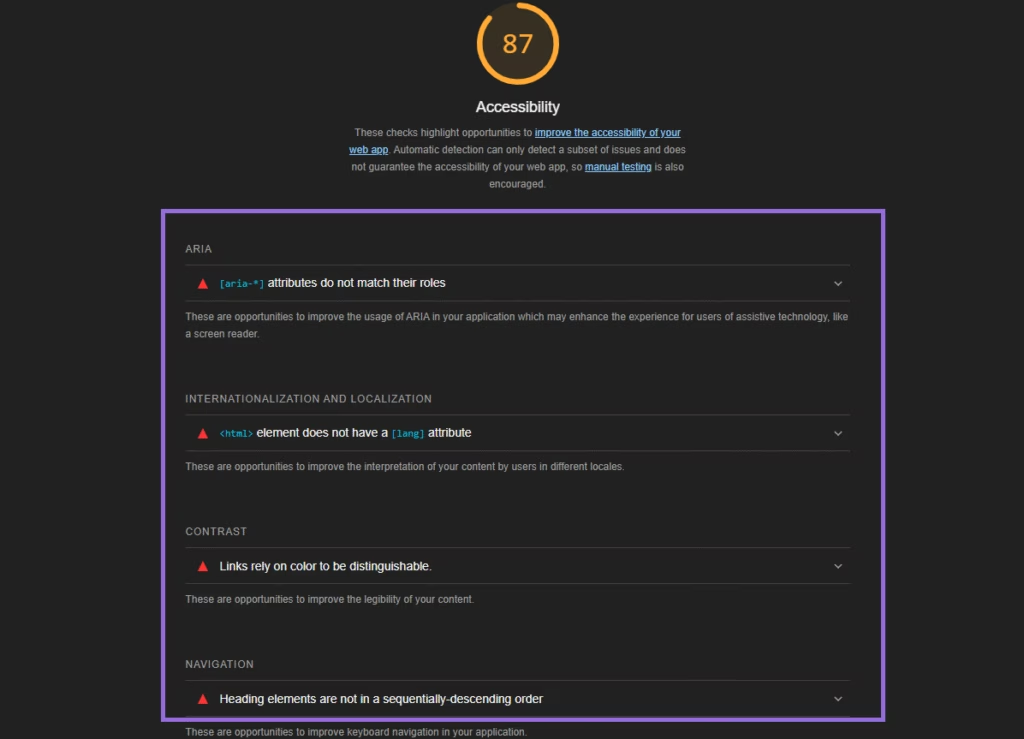
235. Mixed Protocol URLs
Mixed Protocol URLs is a technical SEO filter signal because the presence of HTTP links or assets on an HTTPS site introduces trust and rendering issues. Mixed Protocol URLs is an on-page SEO and security signal, confirmed by Google’s Page Experience standards. These mixed elements can degrade security perception, trigger browser warnings, and harm the indexing of affected resources.
236. Excessive Tracking Scripts
Excessive Tracking Scripts is a technical SEO filter signal because it negatively impacts page speed, user experience, and behavioral metrics. Excessive Tracking Scripts is classified as an on-page SEO and UX performance signal, supported by industry consensus and Google’s Core Web Vitals systems. Pages overloaded with ad networks, analytics tools, or retargeting scripts often experience slower load times, which can degrade user satisfaction, lower engagement, and reduce rankings indirectly through performance and UX signals.
237. Subdomain vs Subdirectory Structure
Subdomain vs Subdirectory Structure is a technical SEO ranking signal that affects how authority and context flow through the domain. Subdomain vs Subdirectory Structure is an on-page SEO and crawl graph signal, confirmed by Google. While Google claims it treats subdomains for SEO similarly to subdirectories, tests and leaked insights show that subdomains may be crawled and ranked separately, requiring stronger link signals to transfer authority.
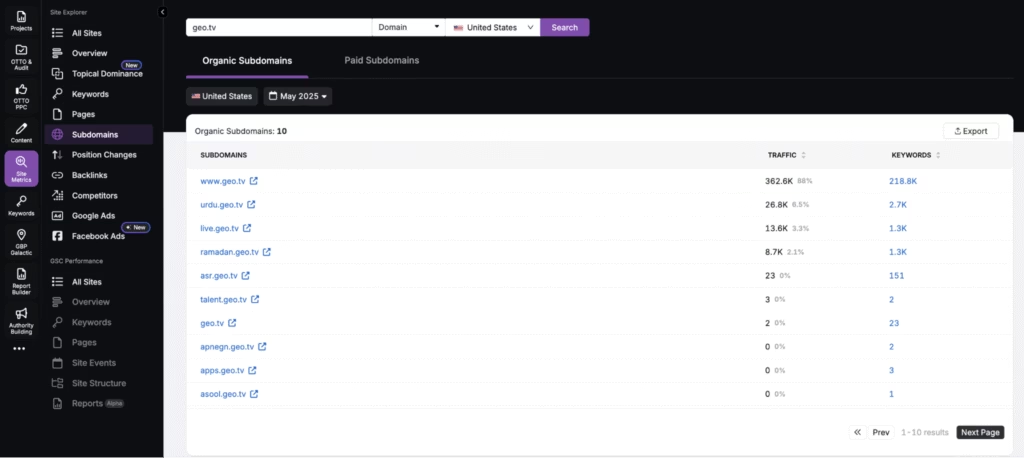
238. Orphan Pages
Orphan Pages is a technical SEO filter signal because pages not linked from any other crawlable location lose ranking ability. Orphan Pages are confirmed through Google’s Crawl Graph systems. Google treats unlinked pages as less important, harder to discover, and often devalues them in rankings due to a lack of contextual integration into the site structure.
239. Lazy Loading for Below-the-Fold Media
Lazy Loading for Below-the-Fold Media is a technical SEO performance signal that delays the loading of off-screen elements until users scroll, reducing initial load time. Lazy Loading is an on-page SEO and rendering optimization signal, confirmed through Google’s documentation. When implemented properly with native HTML loading=”lazy” attributes or JavaScript, lazy loading improves LCP and total page weight. However, incorrect setup (e.g., hiding content from bots) can prevent indexing.
240. Efficient Use of Preload, Prefetch, and Preconnect Tags
Preload, Prefetch, and Preconnect Tags are technical SEO boost signals because they prepare the browser for upcoming resources and reduce the delay in rendering key content. These tags are part of the performance and rendering pipeline signal group. Preload fetches important assets early (e.g., fonts), prefetch fetches resources for future navigation, and preconnect initiates early connections to third-party domains. When used correctly, these enhancements reduce Time to Interactive (TTI) and improve Core Web Vitals, indirectly aiding rankings.
241. Disallowed Scripts
Disallowed Scripts are a technical SEO penalty signal because iframe-based content or blocked third-party domains may raise security flags. Disallowed Scripts are an on-page SEO and Chrome/Safe Browsing signal, confirmed through Google’s developer policies. Use of malicious or privacy-violating script sources can trigger browser warnings or trust degradation, which may impact visibility.
242. Image Recognition Context
Image Recognition Context is a technical SEO boost signal because Google uses computer vision (e.g., via Vision API and MUM) to match image subjects to on-page topics. Image Recognition Context is an on-page SEO and image rendering signal, confirmed through Google’s visual search systems. Pages where image content semantically supports the written content are favored in visual SERPs and entity reinforcement.
243. Image ALT Text Semantics
Image ALT Text Semantics is a technical SEO boost signal because descriptive alt text enhances both accessibility and keyword relevance. Image ALT Text Semantics is an on-page SEO and accessibility signal, confirmed through Google’s Quality Rater Guidelines and Lighthouse reports. Alt text that describes entities or actions related to the page’s topic improves semantic clarity and indexing strength.
244. Video Transcripts
Video Transcripts are a technical SEO boost signal because they provide text-based context for video content, improving accessibility and search indexation. Video Transcripts are an on-page SEO and multimedia indexing signal, confirmed in Google’s indexing and accessibility documentation. Adding accurate transcripts allows Google to interpret the video’s content semantically, increasing its relevance for long-tail queries and enhancing visibility across video and universal search results.
245. Video Hosting Speed
Video Hosting Speed is a technical SEO performance signal because the source and speed of video delivery affect page experience scores. Video Hosting Speed is an on-page SEO and performance optimization signal, supported by Page Experience and Chrome UX data. Videos hosted on fast CDNs like YouTube perform better in loading benchmarks than large, self-hosted files, especially on mobile.
246. Domain Registration Signal
Domain Registration Signal is a technical ranking signal because registration age and expiration influence site trust. Domain Registration Signal is a technical SEO signal confirmed through the createdDate and expiredDate stored in document metadata.
247. Host Age Signal
Host Age Signal is a technical ranking signal because newer domains are sandboxed to filter low-trust or spammy sources. Host Age Signal is a technical SEO signal confirmed through the hostAge field under PerDocData.
248. YMYL Classification Signal
YMYL Classification Signal is a technical ranking signal because Google treats sensitive topics with stricter quality thresholds. YMYL Classification Signal is a technical SEO signal confirmed through attributes like ymylNewsScore and encodedChardXlqYmylPrediction.
249. Personal Site Signal
Personal Site Signal is a technical ranking signal because small personal blogs may receive differential treatment during re-ranking. Personal Site Signal is a technical SEO signal confirmed through the small Personal Site score used in promotion/demotion.
250. Gold Standard Document Signal
Gold Standard Document Signal is a technical ranking signal because human-labeled examples improve system learning and evaluation. Gold Standard Document Signal is a technical SEO signal confirmed through the golden field that distinguishes labeled pages.
By aligning your SEO strategy with the Search Atlas Holistic SEO pillars, you can better meet Google’s expectations and improve your chances of ranking higher in 2025 and beyond.
Catch Manick Bhan (Founder of Search Atlas and LinkGraph) on a podcast as he explains how the XACT framework turns thousands of Google ranking signals into four actionable SEO pillars for a more focused and holistic SEO strategy.
How Google Uses Ranking Factors to Rank Results in SEO
Google uses ranking factors to rank results in SEO by combining signals across content, authority, user experience, and technical performance to determine the most relevant documents for a query. The Google ranking algorithm retrieves and evaluates indexed pages based on factors like keyword relevance, link signals, content freshness, click behavior, and site quality. Google search ranking factors are processed across hundreds of systems and include page-level, domain-level, and session-level inputs. In the SEO ranking process, Google applies weighting to each signal in real time to serve ranked results that match the searcher’s intent.
How Do Google’s Special Algorithm Rules Impact SEO Rankings?
Google’s special algorithm rules impact SEO rankings by applying exception-based filters that override standard ranking systems to manage specific query types, content categories, or abuse patterns. Google’s special algorithm rules are part of the broader Google algorithm for SEO but function as conditional adjustments triggered in limited cases.
Examples of Google’s special algorithm rules include the Exact Match Domain (EMD) update, which demotes low-quality sites using keyword-stuffed domain names, and the DMCA penalty, which reduces visibility for domains with valid copyright violations. Other rules like Query Deserved Freshness (QDF) temporarily boost new content during trending events, while the Top Heavy algorithm penalizes ad-heavy layouts. Special algorithm rules ensure that Google SEO rankings reflect situational fairness, legal compliance, and user trust.
What Is the Relation Between Google Ranking Factors and Google Algorithm Updates?
The relation between Google ranking factors and Google algorithm updates lies in the shifting weight, interpretation, or introduction of new signals during update cycles. Algorithm updates like Helpful Content or Product Reviews refine how existing signals (such as content originality, site authority, or click satisfaction) are scored. Other algorithm updates introduce new ranking systems or demotions.
Although updates may not replace ranking factors, they recalibrate which signals matter more for specific query classes, content types, or industries. Google SEO factors evolve with Google Algorithm Updates to reflect changes in user expectations, spam tactics, and technical innovations in search.
How do Google’s Spam Updates impact SEO Ranking Factors?
Google’s spam updates impact SEO ranking factors by demoting websites that exhibit manipulative or deceptive behaviors in content, links, and technical implementation. Google’s spam updates use systems like SpamBrain to detect unnatural link patterns, low-quality AI-generated content, anchor mismatches, and site-level trust issues.
Spam-related demotions affect the on-page and off-page SEO signals and reduce visibility for pages that violate Google’s spam policies. Sites penalized by spam updates lose the ranking strength of otherwise legitimate signals until trust is reestablished through quality improvements.
What to Know About Google Ranking Factors Besides Google E-E-A-T?
Google ranking factors and E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) work together, but serve different purposes in SEO evaluation. Ranking factors determine how a page ranks, while E-E-A-T helps assess whether it deserves to rank, especially for sensitive queries.
While Google ranking factors include signals like page speed, backlinks, and query relevance, E-E-A-T is not a single factor but a quality framework used in Google’s Search Quality Evaluator Guidelines and reinforced through systems like Qstar and Page Quality scoring. E-E-A-T adds a layer of credibility and quality assessment, especially for YMYL (Your Money or Your Life) content.
Google uses E-E-A-T signals to evaluate the source and accuracy of content, using data from structured author markup, entity associations, site trust, and external citations. Content that ranks well typically satisfies the technical signals of Google SEO guidelines and the ranking factors, and the credibility layer introduced by Google E-E-A-T.