Large Language Models are AI systems trained to understand, generate, and reason over human language at scale. Large Language Models process text, structure meaning, and produce responses by learning patterns across large datasets rather than following static rules. Large Language Models act as the primary interface between human intent and machine output, which positions language as the control layer of modern digital systems.
Large Language Models matter because discovery, customer interaction, and decision-making increasingly occur through AI-generated language rather than traditional interfaces. Businesses now compete inside generated answers rather than ranked pages, which shifts visibility and authority into environments governed by how models retrieve and synthesize information.
LLM Optimization defines how businesses adapt to this shift by aligning content, structure, and data with how language models operate. Businesses gain advantage by optimizing for Large Language Models because optimization strengthens authority, protects reputation, and increases engagement inside conversational and AI-driven discovery flows.
Optimizing for Large Language Models requires structured content, explicit definitions, and topical coverage that match how models retrieve and generate language. This execution defines digital visibility in AI-mediated environments.
What Are Large Language Models (LLMs)?
Large Language Models (LLMs) are artificial intelligence (AI) systems trained on massive volumes of text and code to understand, generate, and evaluate human language. LLMs connect statistical learning with linguistic structure, which moves language processing from rule-based systems to adaptive language intelligence.
LLMs govern how modern digital systems interpret queries, compose responses, and structure language-based interactions. LLMs translate human intent into machine-readable outputs instead of relying on predefined templates or rigid syntax rules.
What are the most common Large Language Models? The most common LLMs include GPT, Claude, Gemini, Grok, DeepSeek, Mistral, and Qwen. These models define how language intelligence operates across consumer platforms, enterprise systems, and custom deployments.
What do Large Language Models optimize in language-driven systems? LLMs optimize how language becomes predictable, coherent, and contextually aligned during generation. LLMs focus on contextual consistency, linguistic coherence, and prompt alignment so outputs remain usable across different tasks and formats.
What do Large Language Models produce? Large Language Models produce language-based outputs that follow user prompts and supplied context. These outputs range from short factual responses to long-form explanations, instructions, and formatted data.
This execution layer explains why language generation now replaces static interfaces across digital systems. LLM behavior therefore defines how information becomes accessible, actionable, and reusable inside modern platforms.
How Do LLMs (Large Language Models) Work and Process Information?
Large Language Models work and process information by learning statistical language patterns from large-scale text and generating responses through probabilistic prediction. This execution model explains how LLMs work and why it produces context-aware outputs instead of returning predefined responses.
What do Large Language Models process? Large Language Models process natural language, code, and structured formats to perform language-driven tasks. These tasks include question answering, translation, summarization, and classification. This behavior relies on patterns learned from large datasets rather than explicit instructions.
How do modern Large Language Models operate internally? Large Language Models operate through deep learning systems built on transformer neural networks. These systems allow the model to understand how words relate to each other across long pieces of text.
What are the core components of transformer models? Transformer models use encoders and decoder components. The encoder reads and interprets input text, while the decoder produces the final response.
The 6 main stages that define how Large Language Models work and process information are listed below.
- Learn from large-scale training data. Large Language Models study massive collections of text from books, websites, and documents. This exposure builds vocabulary, grammar, and basic knowledge that shape how the model understands new inputs.
- Convert text into internal representations. Large Language Models transform words into numerical forms that the system analyzes. This transformation allows the model to compare meanings and detect relationships between terms.
- Build meaning through layered processing. Large Language Models pass information through multiple internal layers that gradually refine raw text into structured meaning and intent.
- Preserve context across long text. Large Language Models track how words relate to each other across sentences and paragraphs. This tracking allows the model to stay consistent within long conversations or documents.
- Generate responses through probability. Large Language Models select each part of the response based on what is most likely to follow given the context. This selection explains why responses appear fluent without pulling from a fixed database.
- Adapt behavior through tuning and prompting. Large Language Models adjust how they respond based on training refinements and user prompts. This adjustment allows one model to perform tasks like translation, summarization, and question answering.
Large Language Models process information through a continuous loop that turns raw text into internal understanding and back into readable language. This loop explains how LLMs transform unstructured input into usable responses rather than retrieving stored facts.
What Does Large Language Models Optimization Mean?
Large Language Model Optimization means improving how LLMs operate and how content interacts with them. LLM Optimization ensures that generated outputs remain accurate, efficient, and usable across real-world applications. This definition covers both system performance and content compatibility inside AI-driven environments.
LLM Optimization operates across model refinement and content alignment. Model refinement improves how the system runs by reducing computation cost, which increase response speed, and stabilizes output quality. Content alignment structures information so LLMs retrieve, interpret, and reuse it with higher precision, which increases consistency and reduces factual drift in generated answers.
What does Large Language Model Optimization affect in practice? AI systems now depend on LLMs to generate responses across search engines, assistants, and enterprise platforms. LLM Optimization determines whether these systems produce grounded answers at scale or propagate inconsistent and biased outputs.
As LLM usage expands, Large Language Model Optimization becomes central to maintaining low operational cost, high factual stability, and sustained trust in AI-generated responses. This execution positions LLM Optimization as a control layer for AI reliability.
Do Businesses Really Need to Optimize for LLM Citations or Visibility?
Yes, businesses need to optimize for LLM citations and visibility because AI-driven systems increasingly mediate how users discover and evaluate information. As AI replaces link-based navigation with synthesized answers, brands compete for inclusion inside responses rather than position on a results page.
Optimization determines whether a brand becomes part of the information layer that AI systems reuse when answering questions. LLMs favor sources that demonstrate topical authority, entity clarity, and factual stability, which means brands without optimization remain excluded regardless of traditional search presence.
Visibility inside LLM responses influences brand perception before any website visit occurs. LLM visibility shapes how AI describes a brand across answers and summaries. Brands that ignore this visibility lose narrative control to competitors and secondary sources.
What Benefits Do Businesses Gain from Optimizing for Large Language Models (LLMs)?
The key benefits of optimizing for Large Language Models are stronger AI visibility, higher response trust, and greater operational control over AI-generated outputs. These benefits affect how brands appear in AI answers, how users evaluate credibility, and how AI-driven demand forms.
The 7 key benefits that businesses gain from optimizing for LLMs are listed below.
- Increases visibility inside AI-generated answers. LLM Optimization positions brand information inside responses produced by systems (ChatGPT, Gemini, and Perplexity). This placement ensures that brands appear at the moment users receive synthesized information rather than after a search click.
- Strengthens trust through AI-level validation. LLM Optimization aligns content and authority signals. AI systems then select a brand as a reliable source. This selection reinforces credibility because users interpret AI-cited sources as pre-validated by the system.
- Improves control over how brands are described by AI. LLM Optimization influences how AI systems summarize products, services, and expertise. This influence reduces the risk of inaccurate or fragmented brand narratives inside generated responses.
- Preserves visibility in zero click AI-environments. LLM Optimization keeps brands present even when users do not visit websites. This presence protects demand generation as conversational and answer-driven search replaces traditional result pages.
- Increases demand quality from AI-driven discovery. LLM Optimization surfaces brands when users ask direct questions with defined intent. These appearances attract users already seeking solutions, which increases lead quality even when traffic volume decreases.
- Reduces cost and latency of AI-powered interactions. LLM Optimization improves how efficiently AI systems generate responses tied to a brand. This efficiency lowers infrastructure cost while improving response speed across AI-driven touchpoints.
- Strengthens governance and output safety. LLM Optimization enables tighter control over tone, compliance, and factual boundaries inside generated outputs. This control reduces reputational risk and regulatory exposure in AI-driven communication.
These benefits occur because LLM Optimization positions brands and systems inside AI-generated decision layers rather than relying on page visits to communicate value.
How Can Businesses Optimize Themselves to Be Cited by Large Language Models (LLMs)?
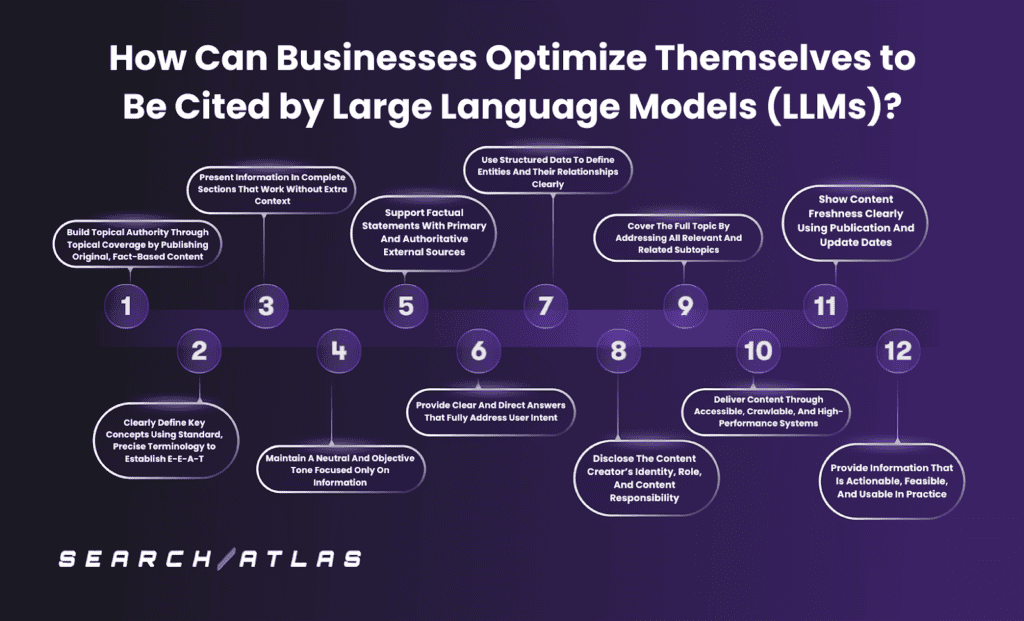
Businesses optimize their presence for Large Language Models by aligning content creation, information structure, and technical delivery with how LLMs select, reuse, and cite sources. LLMs prioritize semantic relevance, entity clarity, and factual consistency when generating responses. Effective optimization increases citation, reuse, and influence inside AI-generated answers rather than visibility in link based search results.
The 12 methods for businesses to optimize their presence for Large Language Models are listed below.
- Publish original, fact based content that demonstrates topical authority.
- Define key concepts using precise and standardized terminology.
- Organize information into complete sections that remain clear without external context.
- Maintain a neutral and objective tone focused on information accuracy.
- Support factual statements with primary and authoritative external sources.
- Provide direct answers that fully resolve user intent.
- Implement structured data to define entities and their relationships clearly.
- Disclose content authorship, role, and accountability transparently.
- Cover the full topic scope by addressing all relevant and related subtopics.
- Deliver content through accessible, crawlable, and high performance systems.
- Signal content freshness using clear publication and update dates.
- Present information in actionable formats that enable real world use.
1. Build Topical Authority Through Topical Coverage by Publishing Original, Fact-Based Content
Building topical authority through original, fact-based coverage ensures that Large Language Models treat a brand as a reliable reference when generating answers. LLMs prioritize, summarize, and reuse information from sources that demonstrate consistent accuracy and subject depth across multiple contexts. Content that presents verifiable metrics, primary data, and documented case studies provides stable material that reinforces topical authority when AI systems extract and cite information inside generated responses. A practical execution involves organizing content into topical clusters supported by original data and real-world examples that remain valid when extracted and reused by AI systems.
2. Clearly Define Key Concepts Using Standard, Precise Terminology to Establish E-E-A-T
Clearly defining key concepts using precise, standard terminology ensures that Large Language Models interpret and represent a brand without ambiguity. LLMs reduce hallucination risk by favoring sources that express concepts through widely accepted definitions and consistent language. A business that demonstrates semantic depth through accurate terminology and structured definitions strengthens E-E-A-T by becoming a safe reference point for AI-generated explanations. A functional approach creates glossary hubs and definition sections that associate the brand with authoritative use of those terms.
3. Present Information In Complete Sections That Work Without Extra Context
Presenting information in complete, self-contained sections ensures that Large Language Models extract and reuse information without requiring surrounding context. LLMs frequently retrieve modular text blocks that directly resolve a query rather than full pages, which makes section independence a primary citation factor. Section design that pairs a clear heading with a full answer and supporting detail produces extraction-ready material for AI systems. A practical execution involves structuring each section so it answers one question fully within 3 to 5 sentences that remain clear when read in isolation.
4. Maintain A Neutral And Objective Tone Focused Only On Information
Maintaining a neutral and objective information-focused tone increases the likelihood that Large Language Models treat a source as citation-worthy. LLMs prioritize sources that present factual, descriptive language without promotional framing or emotional bias because these sources reduce hallucination risk. Neutral phrasing combined with precise terminology signals expertise and reliability to AI systems. A functional approach involves rewriting claims as verifiable statements supported by data rather than persuasive or subjective phrasing.
5. Support Factual Statements With Primary And Authoritative External Sources
Supporting factual statements with primary and authoritative sources ensures that Large Language Models associate a brand with verifiable knowledge. LLMs select references that trace back to high-credibility materials (original research, government publications, and academic institutions) because these sources stabilize generated answers. Direct linkage to these sources transfers trust when AI systems reuse the information inside generated responses. A practical execution involves citing original studies and official data whenever introducing statistics, benchmarks, or technical claims.
6. Provide Clear And Direct Answers That Fully Address User Intent
Providing clear and direct answers that fully address user intent ensures that Large Language Models select a source as the primary response rather than a partial reference. LLMs prioritize content that resolves a question completely within a single block instead of distributing the answer across multiple fragments. Complete resolution reduces ambiguity and increases reuse inside generated responses. A functional approach involves opening each section with a definitive answer that satisfies the core intent before expanding into supporting explanation.
7. Use Structured Data To Define Entities And Their Relationships Clearly
Using structured data to define entities and their relationships ensures that Large Language Models interpret content through explicit meaning rather than inferred context. LLMs rely on machine-readable signals to construct knowledge graphs and validate how concepts relate to one another. Clear entity definitions and relationship mapping increase extraction accuracy and reduce misinterpretation. A practical execution involves implementing structured data that specifies what each entity is and how it connects to others within the topic.
8. Disclose The Content Creator’s Identity, Role, And Content Responsibility
Disclose content creator identity, role, and accountability to ensure that Large Language Models associate information with a verifiable and authoritative source. LLMs favor content linked to clearly defined entities because this linkage enables credibility assessment and traceability. Transparent authorship reduces the likelihood that AI systems classify content as anonymous or unreliable. A functional approach attaches visible author profiles, credentials, and organizational responsibility to each published piece.
9. Cover The Full Topic By Addressing All Relevant And Related Subtopics
Covering the full topic by addressing all relevant and related subtopics ensures that LLMs recognize a source as semantically complete rather than fragmentary. LLMs prioritize semantic depth and contextual breadth over isolated keyword usage because they map knowledge through topic relationships rather than page-level signals. Full coverage reduces the likelihood that AI systems replace a source with partial or competing references. This coverage aligns with the Applications of LLM across search, assistants, and enterprise systems, where models require comprehensive context. A practical approach organizes content into topic clusters that span foundational concepts, advanced implications, and common misconceptions within a single subject area.
10. Deliver Content Through Accessible, Crawlable, And High-Performance Systems
Delivering content through accessible, crawlable, and high-performance systems ensures that Large Language Models discover, interpret, and trust the information before reuse. LLMs depend on clean, reliably delivered content because inaccessible or unstable systems prevent extraction and validation. Technical barriers block inclusion regardless of content quality. A practical execution involves serving content through semantically structured HTML, which maintains crawl access for AI agents, and ensures fast, reliable delivery across devices.
11. Show Content Freshness Clearly Using Publication And Update Dates
Showing content freshness clearly using publication and update dates ensures that Large Language Models associate information with current and reliable knowledge. LLMs favor recent and maintained sources because outdated information increases response risk and reduces user trust. Temporal clarity allows AI systems to evaluate relevance during retrieval and synthesis. A functional approach involves displaying visible publication dates, updating timestamps, and maintaining a regular content revision cycle for high-impact pages.
12. Provide Information That Is Actionable, Feasible, And Usable In Practice
Providing information that is actionable, feasible, and usable in practice ensures that Large Language Models select a source not only for reference but for direct problem solving. LLMs prioritize content that translates abstract information into steps, conditions, and outcomes because this format enables AI systems to generate responses that users apply immediately. Practical information increases reuse because AI systems favor sources that resolve real tasks rather than describe concepts in isolation. A functional approach involves presenting guidance in clear sequences, supported by concrete data and constraints that remain valid when extracted into AI-generated answers.
What Are the Key Applications of Large Language Models?
Large Language Models operate across structured, repeatable applications that convert language intelligence into operational value across business systems. These applications transform how organizations create content, process information, and automate knowledge-driven workflows.
There are 8 main applications of Large Language Models.
1. Copywriting. Copywriting applies Large Language Models to generate persuasive, on-brand text across digital channels. This application accelerates marketing execution by producing consistent messaging for websites, social platforms, and campaigns.
2. Knowledge base answering. Knowledge base answering uses Large Language Models to retrieve and explain information from structured and unstructured sources. This application improves customer support and internal knowledge access by delivering grounded, context-aware answers.
3. Text classification. Text classification applies Large Language Models to categorize content by intent, sentiment, and topic. This application improves moderation, filtering, and analytics by interpreting context rather than relying on keyword rules.
4. Code generation. Code generation applies Large Language Models to write, debug, and translate software. This application increases developer productivity by accelerating routine coding and reducing error resolution time.
5. Text generation. Text generation applies Large Language Models to produce articles, reports, and communications. This application enables scalable content production while maintaining linguistic consistency.
6. Language translation. Language translation applies Large Language Models to convert content across languages with contextual accuracy. This application enables global communication by preserving meaning rather than performing literal substitution.
7. Conversational AI. Conversational AI applies Large Language Models to create context-aware interactions in chat and voice systems. This application replaces scripted responses with adaptive dialogue.
8. Education and research. Education and research apply Large Language Models to support tutoring, analysis, and content synthesis. This application accelerates learning and insight generation across academic and enterprise environments.
What Processes and Techniques Are Used to Train Large Language Models?
Large Language Models train through controlled learning pipelines that transform raw text into predictive language systems capable of reasoning and generation. These pipelines determine how models acquire linguistic knowledge, follow instructions, and adapt to human preferences.
There are 3 main training stages that shape Large Language Models.
1. Pre-training. Foundational learning exposes models to large-scale text collections so models internalize vocabulary, grammar, and semantic relationships. This stage builds general language competence by learning statistical patterns across diverse domains.
2. Task and instruction adaptation. Task and instruction adaptation adjusts model behavior for specific use cases such as summarization, translation, and question answering. This stage relies on curated examples that teach models how to respond in structured and purposeful ways.
3. Behavioral alignment with human feedback. Behavioral alignment tunes model outputs to match human expectations for safety, usefulness, and tone. This stage uses preference signals to discourage harmful or misleading responses and reinforce desired behavior.
There are 5 enabling techniques that support these stages.
1. Sequence-based neural architectures. Sequence-based neural architectures allow models to process entire text sequences and capture long-range dependencies.
2. Subword representation. Subword representation converts text into manageable computational units that preserve meaning across languages and domains.
3. Context weighting mechanisms. Context weighting mechanisms determine which parts of a sequence influence each prediction most strongly.
4. Lightweight adaptation methods. Lightweight adaptation methods update limited model components to reduce training cost and deployment complexity.
5. External knowledge integration. External knowledge integration connects models to reference sources that improve factual accuracy and updateability.
How Does Large Language Model Optimization Differ from General AI Optimization?
Large Language Model Optimization differs from General AI Optimization by focusing on language behavior rather than system performance. Large Language Model Optimization controls how language models interpret, generate, and apply text-based information, while GEO controls how generative AI systems retrieve, summarize, and cite digital content. This distinction separates language execution from content visibility inside AI-generated answers.
What does Large Language Model Optimization optimize? Large Language Model Optimization structures how language-based systems generate accurate, coherent, and reusable text outputs. This optimization focuses on prompt design, data quality, and contextual structure that govern how a language model processes and produces information.
What does GEO optimize? GEO structures digital content so AI search platforms retrieve, interpret, and cite information reliably. This optimization focuses on entity clarity, factual consistency, and semantic structure that determine how brands appear inside AI-generated summaries.
Large Language Model Optimization exists to refine how AI systems understand and express language, while GEO exists to control how AI systems represent brands and information publicly. Large Language Model Optimization improves language behavior inside models, while GEO controls visibility and authority inside generative search environments.
Does Optimizing for One Large Language Model Improve Visibility Across Other Models?
Yes, optimizing for one Large Language Model improves visibility across other models because most LLMs prioritize the same core signals of structure, clarity, and factual reliability. These systems evaluate how information is organized, how entities are defined, and how consistently facts appear across sources.
Optimization improves cross-model visibility by aligning content with shared retrieval and generation patterns used by language models. LLMs extract information based on semantic relevance, entity consistency, and contextual completeness, which makes improvements transferable across platforms (ChatGPT, Gemini, and Perplexity).
Cross-model impact occurs because LLMs learn from overlapping training data and apply similar selection logic during answer generation. Content that remains clear, verifiable, and well-structured performs reliably even when models differ in architecture or deployment environment.
How Can Businesses Integrate LLM Optimization with SEO and Content Strategies?
Businesses integrate LLM Optimization with SEO and content strategies by aligning how content is created, structured, and distributed with how AI systems retrieve and generate information. This integration shifts optimization from keyword placement toward topic authority, entity clarity, and answer-level relevance.
How does LLM Optimization strengthen SEO performance? LLM Optimization strengthens SEO by prioritizing topic coverage and contextual completeness rather than isolated queries. This approach improves both traditional rankings and AI-based selection because search engines and AI systems evaluate relevance through semantic relationships rather than keyword frequency.
How do content strategies adapt to LLM Optimization? Content strategies adapt by structuring information in conversational, question-driven formats that resolve user intent directly. These formats improve extractability for AI systems while preserving usability for human readers.
What role does Technical SEO play in this integration? Technical SEO supports this integration by ensuring content remains accessible, crawlable, and machine-readable. Schema, clean HTML structure, and performance optimization allow search engines and AI systems to interpret and trust the same content layer.
This integration ensures that SEO performance and AI visibility reinforce each other rather than compete for different optimization priorities.
Which Types of Content and Data Structures Improve LLM Optimization Results?
There are 3 content and data structure types that improve LLM Optimization results are factual authority, extractable structure, and contextual completeness. LLMs select sources based on reliability, machine readability, and semantic clarity rather than format popularity.
How does factual authority influence LLM selection? Factual authority determines whether content provides verified, original, and domain-specific information that AI systems reuse safely. High-authority sources (official documentation, original research, and detailed technical) references because these materials reduce hallucination risk during answer generation by anchoring outputs in verifiable facts.
How does extractable structure affect AI reuse? Extractable structure determines how easily AI systems isolate and reuse information from a page. Clearly defined sections, tables, and question-driven blocks improve extraction accuracy because LLMs retrieve information in modular segments rather than full documents.
How does contextual completeness improve response quality? Contextual completeness determines whether a source resolves a topic fully within its scope rather than addressing isolated fragments. Comprehensive guides, structured FAQs, and interlinked subtopics increase reuse frequency because AI systems favor sources that resolve intent without requiring additional references.
These 3 factors define LLM Optimization effectiveness by showing whether content is safe to reuse, easy to extract, and sufficient to resolve user intent inside AI-generated answers.
How Long Does It Typically Take for a Business to See Results from LLM Optimization?
A business typically sees early LLM Optimization results within 2 to 12 weeks, while consistent AI-driven returns form over 4 to 6 months. Early results reflect initial model alignment and content readiness, while long-term results reflect repeated selection and reuse inside AI-generated responses.
What happens during the first 2 to 12 weeks of LLM Optimization? The first 2 to 12 weeks produce measurable improvements in content extractability and AI visibility because AI systems begin recognizing structured, aligned sources. These early signals confirm that content entered the AI retrieval and generation layer.
What happens during the next 4 to 6 months of LLM Optimization? The next 4 to 6 months increase response consistency and citation frequency because AI systems test reliability across related prompts. Repeated reuse strengthens visibility and stabilizes return from AI-driven discovery.
Why does LLM Optimization require sustained time rather than instant results? LLM Optimization requires sustained time because AI systems validate accuracy through repetition and cross-context agreement. Performance stabilizes only after the same sources appear across multiple independent answer scenarios.
What Common Pitfalls Reduce a Business’s Visibility in Large Language Models?
The most common LLM visibility pitfalls that reduce a visibility of a business are weak entity consistency, low machine readability, missing trust signals, keyword-centric content strategies, and limited digital presence. These pitfalls reduce visibility because Large Language Models select sources based on clarity, authority, and cross-source validation rather than keyword placement or page volume.
How does weak or inconsistent entity recognition reduce LLM visibility? Inconsistent brand names, descriptions, or contact details fragment how AI systems recognize a business across sources. This fragmentation prevents LLMs from confidently associating content with a single authoritative entity and lowers citation likelihood.
Why does low machine readability reduce LLM visibility? Content that lacks clear summaries, headings, and extractable structures becomes difficult for AI systems to parse and reuse. Information that does not resolve intent in modular blocks remains excluded from AI-generated answers.
How do missing trust signals reduce LLM visibility? Absence of clear authorship, outdated information, and lack of third-party validation weaken credibility assessment inside AI systems. LLMs deprioritize sources that do not demonstrate Expertise, Experience, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness consistently.
Why does over-optimizing for traditional SEO reduce LLM visibility? Content designed around keyword density rather than semantic clarity appears artificial to AI systems. LLMs favor natural language explanations and contextual completeness over repetitive keyword patterns.
How does a limited digital presence reduce LLM visibility? Brands that appear only on their own websites lack the repetition required for AI systems to confirm authority. Sparse mentions across forums, publications, and industry platforms prevent LLMs from validating a business as a recognized leader.
How Frequently Should Businesses Update Content to Maintain LLM Optimization Performance?
Businesses maintain LLM Optimization performance by updating content according to how quickly information becomes outdated inside AI retrieval and generation pipelines. Large Language Models exhibit strong recency bias and replace older sources with newer ones when multiple answers satisfy the same intent.
How often should core LLM content be updated? Core informational pages require updates every 90 days because competitors, phrasing patterns, and usage context shift even when the subject remains the same.
How often should volatile LLM content be updated? Topics tied to regulations, pricing, technology changes, or trends require monthly updates because AI systems favor recently validated information when selecting sources.
How often does outdated content lose LLM visibility? Content that remains unchanged for 6 to 9 months risks displacement by more recent competitors because LLMs downgrade sources that fail recency validation.
How often should product and service information be refreshed? Product and service content requires immediate updates whenever attributes change because LLMs deprioritize sources that return inaccurate or obsolete details.
Is It Possible for Businesses to Track Traffic from Large Language Models?
Yes, businesses track traffic from Large Language Models by identifying how AI platforms route users to external websites and how those visits appear inside analytics systems. AI platforms do not follow traditional referral patterns because this traffic appears misclassified without explicit segmentation.
How does Large Language Model traffic become trackable in analytics systems? Large Language Model traffic becomes trackable when analytics systems isolate sessions originating from AI interfaces. These platforms route users through identifiable domains and redirect behaviors that separate AI traffic from organic search and direct traffic.
How does segmentation improve tracking accuracy? Tracking accuracy improves when businesses segment AI-originated sessions into dedicated traffic groups rather than merging them with generic referrals. This segmentation enables attribution of conversions and engagement to AI-driven discovery instead of treating visits as anonymous.
Specialized visibility tools extend tracking by monitoring brand mentions, citations, and referral patterns inside AI systems. These tools reveal both on-site impact and off-site influence that standard analytics does not capture.
Which Tools Are Most Effective for Monitoring and Optimizing LLM Performance?
The most effective tools for monitoring and optimizing LLM performance measure output quality, cost efficiency, latency, and behavioral consistency across production environments.
The 5 most effective tools for LLM Optimization are Search Atlas LLM Visibility Tool, Langfuse, Braintrust, Helicone, and Arize Phoenix.
1. Search Atlas LLM Visibility Tool. Search Atlas tracks how brands and content perform inside Large Language Model responses across major AI systems. Search Atlas measures where content appears, how it is reused, and which competitors displace it inside AI-generated outputs. Search Atlas connects LLM Optimization with GEO execution by linking performance insights to content, SEO, and technical workflows. This execution focus positions Search Atlas as the most complete system for unifying LLM Optimization with public AI visibility.
2. Langfuse. Langfuse monitors LLM behavior through real-time observability and detailed usage analytics. Langfuse enables prompt iteration, model comparison, and cost tracking across deployments. This visibility enables data-driven optimization of prompt design and model selection inside production LLM applications.
3. Braintrust. Braintrust evaluates and benchmarks LLM outputs through controlled experiments and accuracy scoring. Braintrust supports prompt refinement, model comparison, and performance validation for enterprise-scale AI systems. This evaluation focus fits teams that prioritize output accuracy and model governance.
4. Helicone. Helicone optimizes LLM performance through intelligent routing, caching, and cost analytics. Helicone enables developers to monitor and fine-tune applications across providers such as OpenAI, Anthropic, and Google. This routing and analytics layer fits teams focused on infrastructure-level LLM efficiency.
5. Arize Phoenix. Arize Phoenix provides open-source observability and experimentation for LLM applications. Arize Phoenix supports prompt testing across datasets and applies LLM-based evaluation to reduce hallucination and improve accuracy. This experimentation focus fits teams that require transparent optimization workflows.
Among available LLM Optimization tools, Search Atlas LLM visibility provides the most complete system because it connects LLM performance monitoring with SEO, AEO and GEO execution and content-level remediation rather than isolating optimization inside engineering workflows.
What Metrics and KPIs Should Businesses Track to Measure LLM Optimization Effectiveness?
The most important LLM Optimization metrics are output accuracy, cost efficiency, and response reliability because LLM Optimization focuses on improving how language models perform inside real-world systems.
Output accuracy measures whether Large Language Models produce correct, relevant, and contextually aligned responses for defined tasks. Higher accuracy indicates stronger alignment between model behavior and business requirements.
Cost efficiency measures the compute and spending required for each successful response over time. Lower-cost per output indicates that optimization improves scalability without sacrificing quality.
Response reliability measures how consistently Large Language Models deliver stable outputs across repeated prompts and similar contexts. Higher consistency indicates that optimization reduces variance and operational risk.
These 3 metrics define LLM Optimization effectiveness by showing whether outputs remain correct, efficient, and dependable across production environments.
What Implementation Challenges Should Businesses Expect When Executing LLM Optimization?
Businesses need to expect high costs, data quality constraints, and integration complexity when executing LLM Optimization. These challenges often delay or block deployment before systems reach production readiness.
High costs arise from infrastructure requirements, model training, and ongoing inference at scale. These costs increase when workloads grow or when optimization targets real-time performance.
Data quality constraints appear when training and retrieval sources contain incomplete, biased, or outdated information. These constraints limit output accuracy and reduce the effectiveness of optimization efforts.
Integration complexity emerges when LLM systems need to connect with existing data pipelines, security layers, and application logic. This complexity increases deployment time and raises the risk of operational failure.
How Can LLM Optimization Impact Brand Authority, Reputation, and Customer Engagement?
LLM Optimization impacts brand authority, reputation, and customer engagement because AI systems select and recommend brands they interpret as accurate, consistent, and trustworthy. Large Language Models evaluate whether a brand appears reliable and well-defined before presenting it inside AI-generated answers.
LLM Optimization strengthens brand authority through structured content that reinforces entity clarity, factual consistency, and topical depth. These signals increase the likelihood of brand selection inside generated explanations and recommendations.
LLM Optimization protects brand reputation by preventing inaccurate, incomplete, or misleading representations inside AI-generated responses. Validated content directs generative models toward correct brand portrayal rather than fragmented narratives.
LLM Optimization improves customer engagement by positioning brands directly inside conversational discovery flows. This positioning allows users to encounter brands at the moment of decision rather than after navigating multiple pages.
What Is the Future of Large Language Models and Their Impact on Businesses?
The future of Large Language Models centers on specialization, multimodal capability, and agentic operation across business systems. Organizations increasingly deploy LLMs as operational partners rather than experimental interfaces, which shifts AI from reactive tools to proactive execution layers.
Current adoption patterns show that businesses integrate LLMs into content creation, customer service, analytics, and workflow automation. Industry projections indicate that most enterprises will rely on LLMs for core functions within the next 2 years, which restructures how work scales across digital operations.
Large Language Models are expanding beyond text to process images, audio, and structured data inside a single reasoning flow. Businesses that align data, processes, and governance with these multimodal capabilities gain stronger performance and lower operational friction as AI replaces manual decision layers.
Agentic behavior will define the next phase of LLM deployment by enabling models to plan, execute, and monitor tasks autonomously. This behavior shifts business value from isolated automation toward system-level orchestration driven by AI.